Mutation PPT
advertisement

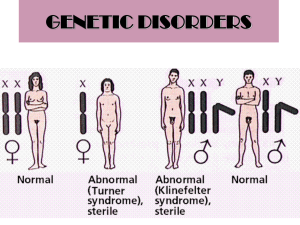
Mistakes in Meiosis Including Mutations & Non-disjunction What is a Gene? • A gene is the basic unit of heredity in a living organism • Genes hold the information to build and maintain cells and pass genetic traits to offspring. What is a Gene? • A gene is holds the information for the production of a particular protein. • A gene is the basic instruction: a sequence DNA What is a Gene? • Remember that DNA is made up of four nucleotide bases: A, T, G, C • Each gene is a string of hundreds of base pairs in a particular sequence. • An allele is one variant of that instruction. Mutations • Mutations are changes in the genetic makeup of a cell • They are changes in the sequence of base pairs • Mutations can change the protein that the gene codes for. Mutations • Can involve large regions of a chromosome or just a single nucleotide pair Causes of Gene Mutations • Mutations can occur spontaneously during DNA replication • Many mutations occur as a result of exposure to mutagens, or mutation causing agents in the environment Mutagens • • • • • X-rays UV light radioactivity chemicals cigarette smoke Mutations • Results of a mutation on the organisms may be: – Deleterious – Positive – no effect Mutations • Species have evolved as a result of mutations that have given an organism a positive benefit that has been naturally selected • Effects of a mutation may not surface immediately Alterations of Chromosome Structure • There are several different mutations that alter the chromosome structure: – Deletions – Duplication – Substitutions – Inversions – Translocations – Point mutations (insertion, deletions, substitutions of a single base pair) Alteration of Chromosome Number • Aneuploidy – incorrect number of chromosomes • Polyploidy – more than 2 pairs of each chromosome Deletions • With a deletion, a segment of a chromosome is lost • Or a single base pair is lost Duplications • With a duplication, the same linear stretch of DNA within a chromosome is repeated, often several to many times in the same chromosome or in a different one Inversions • With an inversion, a segment of DNA within a chromosome may flip upside down but remain in place Translocation • With a translocation, a stretch of one chromosome’s DNA moves to another location in the same chromosome or a different one Base-pair substitutions • The replacement of one nucleotide and its partner with another pair of nucleotides Insertions and Deletions • Additions or losses of one or more nucleotide pairs in a gene • Usually have a more deleterious effect than substitutions http://www.larasig.com/node/1806 Insertions and Deletions • Because mRNA is read as a series of nucleotide triplets during translation, the insertion or deletion may alter the reading frame (triplet grouping) of the gene • All the nucleotides that are downstream of the deletion or insertion will be improperly grouped into codons Alteration of Chromosome Number • Sometimes the movement of chromosomes during meiosis goes wrong • When this happens the gamete may end up with an unusual number of chromosomes • This is called nondisjunction Nondisjunction • The members of a pair of homologous chromosomes do not move apart properly during meiosis I Or • The sister chromatids fail to separate during meiosis II • In these cases, one gamete receives two of a chromosome and another gamete receives no copy Nondisjunction • If either of the aberrant gametes unites with a normal one, the offspring will have an abnormal chromosome number, known as aneuploidy • If the chromosome is present in triplicate in the zygote, (the cell has a total of 2n + 1 chromosomes) then the cell is trisomic for that chromosome • trisomy 21 = Down syndrome Nondisjunction • If a chromosome is missing (cell has 2n-1 chromosomes) the cell is monosomic for that chromosome • Some organisms have more than two complete sets of chromosome sets and are termed polyploidy • 3n = triploidy • 4n = tetraploidy Syndromes Associated with Nondisjunction • XXY Klinefelter syndrome – have low levels of testosterone causing small testicles and the inability to make sperm. They also have learning disabilities and behavior problems such as shyness and immaturity • XXX Triple X syndrome – Individuals show no significant clinical manifestations, although there is usually some degree of mental retardation. • X Turner syndrome – is characterized by retarded growth that leads to a small stature and frequent infertility. • Trisomy 21 Down syndrome – Mental retardation and characteristic physical features Animation of nondisjunction in meiosis I Animation of nondisjunction in meiosis II That’s all Folks