Digestibility carbohydrates
advertisement

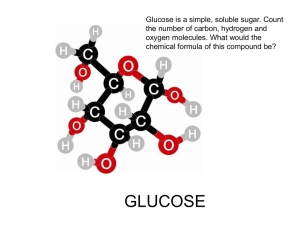
N-free extracts, digestible carbohydrates • monosacharides – pentoses, • ribose (RNS); • deoxyribose (DNS) – hexoses, • glucose (grape sugar, blood sugar, brain tissues, muscle tissues, starch, cellulose); • fructose (fruit sugar, green leaves, fruits); • mannose (its polymers contain yeasts and bacteria); • galactose (milk sugar component) • disaccharides – sucrose (glucose + fructose; beet sugar, cane sugar, green leaves, fruits, vegetables) – lactose (glucose +galactose, milk sugar) – maltose (2 glucose, compound of starch) • trisaccharides – raffinose (glucose + fructose + galactose, roots, molasses) Monosaccharides hexoses pentoses Disaccharides sucrose maltose lactose isomaltose Sweetening effect of different sugars • • • • fructose sucrose glucose lactose 1,5 1,0 0,6 0,4 • polysaccharides – starch • glucose maltose starch dextrin • 15-30% amilose + 70-85% amilopectin • • • • important energy source high digestibility identifying parameter of different feedstuffs grains 50-70%, potato 14-18% – glycogen • the stored polysaccharide in the animals (foods of animal origin) Composition of starch amilopectin amilose Digestion and absorption of saccharides • starch • digestion starts in the mouth, saliva contains α-amilase • starch molecules will be splitted to shorter chains, called dextrines • the determinant part of starch digestion takes place in the small intestine by the α-amilase of pancreatic juice • the digestibility of some starches increase after heat treatment (potato) • disaccharides (maltose, sucrose, lactose) • splitting to monosaccharides mostly the disaccharidase enzymes, produced by the enterocytes (maltase, sucrase, lactase) • young animals have high lactase activity, that declining with the age • about 10-15% of adult people can’t produce enough lactase, resulting lactose intolerance) • some people and animals can’t secrete sucrase enough Digestion and absorption of saccharides Monosaccharides can get through the intestinal cell membranes and reach the blood. The membrane transport can be active (needs ATP energy) or passive (doesn’t need energy) • glucose, galactose sodium dependent active transport • fructose facilitated diffusion (it is slower compared to glucose) • a fructose and galactose are converted to glucose in the liver • organic acids – naturally occurring (oxalic acid, citric acid) – in fermented feeds (lactic acid, acetic acid, butyric acid) – as preservation materials (propionic acid, formic acid) • alkaloids, glycosides – plants containing only in small amounts – have an influence on the smell, savouriness – they are anti-nutritív, poisonous, (potato - solanin; lupine seeds -lupinin; rape seed – glycosides) N-free extract, starch and sugar content of some feedstuffs (%) N-free extr. starch sugar wheat 68,8 61,1 2,7 barley 67,1 50,1 1,7 peas 52,9 41,1 5,6 lupin seed 33,1 8,1 4,6 extracted soybean meal 30,2 6,7 9,6 milk powder (defatted) 51,8 - 47,7 Human nutritional aspects • In Hungary the energy intake, coming from starch takes 42% of the total • Nutritional goal would be 55-58% • recommended sugar intake : 60g/day • requirement: 30-40 g/day • consumption: man: 92g/day woman: 85g/day • we use too much added sugar