medicinal plants - muhammad1988adeel
advertisement

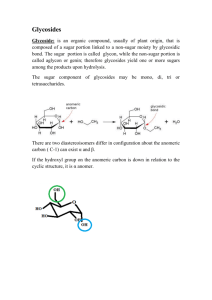
PLANT AND SOCIETY ESTELLE LEVETIN & KAREN MCMAHON Chapter 19 MEDICINAL PLANTS • Medicinal properties of plants due to their secondary metabolites like • Alkaloids • Terpenoids • Glycosides • Saponins • Phenolic compounds • Concentration is important ALKALOIDS • • • • • • • • Diverse group of compounds 3,000 identified in 4,000 species Most of them occur in herbaceous dicots Fabaceae Solanaceae Rubiaceae Vary in their chemical structure Contain nitrogen, alkaline and bitter taste • • • • • • • • • • Alkaloids affect the psychology of animals Neurotransmitters Some are hallucinogenic or poisonous Quantity of dose Caffeine Nicotine Cocaine Morphine Quinine and Ephedrine ASPIRIN Salix spp. ASPIRIN • Most widely used synthetic drug • America alone consume 80 million pills a day • Bark of willow trees (Salix spp.) an effective treatment for fever and relieving pain • Salicin, glycosides of salicylic acid occurs in many sp. of Salix • Aspirin valued for three classical properties • Anti-inflammatory • Anti-pyretic (fever reducing) • Analgesic (pain relieving) • Used in prevention of heart attacks, strokes, ovarian cancer • Enhance the immune system in protecting body against bacteria and viruses • Salicylic acid found in many plants • Capable of being translocated through phloem • Believed to be naturally occurring growth hormones • Provides protection to plants • Plants respond to pathogens by activating network of defenses Systemic acquired resistance • Salicylic acid, signal turns on this system response • Results in synthesis of specific proteins that increase resistance • External application of salicylic acid or even aspirin (acetylsalicylic acid) to plants stimulate this immune response • Stimulation of salicylic acid in an infected plant turn on responses in neighboring plants • Healthy plants nearby absorbed the airborne methyl salicylate molecules • Converting back to salicylic acid • Stimulated defense make healthy plants more resistant to pathogen Atropa belladonna (Solanaceae)) Atropa belladona • Used as drug due to alkaloid Atropine • Called deadly nightshade because it is very poisonous • women use drops from the leaves to make their pupils expand and produce wide-eyed, innocent look • used to treat glaucoma GLYCOSIDES • Widespread in plant kingdom • A sugar molecule (glyco-) attached to active component • Cyanogenic glycosides • Cyanogenic glycosides release cyanide (HCN) upon breakdown e.g., Cassava • Cardioactive glycosides and saponins Cardioactive glycosides • Cardioactive glycosides and saponin contain a steroid molecule as the active component • Cardioactive glycosides effect on contraction of heat muscles • Digitalis • Milkweeds and Oleander contain cardioactive glycosides Cardioactive glycosides Foxglove and Control of heart disease • Several million heart patients rely on digitalis in U.S • Digitalis purpurea, purple foxglove, attractive biennial • Ornamental plant • Leaves contain over 30 glycosides (digoxin, digitoxin) Digitalis purpurea Cyanogenic glycosides • Seeds, pits, bark of many members of rose family (apples, pears, almonds, apricots, peaches) contain amygdalin • (Pits of apricots rich source of amygdalin (used in preparation of laetrile for cancer treatment) • Laetrile releases HCN only in presence of tumor cells and selectively destroys them MALARIA AND FEVER BARK TREE • Disease initiated through bite of female Anopheles mosquito • Quina-quina belongs to family Rubiaceae (coffee family) • Quinine attacks merozoite stage, killing the parasite in bloodstream Sources of Quinine – Cinchona succirubra Efficacy of Quinine • Quinine is traditional and effective for malaria • Synthetic preventatives such as chloroquine, maloprim, and fansidar have largely replaced the use of quinine • Many strains of Plasmodium have developed resistances to the synthetics and the synthetics are more toxic Lippia as a sweetener • In Pre-Columbian America, several plants of the genus Lippia were used as sweeteners. (F. Verbenaceae – the verbenas) • In the 20th century, L. dulcis was chemically analyzed and a new sweetener was found, hernandulcin, that is 800 to 1000 times sweeter than sucrose Lippia dulcis – sweetener from Scientific Common Name Name Aloe vera Cannabis Sativa Burn Family Liliaceae Active Medicinal Use Principle Aloin Marijauna Cannabaceae THC Cinchona Fever Rubiaceae Quinine sp. Bark Tree Skin injuries Chemotherapy Malaria Scientific Name Common Family Active Medicinal Use Name Principle Ephedra sp. Ephedra Ephedraceae Ephedrine Asthma Papaver Chaul- Papaveraceae Morphine Pain, Somniferum moogra cough Eucalyptus Eucalyptus Myrtaceae Eucalyptol Anesglobulus thetic RECOMMENDED LINKS • http://books.google.com.pk/books?id=AUOrV71X3AoC&pg=PA203&dq=as pirin+pathway+in+plants&hl=en&ei=WfshTvLLJsSzrAe1zsjlAg&sa=X&oi=bo ok_result&ct=result&resnum=2&ved=0CDIQ6AEwAQ#v=onepage&q=aspir in%20pathway%20in%20plants&f=false • http://books.google.com.pk/books?id=AxUhFMcwSrMC&printsec=frontco ver&dq=salicylic+acid&hl=en&ei=d_8hTojxDYjmrAelyvyCAg&sa=X&oi=boo k_result&ct=result&resnum=1&ved=0CC0Q6AEwAA#v=onepage&q&f=fals e