Powerpoint Presentation: Phenylketonuria
advertisement

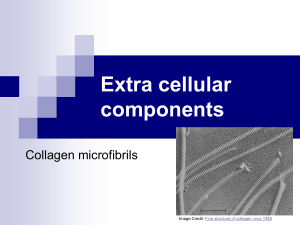
PHENYLKETONURIA (PKU) The normal metabolism of phenylalanine (pathways a and b) BREAKDOWN Dietry sources, particularly plant proteins PHENYLALANINE PHENYLALANINE HYDROXYLASE (a) TYROSINE (b) BODY PROTEINS © 2008 Paul Billiet ODWS The abnormal metabolism in phenylketonuric subjects (pathway c) HYDROXYPHENYLACETIC ACID Dietry sources, particularly plant proteins (c) PHENYLALANINE HYDROXYLASE PHENYLALANINE* (a) (c) (b) PHENYLACETIC ACID* *Agents, thought to be responsible for mental retardation © 2008 Paul Billiet ODWS BODY PROTEINS Test Ferric chloride + urine of new born baby Green colour in the presence of ketone bodies © 2008 Paul Billiet ODWS Treatment A strictly controlled phenylalanine free diet up to the age of about 14 years old phenylalanine is itself an essential amino acid small doses must be supplied After this age the growth and development of the brain is not affected by high levels of phenylalanine in the body © 2008 Paul Billiet ODWS Frequency 1 in 10 000 in Caucasians of NW Europe © 2008 Paul Billiet ODWS Causes 1. 2. A single mutant recessive allele of the Phenylalanine Hydroxylase (PAH) gene Locus : Long arm of Chromosome 12 Dietary excess of plant proteins which results in the exhaustion of a protein cofactor (pterin) needed by the enzyme © 2008 Paul Billiet ODWS Evolution Heterozygotes (carriers) are thought to be less susceptible to toxins produced by the moulds Aspergillus and Penecillium These grow on foods in damp wet climates (e.g. NW Europe) Heterozygous women show lower spontaneous abortion rates © 2008 Paul Billiet ODWS