Animal Kingdom
•
•
•
•
•
Muticellular
Eukaryotic
Heterotrophs
Approximately 35 phyla
Most phyla cells are
organized into tissues
that make up organs.
• Most reproduce sexually.
• Motile sperm have
flagella
• Nonmotile egg is much
larger than sperm.
Animal Body Structures
• The term Symmetry refers
to a consistent overall
pattern of a structure.
• Asymmetrical – Having
no distinctive body shape.
• Radial Symmetry Similar part branch out in
all directions from a central
line.
• Bilateral Symmetry –
Having two similar halves
on either side of a central
plane (mirror images of
each side)
Asymmetrical
Body Cavities of Animals
• Coelom- body cavity
• Acoelomate-not having a
body cavity
• Pseudocoelomate-not a
true body cavity.
• Coelomate-animal
having a true body
cavities
Animals and their body cavity
Invertebrates
• Animals that do not
have a backbone.
• Invertebrates
constitute the
greatest number of
animal species.
• Invertebrates are the
most of the
individual animals
alive today
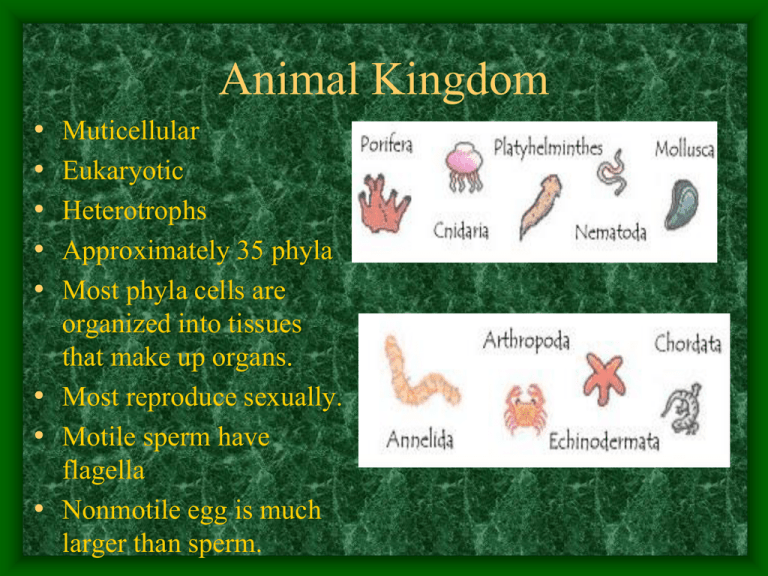
8 Phyla of Invertebrates
• Porifera
• Cnidaria
• Platyhelminthes
• Nematoda
• Annelida
• Molluska
• Arthropoda
• Echinodermata
Porifera (Sponges)
•
•
•
•
8000 species
Very porous tissue
Filter feeders
Contain spicules
(skeleton) & spongin
(soft tissue).
• Sessil adults (nonmotile),
motile larva
• Asymmetrical body plan
Sponges of the Ocean
Giant Barrel Sponge
Venus flower basket
Vase sponge
Yellow sponge
Cnidaria (Coelenterates, means
“hollow gut”)
• 9500 species
• Two body forms
- medusa: bell shape
- polyp: vase shape
Have stinging cells
called cnidocyts
Examples include:
jellyfish, coral, hydra,
sea anemone, sea fan.
Cnidarians of the Ocean
Jellyfish
Jellyfish
Coral
Hydra
Sea anemone
Brain Coral
Platyhelminthes (Flatworms)
• 20,000 species
• Flat bodies and
unsegmented
• Mostly parasitic, some
free living
• Bilateral symmetry
• Acoelomates no body
cavity
• Parastic
- tapeworm
-blood fluke
-sheep liver fluke
-beef fluke
•Free-living
-planarians
-marine flatworm
Platyhelminthes of the World
Blood fluke
Marine flatworm
Planarian
Tapeworm
Nematoda (Roundworms)
•
•
•
•
80,000
Unsegmented
Many parasitic
Bilateral symmetry
• Example include:
-pinworm
-hookworm
-heartworm
-Trichinella
(porkworm)
-Ascaris
Nematoda’s of the World
Ascaris
Heartworm of a dog
Hookworm
Trichinella
(porkworm)
Annelida (segmented worms)
• 12,000 species
• Repeating body
segments
• Bristles in most
species.
• Bilateral symmetry
• Examples include:
-earthworm
-leeches
-sandworms
-clamworms
-fanworms
-Christmas tree
worm
Annelida’s of the world
Clamworm
Christmas
Tree Worm
leech
Mollusca
(soft-bodied invertebrates)
• 2nd largest group of
invertebrates and of all
other animals
• 100,000 species
• All have a mantle.
• Some have a shell
covering the soft body.
Classes of Mollusca
*Polyphacophora
(bearing many plates)
-chitons
*Bivalves
(two siphons)
-clams
-oysters
-mussels
-scallops
*Gastropods
(Stomach-footed)
-slugs
-snails
-nudibranch
*Cephalopods
(Head-footed)
-squids
-octopus
-nautilus
-cuttlefish
Polyphacophora
Chitons
Bivalves
Mussels
Clams
Oysters
Scallops
Gsatropods
Snail
Slug
Nudibranch
Cephalopods
Giant Squid
Octopus
Nautilus
Cuttlefish
Arthropoda (jointed legs)
• Largest phylum of the
animal kingdom
(1 million species)
• Has a exoskeleton
• Many species undergo
metamorphosis
(complete or incomplete
metamorphosis)
Classes of Arthropods
• Insecta (6 legs)
• Crustaceans (10 or more legs)
-Largest class
(800,000 species)
include: fly, beetles,
bee, grasshopper,
•
moths, & butterflies
• Arachinids (8 legs)
include: spiders,
scorpions, mites, ticks,•
& horseshoe crabs
include: lobsters, crabs,
crayfish shrimp, barnacles
Chilopoda (1pair of legs per
segment) flat body, carnivorous
include: centipeds
Diplopoda (2 pair of legs per
segment) round body,
herbivorous include: millipeds
Insects and Metamorphosis
• Complete
Metamorphosis
-process an
insect passes
through three
separate stages
of growth, as
larva, pupa,
and adult.
•
Incomplete Metamorphosis
A life cycle of
certain insects,
such as crickets
and grasshoppers,
characterized by
the absence of a
pupa stage between
the nymph and
adult stage.
Insecta
Praying
Mantis
Unicorn Beetle
Hercules Beetle
Insects have been present for about 350 million years, and
humans for only 130,000 years. The oldest known fossil of an
insect dates back 400 million years and is a springtail
More Insects
Walking Stick
Damselfly
Dragonfly
Giant
Vinegar Bug
Katydid
Locust Ladybug &
Aphid
Arachnids
Brown Recluse
“fiddleback”
Tick
Tarantula
Mite
Black widow
Scorpion
Crustaceans
Lobster
Water fleas or
Daphnia
Barnacles
Shrimp
Crayfish or
“crawdads”
Snow Crab
Chilopoda (Centipedes)
Australian centipede
Amazon Giant Centipede
Redheaded Centipede
Chinese Redheaded Centipede
Diplopoda (millipede)
African Giant Black Millipede
Echinodermata (spiny-skinned)
• 6000 species
• Examples include:
Starfish (sea stars)
• Radial Symmetry
Sea Urchin
• Water vascular system
for movement
• Usually have a fivepart body plan
Sand dollars
Sea cucumbers
Brittle star
Echinoderms
Feather Star
Brittle star
Sea Urchin
Starfish
Sand Dollar
Sea cucumber
Starfish and Clams
Tube feet
Water vascular system
Eating a Clam
Regeneration
Animal (Chordates)
• pharyngeal slits - a
series of openings that
connect the inside of
the throat to the
outside of the "neck".
These are often, but
not always, used as
gills.
• post-anal tail - an
extension of the body
past the anal opening.
• dorsal nerve cord - a
bundle of nerve fibers
which runs down the
"back". It connects the
brain with the lateral
muscles and other
organs.
• notochord cartilaginous rod
running underneath,
and supporting, the
nerve cord.
Chordates
• Subphylums
Cephalochordata
lancelet
*lancelets
-Urochordata
*tunicate
-Vertebrata
*all animals
with a
backbone
Larva
Adult
Tunicate “Sea Squirt”
Vertebrates
• Animals with an internal
skeleton made of bone are
called vertebrates.(Some are
made of cartilage)
• Vertebrates include: primates,
such as humans and monkeys;
amphibians; reptiles; birds; and,
fish
• Although vertebrates represent
only a very small percentage of
all animals, their size and
mobility often allow them to
dominate their environment.
Classes of Vertebrates
• Agnatha
(Sucker fish)
-jawless
-eel-like
-scale less
-skeleton made of
cartilage
-most lamprey are
parasitic
• Examples include:
-hagfish
-lamprey
Agantha
Mouth of
lamprey
Hagfish
Chondrichthyes
(Cartilaginous Fish)
• Hinged jaws
• Examples include:
– Sharks
• Paired fins
– Rays
• Skeleton made entirely
of cartilage
• They have placoid
scales (sharks-rough
teeth-like scales)
– Skates
– sawfish
Chondrichthyes
Sawfish
Skate
Hammerhead shark
Great White Shark
Stingray
Osteichthyes (bony fish)
• Hinged jaws
• Paired fins
• Fish with skeleton
made entirely of bone
• Largest class of
vertebrates (23,500)
• 3 main groups
-Lobe-finned fish:
coelacanths
-Lung-fish:
lungfish
-Ray-finned fish:
bass, perch, eel,
gar, catfish,
sea horse, flounder
& marlin
Lobe-finned fish
(Coelacanths)
Lungfish
Ray-finned fish
Largemouth bass
Seahorse
Alligator gar
180 lbs
flounder
flounder
More Ray-finned fish
Clown fish
Puffer fish
Archer fish
Morey Eel
Ray-finned fish
Crappie
Crocodile fish
Paddlefish
Blue Marlin
Amphibian
(both life or double life)
• Live part of its life on
land and part in the
water.
• Some may live in the
water during the larva
stage than move to land,
but only return to the
water for reproduction.
• Moist, smooth skin
• 3 main groups:
– Urodela (visible tail)
salmander, mudpuppy,
siren, & newts.
– Anura (without tail)
frogs and toads
– Apoda (no legs)
caecilian
Urodela (Visible Tail)
California Tiger
Salamander
Mudpuppy
Siren
Red-Spotted Newt
Anura (Without Tail)
Green Rock Frog
(poisonous)
Bullfrog
Leopard Frog
Poisonous Dart Frog
American Toad
Apoda (no legs)
Sir Lanka Caecilian
Reptilia
• Dry, rough, leatherylike scales
(waterproof)
• Eggs that have a
leathery shell
• Descendents of
dinosaurs
• Examples include:
–
–
–
–
Snakes
Lizards
Turtles
Alligators and
Crocodiles
Snakes
Rattlesnake
Cottonmouth (water moccasin)
Coral snake
Copperhead
Lizard
Mountain Boomer
(collared lizard)
Gecko
Gila monster
(poisonous)
Beaded lizard
Horned Lizard
(horny toad)
Komodo Dragon
Turtles
Snapping Turtle
Box turtle
Alligator Snapping
Turtle
Sea Turtle
Giant Tortoise
Alligators or Crocodiles
Alligator
Crocodile
Aves (birds)
• Aves comes from the
• Have hollow bones
word meaning
aviation
• Only animal to have
feathers
– Down feathers
(insulation)
– Contour feathers
(flight)
(flight)
• Have a syrinx (sound)
• Descendents of
reptiles
• 9000 species
Aves (birds)
Scissortail
Flycatcher
California
Condor
Emu
Penguin
Hummingbird
Bald Eagle
Mammalia (Mammals)
• Body covered with
hair, fur, subcutaneous
fat
• 4600 species
• Milk produced in
mammary glands
• Respiration with the
use of a diaphragm
(muscular sheet that
lies between the lungs
and abdominal area)
• Orders Include:
-Monotremes (egg laying
mammals)
-Duck-billed
platypus, Spiny
anteater (short
beaked
echidna)
-Marsupials (pouched
mammals)
-Opossum, kangaroo,
koala bear
More Mammals
• Placentals
– Young develop entirely in the mothers uterus
– Young nourished through the placenta via the
umbilical cord
– Largest group of mammals (4500)
Monotremes
Spiny Anteater
(echidna)
Duck-billed
Platypus
Marsupials
Opossum
Koala bear
Wombat
Kangaroo
(wallaby)
Placentals
Buffalo (Bison)
Whitetail Deer
Dolphin
Humans
Bat
Killer whale
More Placentals
Armadillo
Aarvark
Elephant
Manatee
porcupine
Hedgehog
Happy
Easter!
This is why you should study Biology!!!