Cell Growth and Reproduction

Mitosis
The Cell Theory
• All living things are made up of one or more cells
• Cells are the basic unit of structure and function in living things
• All cells come from preexisting cells
Section Summary
• The genetic material is deoxyribonucleic acid (DNA).
• DNA is packaged into chromatin, which condenses to form chromosomes.
Section Summary
• During interphase of the cell cycle, the cell lives, grows, and replicates its DNA.
• In mitotic phase (M phase), the chromosomes distribute to daughter cells.
• A duplicated chromosome consists of two sister chromatids.
Human Karyotype
Chromosome numbers
Agrodiaetus butterfly
Alfalfa
268
32
This insect has one of the highest chromosome numbers among all animals.
Cultivated alfalfa is tetraploid, with 2n=32. Wild relatives have 2n=16.
Aquatic Rat
Jack jumper ant
92
2
American Badger 32
Previously thought to be the highest number in mammals, tied with Ichthyomys pittieri.
2 for females, males are haploid and thus have 1; smallest number possible.
American Black Bear 74
Kamraj (fern) 94
Kangaroo 16
Koala 16
Lion 38
Maize 20
Mango 40
Meerkat 36
Mosquito 6
Mouse 40
http://www.oocities.org/ganmni/
Genes
• Every cell’s DNA is organized into genes.
• Genes are units of inherited information that carry a code for specific traits or functions.
Genes
• Many genes code for proteins.
• The information contained in genes is responsible for inheritance — the passing down of traits from parent organisms to their offspring.
DNA
• The nucleus contains the cell’s DNA.
• For much of a cell’s life, its DNA exists as a mass of very long fibres called chromatin, a combination of DNA and protein.
• Chromatin is very thin and not usually visible with a light microscope.
Chromosomes
• As a cell is preparing to divide, its chromatin fibres condense, becoming visible compact structures called chromosomes.
Chromosomes
• A chromosome consists of one long, condensed DNA molecule containing hundreds or thousands of genes.
Chromosome
Chromatin
The Components of DNA
DNA consists of a long chain of subunits called nucleotides.
A nucleotide has three parts:
1. A ring-shaped sugar called deoxyribose
2. A phosphate group
3. A nitrogenous base (or base, for short): a single or double ring of carbon and nitrogen atoms
DNA limits cell size
• Nucleus contains blueprints for cell proteins
• Proteins used by almost all organelles to function
DNA limits cell size
• There is a limit of how quickly proteins can be copied and made in nucleus
• Cell cannot survive unless DNA can support protein needs of cell
Cell Cycle
• Cell Cycle: Sequence of growth and division of the cell.
Phases of Cell Cycle
• INTERPHASE:
– The longest phase
– Cell grows in size
– Cell carries on metabolism
– Chromosomes are duplicated to prepare for division
Phases of the Cell Cycle
• After Interphase, cell enters period of division, called Mitosis.
Mitosis:
• Forms two identical daughter cells each with a complete set of chromosomes
Mitosis
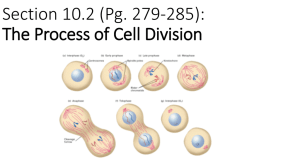
Phases of Mitosis
Four phases:
• Prophase
• Metaphase
• Anaphase
• Telophase
Prophase
• chromosomes condense
• nucleolus and nuclear envelope disintegrates
• centrioles migrate to opposite ends
• spindles form between centrioles
Prophase
Chromosome
Long stringy chromatin coils up into visible chromosomes
Chromatin
Prophase
• Each duplicated chromosome is made of two halves called sister chromatids.
• Sister chromatids are held together by a centromere
Centromere
Sister chromatids
Spindle fibers
Disappearing nuclear envelope
Double stranded chromosome
Prophase
Metaphase
• Double stranded chromosomes attach to spindle fibers by centromeres
• Double stranded chromosomes pulled by spindle fibers and line up on equator
Metaphase
• This arrangement of the chromatids ensures that each new cell receives identical and complete set of chromosomes
Anaphase
• Centromeres split
• Sister chromatids separate
• Shortening of spindle fibers pull apart chromatids to opposite poles
Telophase
• Begins once chromatids reach opposite poles
• Chromosomes begin to unwind
• Spindle breaks down
Telophase
• Nucleolus and nuclear envelope reappears around new set of chromosomes
• Two identical daughter cells formed
Cytokinesis
• After Telophase, the cell’s cytoplasm divides.
• Animal Cells: the plasma membrane pinches together, forming two separate cells.
• Plant Cells: Cell plate laid across cell’s equator—there is no pinching off. Cell membrane forms around each cell and new cell walls form on each side of cell plate
Cytokinesis
What are the results of Mitosis?
• Two identical daughter cells
– Single celled organism remains a single cell but has replicated itself
– Multicellular organisms have grown or created another cell that will work together as tissue to perform a certain function
Mitosis Animation
CellsAlive
Cell Growth and Reproduction
Section Quiz:
1.
The stringy structures in the cell nucleus that contain DNA are __________. a. Centromeres b. Chromatin c. Genes d. Chlorophylls
Cell Growth and Reproduction
Section Quiz:
2. What phases are the following cells in?
Cell Growth and Reproduction
TELOPHASE
Cell Growth and Reproduction
PROPHASE
Cell Growth and Reproduction
METAPHASE
Cell Growth and Reproduction
ANAPHASE
Cell Growth and Reproduction
CYTOKINESIS
Cell Growth and Reproduction
INTERPHASE
Control of the Cell Cycle
• What happens when MITOSIS goes WILD?
– CANCER
Control of the Cell Cycle
• Cancer:
– Malignant growth due to uncontrolled cell division
– Caused by environmental factors
– Changes in enzyme production
Figure 1
Lung cancer cells (530x).
These cells are from a tumor located in the alveolus (air sac) of a lung.
Cancer
• Cancerous cells form masses of tissues called MALIGNANT tumors.
• Tumors starve normal cells from nutrients
• Wait! But can’t I have a BENIGN tumor?
– YES! Benign tumors are masses of tissues that are harmless. (BENIGN = HARMLESS)
– Created by slower growing cells that clump together to form lump
Control of the Cell Cycle
• Can I prevent Cancer?
– Diets high in fiber and low in fat
– Take vitamins
– Daily exercise
– Refrain from smoking and use of other tobacco products
– Avoid exposure to UV light (in sunlight)
– Avoid exposure to X-rays