Powerpoint Presentation: Extra
Extra cellular components
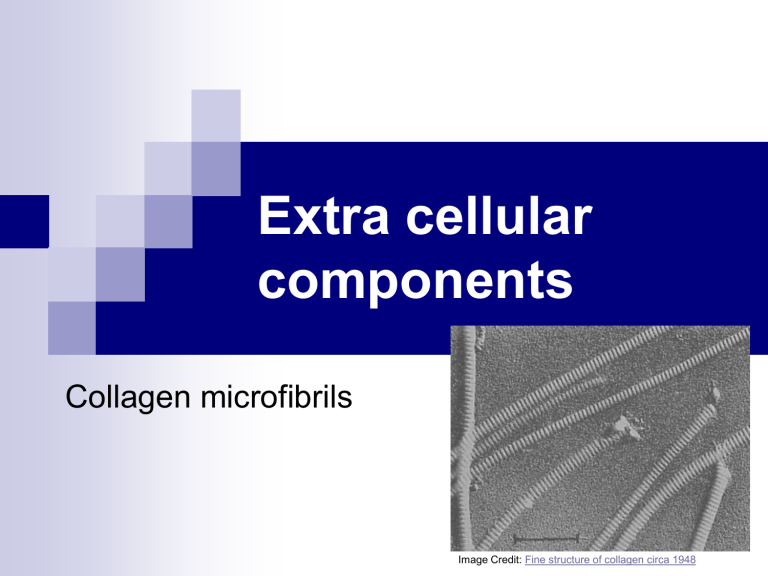
Collagen microfibrils
Image Credit: Fine structure of collagen circa 1948
The extracellular matrix
Plant cell secrete cellulose and other carbohydrates
Fungi and insect cells secrete chitin
Bacteria secrete murin
Animal cells secrete proteins (e.g. collagen) glycoproteins and other conjugated proteins
© 2010 Paul Billiet ODWS
Functions of extracellular matrix
Mechanical, they give tissues strength and elasticity
Protection against extracellular change and retention of water
Control of cell behaviour by binding of growth factors and interaction with cellsurface receptors
© 2010 Paul Billiet ODWS
Animal tissues
Image Credit; www.steve.gb.com/
THE PLANT CELL WALL
The formation of a cell plate starts as soon as the nucleus has divided
© 2010 Paul Billiet ODWS
Cell plate to cell wall
The cell plate becomes the middle lamella that glues the cells together
© 2010 Paul Billiet ODWS
New cell wall material is secreted either side of the middles lamella
= primary cell wall (no cellulose)
Growth of the cell is orientated by the appearance of cellulose microfibrils
© 2010 Paul Billiet ODWS
Plasmodesmata
Sap vacuole
The secondary cell wall consists of cellulose microfibrils secreted inside the primary cell wall
When this forms the cell stops growing and takes its final form