Document
advertisement

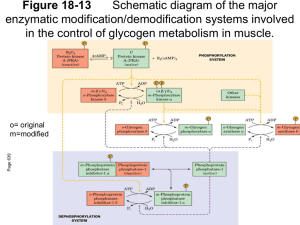
Coordinated regulation of glycolysis/gluconeogenesis High blood glucose Insulin secretion Synthesis of hexokinase II, PFK-1, pyruvate kinase Movement of GLUT4 to plasma membrane of myocyte Activation of insulinsensitive protein kinase Activation of protein kinase B p.903 p.887 Glucose Glucose p.903 GLUT2 Pancreatic b cell Glucose Glycolysis pyruvate Citric acid cycle NADH,FADH2 Oxidative phosphorylation ATP K+ closed ATP-gated K+ channel Ca2+ -+ -+ -+ -+ +- +- +-+ +- +- +- +- +- +- Membrane depolarization Open Ca2+ Voltage-dep. Ca2+ channel Insulin secretion Movement of GLUT4 to plasma membrane of myocyte Glc Insulin Glc Glc Glc Glc Glc p.396 Glc Glc Glc Glc Insulin receptor GLUT4 Cytosol of myocyte p. 588 Activation of insulin-sensitive kinase Insulin Insulin receptor Insulinsensitive kinase Insulinsensitive kinase GM GM Glycogen phosphorylase PP1 Glycogen synthase b a Phosphorylase kinase Glycogen synthesis Glycogen degradation p.587 Activation of protein kinase B (PKB) Insulin Insulin receptor PIP2 PI3-K PIP3 IRS-1 PDK-1 PKB GSK-3 IRS-1 GSK-3 Glycogen synthase b Glycogen synthase a Glycogen synthesis GSK3 inactivate glycogen synthase by phosphorylation p.587 Phosphorylation by Casein kinase II GSK3 P P GSK3 P P p.587 GSK3 can be inactivated by phosphorylation PKB P P p.578 High blood glucose affect hexokinase IV activity Glc nucleus Glc Glc Glc Glc Glc Glc GLUT2 Hexokinase IV Regulator protein Hexokinase IV Regulator protein Glc Fru Fru Regulator protein Fru Glc Glc Hepatocyte Insulin regulate PFK-1 activity Insulin Insulin receptor PFK-2 FBPase-2 PFK-2 Phosphoprotein phosphatase FBPase-2 Fru Fru F6P F6P PFK-2 Fru FBPase-2 F2,6BP Fru PFK-1 F1,6BP FBPase-1 Low blood glucose Glucagon secretion Inactivation of pyruvate kinase L (liver form) Activation of FBPase-2 and inactivation of PFK-2 Inactivation of glycogen synthase Activation of glycogen phosphorylase Regulation pathway initiated by p.436 glucagon secretion glucagon Glucagon receptor b GTP GDP g a Adenylyl cyclase cAMP ATP GM Pyruvate Protein A kinase L Gkinase M PFK-2 FBPase-2 PFK-2 FBPase-2 Pyruvate kinase L Regulation of PFK-1 by glucagon Protein kinase A Fru F1,6BP PFK-2 FBPase-2 PFK-2 Fru FBPase-2 F6P PFK-1 Fru F2,6BP FBPase-1 Fru F6P Fru F2,6BP Regulation of glycogen synthesis and breakdown by glucagon Inhibitor-1 GM Glycogen phosphorylase Protein kinase A PP1 Glycogen synthase b a Phosphorylase kinase Glycogen synthesis Glycogen degradation Protein kinase A Inhibitor-1 p. 588 Hexokinase • There are four isozymes (I, II, III and IV) of hexokinase encoded by four different genes. • Hexokinase I and II are allosterically inhibited by their product, glucose 6phosphate. Hexokinase IV is not inhibited by G-6-P. Hexokinase • Hexokinase I and II are the predominant forms existing in muscle. Hexokinase IV is the predominant form in liver. • Hexokinase I and II will be half-saturated at about 0.1mM, but hexokinase IV will not be half-saturated until 10mM. Hexokinase • Hexokinase has different functions in liver and muscle. • Muscle consumes glucose, using it for energy production. • Liver maintains blood glucose homeostasis by removing or producing glucose. Muscle hexokinase • Because blood glucose concentration is about 4 to 5 mM, hexokinase in the muscle (which will be half saturated at 0.1mM) is always working at or near its maximal rate. Liver hexokinase • However, liver hexokinase (halfsaturated at 10mM) will not ever reach its maximal rate even after meal. Phosphofructokinase-1 • PFK-1 catalyze the committing step of glycolysis. • This enzyme is regulated by ATP, AMP, ADP, citrate and fructose 2,6bisphosphate. ATP regulate the affinity of PFK-1 towards its substrate F-6-P • Not only as a substrate, ATP is also one of the end product of the glycolytic pathway. • ATP inhibit PFK-1 by binding to an allosteric site and lowering the affinity of the enzyme for F-6-P. Molecules regulate PFK-1 and FBPase-1 activity PFK-1 ATP citrate ADP AMP F2.6BP FBPase-1 • ADP and AMP relieve the inhibition by ATP. • Citrate increases the inhibitory effect of ATP. • F-2,6-BP is the strongest activator of PFK-1. Regulation of gluconeogenesis Pyruvate carboxylase FBPase-1 Pyruvate carboxylase • Pyruvate carboxylase is being positively regulated by acetylCoA. • The accumulation of acetylCoA signals that cell’s energy demands are met. • Acetyl-CoA also indirectly inhibit pyruvate dehydrogenase complex.