LIFE
and its
VARIOUS
IDIOSYNCRACIES
muahahaha
Atoms
Chemical Level
molecules
cells
Cellular Level
tissue
Tissue Level
Organ
Organ Level
Organ
System
Organismal
Level
Organism
Life’s Functions
….ooh
1. Protect Your Insides!!!
•
Skin (from the integumentary system): Protects your organs
from drying out and from being exposed to harmful external
factors such as bacteria, heat, and chemicals.
•
Cells: Must be able to properly regulate what stays/comes in
and what goes out or is kept out of its membrane.
2. Movement
•
The muscles in the muscular system pull on the bones in the
skeletal system in order to manipulate the movement of limbs,
fingers etc. The muscles also control facial expression.
•
Movement within organ systems (ex: blood being pumped in
the cardiovascular system) that allow the systems to function
properly.
3. Responsiveness
•Ability to detect and respond to changes in the environment (scientific
term = stimuli). The nervous system plays a principal role in warning the
body of any such stimuli.
4. Digestion
•The breaking down of foods into molecules via the digestive system
that are absorbed into the blood and distributed to all body cells via
the cardiovascular system.
5. Metabolism
•
The sum of all the chemical reactions that occur in living cells (or in
an organism). Anabolic: building up molecules to form more
complex structures; Catabolic: breaking down of complex
structures into molecules/ simpler structures followed by the
release of energy.
6. Excretion
•The removal of wastes from the body with help of the digestive system
(indigestibles--feces) and the urinary system (nitrogenous wastes—
urine).
7. Reproduction
•Cellular reproduction: 1 cell divides into 2 cells.
•Organismal reproduction: reproductive system
8. Growth
•Cells reproduce and keep on building up in order for body structures to
grow.
Organ Systems
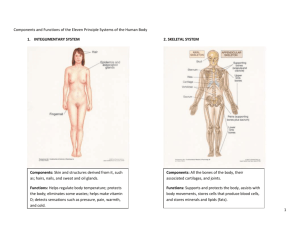
Integumentary System (skin)
• Waterproofs body
• Protects deeper tissues
• Perspiration- excretes salts and urea to regulate body temperature
• Skin
– pain receptors
– temperature
– pressure
Skeletal System
•bones- store minerals
•cartilage
•ligaments
•joints
•supports body and provides a frame
•hematopoiesis: formation of blood cells (inside cavities of skeleton)
Muscular System
• movement muscles contract
• “machines” of the body
• Muscle attached to bone
• Different from hollow organs like the heart which moves fluids
throughout the body
Nervous System
•Brain
•Spinal cord
•Nerves
•Sensory preceptors- senses changes and sends signals (through electrical
signals) to the brain and spinal cord
Lymphatic system
•Organs:
-Lymphatic vessels- constantly keep blood circulating throughout the
body
-Lymph nodes- cleanse body and store immunity cells
-Spleen
-Tonsils
Endocrine System
•Produces hormones and releases them into the bloodstream which are then sent
different organs
•Glands:
-Pituitary
-Thyroid
-Parathyroid
-Adrenals
-Thymus
-Pancreas
-Pineal
-Ovaries (female) and testes (male)
Hormones regulate processes
Respiratory system:
•keeps body supplied with oxygen
•removes carbon dioxide
•consists of:
-nasal passages
-pharynx
-larynx
-tracheas
-bronchi
-lungs
Digestive System
• organs:
– oral cavity
– esophagus
– stomach
– small and large intestines
– rectum
• break down foods and deliver nutrients into the bloodstream
• undigested food leaves body through anus as feces
• after the breakdown of food is completed in the small intestine, water
must be reclaimed
• liver
– bile- breaks down fats
• pancreas
– delivers digestive enzymes to the to small intestine
Cardiovascular System
•Heart pumps blood into the blood vessels, which transports the stuff in the
blood to tissue cells, which then exchanges stuff with the blood vessels which
transports the blood back to the heart. Then the cycle repeats continuously.
•Stuff = oxygen, carbon dioxide, wastes, nutrients, hormones. On the first trip,
the blood sends oxygen, nutrients (the good stuff) to the tissue cells. It’s on the
return trip that the wastes are picked up from the blood so that it can be
disposed of.
-Arteries carry blood away from heart and into the capillaries. The blood then
returns to the heart via the veins.
Urinary System
• nitrogen containing waste
– urea and uric acid- result of the breakdown of proteins and nucleic acid during
digestion
• removes nitrogen containing waste from the blood which is then released from the body in
urine
• regulates acid-base balance of blood and the balance of water and salt
• organs:
– kidneys
– ureters
– bladder
– urethra
Reproductive System
produce offspring
Male reproductive system:
Testes-produce sperm
Scrotum
Penis accessory glands
Duct system- carries sperm out of the body
Female reproductive system:
Ovaries- produces eggs (ova)
Uterine tubes
Uterus- where the development of a fetus occurs
Vagina
Go to these links for pictures!!!!
•http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/skin.html Skin
•http://www.stpeters.k12.nf.ca/skeletal_system.htm Skeletal System
•http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/modmuscularsys3.jpg Muscular System
•http://www.infovisual.info/03/038_en.html Nervous System
•http://www.umm.edu/endocrin/images/endocrine.gif Endocrine System
•http://www.worldinvisible.com/images/apolog/body/bloodjci.gif cardiovascular
system
•http://www.gorhams.dk/assets/images/lymfesystemet.gif Lymphatic System
•http://www.emc.maricopa.edu/faculty/farabee/BIOBK/humrespsys_1.gif
Respiratory System
•http://www.umm.edu/digest/images/digest.gif Digestive System
•http://www.sirinet.net/~jgjohnso/urinarysys10.jpg Urinary System
•http://www.uh.edu/~tgill2/image008.jpg and
http://www.uh.edu/~tgill2/image010.jpg for female & male Reproductive Systems
sources
• http://www.answers.com/topic/metabolism
• http://yucky.kids.discovery.com/noflash/bod
y/pg000131.html
• http://yucky.kids.discovery.com/flash/body/
pg000123.html
• http://sln.fi.edu/biosci/systems/respiration.ht
ml
• Google!