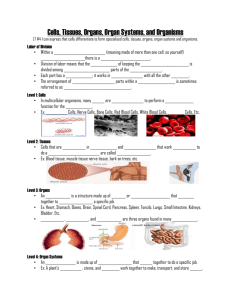
Define: Cell, Tissue, organ, and organ system
advertisement

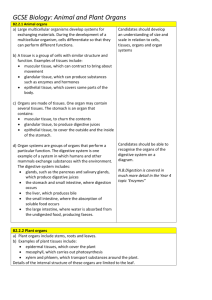
From Cells to Organisms Organisation of Life Lesson Objectives 1. Define: Cell, Tissue, organ, and organ system (DK). 2. Describe two types of tissue (DK) 3. Describe two types of organs (DK) 4. Create a flow chart illustrating relationship between cells, tissues, organs, systems and organisms (PK) Levels of Organization Cell—Basic unit of structure and function in organisms. Some organisms, like bacteria and protists, are unicellular (made entirely of one cell). Some organisms, like fungi, plants, and animals, are multicellular (made of many cells). In multicellular organisms, cells exhibit cell specialisation. They take on specific jobs and look different from each other. The cells also exhibit division of labor. They split up the work of the organism. Levels of Organization Tissues—Groups of similar cells that work together to perform a specific function. 4 major tissue types in animals Epithelial tissue Connective tissue Muscle tissue Nervous tissue Levels of Organization Organs—structures made of different types of tissues that work together to perform a specific function. Examples Heart Lungs Stomach Small intestine Liver Large Intestine Gall Bladder Plant Roots Plant Stems Plant Leaves Levels of Organization Organ Systems—Groups of organs that work together to perform a specific function. Examples: Digestive system Circulatory system Respiratory system Nervous system Muscular system Skeletal system Integumentary system (skin) Vascular system in plants Levels of Organization Organism—A thing. Examples: complete, individual living A single person A single plant A single bacterium A single protist Write your answers in complete sentences Q 1: A (tissue, organ, system) is a group of the same kinds of cells that work together. Choose the right answer. system organ tissue Q 2: Some tissues and organs work together like the members of the team. The parts that work together are called a _____________. cell system group Q 3: The mouth, teeth, tongue, stomach and intestines all work together. Therefore they are called the important parts of __________________. digestive system circulatory system muscular system Q 4: Brain, heart and lungs are some of the important _______________ in a body. organs tissues cells system Q 5: Different tissues work together to form _________ . cells system organs Q 6: Different systems work together to form organs. True or false? false true Organization of Vertebrate Body Tissues are groups of cells that are similar in structure and function In humans, there are four primary tissues: -Epithelial, connective, muscle and nerve 11 Organization of Vertebrate Body Organs are combinations of different tissues that form a structural and functional unit Organ systems are groups of organs that cooperate to perform the major activities of the body -The human body contains 11 principal organ systems 12 Organ Systems The five main organ systems that we will be focusing on in this unit are: The Respiratory System The Circulatory System The Reproductive System The Digestive System The Excretory System Organization of Human Body NO Thank you! 14 Digestive System The organs or parts of the body that work together to break down food into a smaller, more useable form. NO Thank you! 15 Circulatory System The system that carries oxygen and nutrients to all cells in the body and takes wastes away from the cells; it consists of the heart, blood vessels and blood. NO Thank you! 16 Respiratory System The system involved in the inhalation of and diffusion of oxygen into the blood stream, and the removal of carbon dioxide from the body via exhalation NO Thank you! 17 Excretory System The system responsible for the removal of excess water and waste from cell reactions in the body Reproductive System The male and female reproductive systems are responsible for the production of sperm and ova (eggs), the fertilisation of ova by sperm, and the gestation of a fertilised ova into a foetus (unborn baby)