Document
advertisement
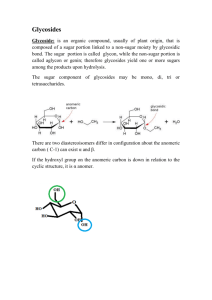
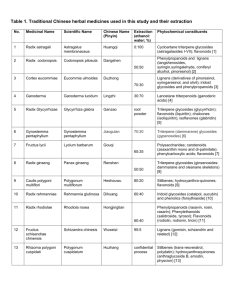
II. Poisonous Plants Acute vs. chronic toxicity a) internal poisons b) allergens c) cell modifiers: mutagens, teratogens and lectins a. Internal Poisons Alkaloids Glycosides Oxalates Resins Alkaloids N-containing heterogenous group of medicinal, toxic, and psychoactive compounds Found in high concentrations in the Apocynaceae, Berberidaceae, Fabaceae, Papaveracea, Ranunculaceae, Rubiaceae, and Solanaceae Not found in the Lamiaceae, Rosaceae, and the Gymnosperms Glycosides combination of sugar(s) or glycone and another compound (aglycone) glucose is the most common sugar toxicity is associated with aglycone moiety Cynogenic glycosides Hydrolized to HCN and sugar Amygdalin is found in seeds of apples, pears, apricot, bitter almonds, wild and domestic cherries, peaches and plums. HCN blocks the action of cytochrome oxidase in respiration causing cellular asphyxiation Anthraquinone glycosides Hydrolysis of anthraquinones Found in aloe and rhubarb Cardioactive glycosides Aglycones are steroidal Act on the heart (paralysis) Found in Digitalis (foxglove) and Antirrhinum (snapdragon) Saponin glycosides Aglycone forms a steroid or triterpene that form colloidal dispersions in water Irritates mucous membranes and destroys blood cells. Found in yams, ginseng, licorice, beech, poke, alfalfa, and english ivy Coumarin glycosides Aglycone is a benzopyranone Causes internal bleeding and dermatitis Not common Found in Artemesia species (sagebrush) Oxalates organic acid that forms in crystals in vacuole Reach dangerous levels in oxalis, rhubarb, dock and purslane Resins Amorphous products of complex nature. Insoluble in water and do not contain N Mixture of oils, gums and sugars Found in water hemlock, milkweed, rhododendron and azaleas Allergens Pollen can cause: Anaphylatic shock Allergenic rhinitis (hayfever) Asthma Dermatitis Photodermatitis Mutagens can cause: Replacement of nucleotide in DNA Loss of addition of nucleotide causing more serious mutagenesis Nondisjunction of chromosomes (extra chromosomes) Polyploidy (extra set of chromosomes) Teratogens Effects on somatic cells of growing embryos usually resulting in malformed organs Lectins Can be highly toxic Proteins with carbohydrate chains attached Some examples are ricin (castor bean), curcin and abrin (rosary pea) ricin inhibits protein synthesis by inactivating ribosomes Some lectins can stimulate cell proliferation Tannins bitter tasting polyphenols that bind and precipitate proteins