BI11_LG_U08 - BC Learning Network
advertisement
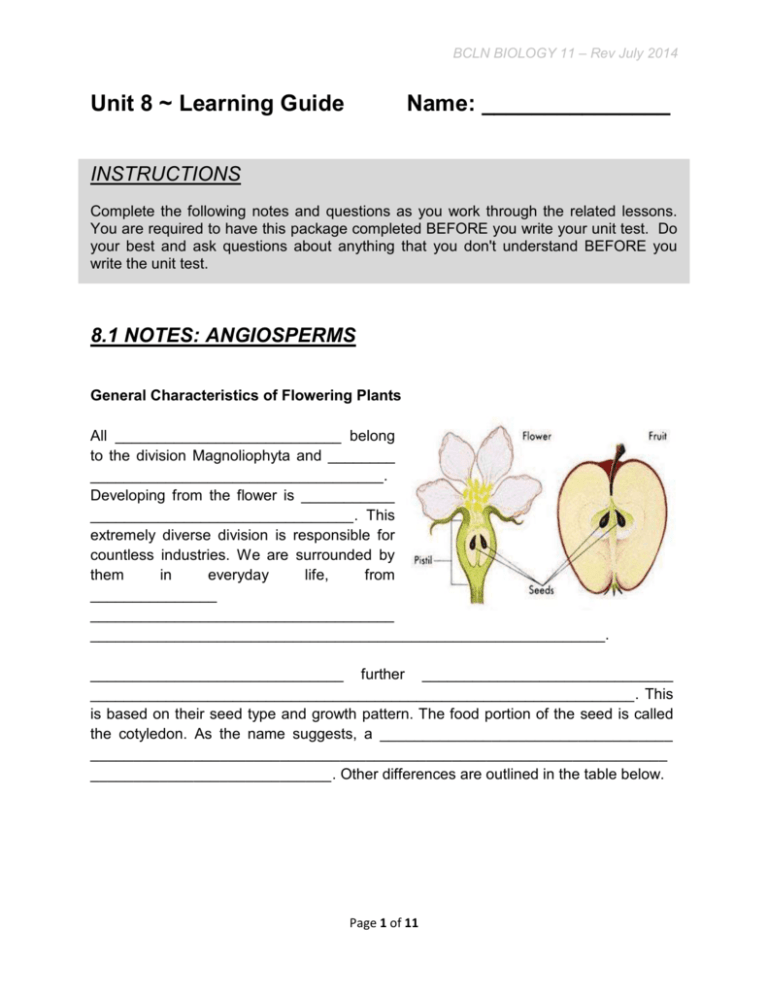
BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Unit 8 ~ Learning Guide Name: _______________ INSTRUCTIONS Complete the following notes and questions as you work through the related lessons. You are required to have this package completed BEFORE you write your unit test. Do your best and ask questions about anything that you don't understand BEFORE you write the unit test. 8.1 NOTES: ANGIOSPERMS General Characteristics of Flowering Plants All ___________________________ belong to the division Magnoliophyta and ________ ___________________________________. Developing from the flower is ___________ _______________________________. This extremely diverse division is responsible for countless industries. We are surrounded by them in everyday life, from _______________ ____________________________________ _____________________________________________________________. ______________________________ further ______________________________ _________________________________________________________________. This is based on their seed type and growth pattern. The food portion of the seed is called the cotyledon. As the name suggests, a __________________________________ ___________________________________________________________________ ____________________________. Other differences are outlined in the table below. Page 1 of 11 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Comparison of Monocot versus Dicot Angiosperms Characteristic Monocot seed seed leaf (1st leaf to form in germination) vascular bundles (xylem and phloem) veins in leaf flower parts (such as petals and sepal) A Visual Comparison of Monocots versus Dicots Page 2 of 11 Dicot BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Monocots and Dicots also ________________________________________________ _______________________. _______________________ have a tap root system. Monocot have a ____________________________________________. Monocot Dicot The Flower The development of the flower and the fruit are the key to the success of the angiosperms. These specialized structures create a symbiotic relationship with certain animals to aid in fertilization as well as dispersion of the species. _________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________. After it is fertilized the flower will develop into a fruit which may be harvested and eaten by animals. _____________________________________________________________________ ___________________________to be dropped with a bit of extra fertilizer. Page 3 of 11 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Flowers_______________________________ _____________________________________ _. The ______________________________ ______________________________. In most flowers this is fused together to form a _______________. The _________________ _____________________________________ ___________________. Eggs are stored in the ovary until they are fertilized. Special chemicals prevent sperm from fertilizing the eggs of flowers that are not the same kind. The _________________________________ _________________________________. The stamen ______________________________ ____________________________________ ______________________________. Sexual reproduction occurs when pollen from an anther is transferred to the stigma. Pollination is often aided by insects that have evolved with these plants. Plants can self- fertilize or cross-fertilize (pollen transferred to stigma of a different plant). Types of Fruit The ___________________________________________ __________________________________. The fleshy part of the fruit develops from the ovary and ovary wall of the flower. The function of this flesh varies in different plants but it to some __________________________________________________ ________________________________________. The fruit can take on a specialized shape to be transported by wind (e.g., maple) or water (e.g., coconut) or can develop into a fruit that offers an animal nutrition in exchange for transport. We commonly think of apples, bananas, oranges or melons as fruits, however, many other foods we don't consider are fruits as well. Foods such as ____________________________ ___________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________ _____________________________________ because they develop from a flower. Page 4 of 11 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Angiosperm Reproduction As with the gymnosperms, ________________________________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _________________________________________________________. Flowers hold male and female reproductive organs. The ___________________________________ ______________________________________________________________________. It is here where meiosis takes place. In ________________________, meiosis produces the _________________________ that _____________________________ _____________________________________ and in __________________________ meiosis produces ________________________________ that __________________ ____________________________________________________________________ ___________________________________________________________, around the embryo sac, and provides a passage for sperm to swim to the egg. Two sperm will enter the embryo sac. _________________________________________________ ________________________________________________________________. This process is called ___________________________________________. The fertilized polar nuclei will develop into a triploid (3n) endosperm that ______________________ ____________________________________ that develops from the zygote (fertilized egg). Still surrounding the seeds at this point is the fruit that has developed from the ovary wall. The fruit can function in various ways to aid in dispersal. Diagram of Angiosperm Reproduction Page 5 of 11 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 Economic Importance of Angiosperms "To some black gold refers to oil. To others, it refers to coffee" - Mark Pendergast As with gymnosperms, _______________________________ _________________________________. However, ________ __________________________________________________ ___________________________. Hardwoods are _________ ___________________________________________________ due to their varying colours and grain patterns. The durability and strength of hardwoods mean they are used for more expensive ________________________________________. Birch, maple, and oak are each examples of hardwoods that are commonly used for these purposes. When we think of angiosperms, we think of flowers and fruit, which both have obvious economic implications. Many angiosperms have a less woody or herbaceous tissue and ___________________________________________________ ______________________________. For example, with sugar beets the root is used to make sugar and with sugar cane the stalk of the plant is used. _____________________________ _____________________________________________________________________ _____________________________________. We do not only consume the fruit. One group of fruits has an extremely large effect on world nutrition. These are the grains. ___________________________________ are consumed worldwide as a base of consumption providing starch to the diet. Other uses of angiosperms are seen in drinks such as __________________________ _____________________________________. Cotton is used in _________________. ___________________ was derived from the rubber tree. Now most rubber is synthetic. _____________________________________________________________ _____________________________________________ that were derived from plants. Page 6 of 11 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 8.1 PRACTICE: ANGIOSPERMS 1. Describe how angiosperm seeds differ from gymnosperm seeds. (2 marks) 2. Indicate whether the following statement applies to a monocot (M) or a dicot (D). (4 marks) _____ a. Plant develops with one cotyledon _____ b. Plant has net-like veins. _____ c. Plant has vascular bundles arranged in circles. _____ d. Plant has flower petals arranged in multiples of three. 3. Describe three functions of fruit with respect to plant survival. (3 marks) Page 7 of 11 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 4. Label the diagram below with the following terms. Please provide a brief explanation the function of each structure. Please be neat. (14 marks) o sepal o stigma o filament o petal o anther Page 8 of 11 o style o ovary BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 5. What is the dominant stage in the angiosperm life cycle? Is this stage diploid or haploid? (2 marks) ~ END OF BIOLOGY 11 UNIT 8 LEARNING GUIDE ~ Page 9 of 11 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 UNIT 8 ANSWER KEY 8.1 NOTES: ANGIOSPERMS 1. Describe how angiosperm seeds differ from gymnosperm seeds. (2 marks) - gymnosperm have naked seed whereas angiosperm have fruit covering their seeds 2. Indicate whether the following statement applies to a monocot (M) or a dicot (D). (4 marks) _____ a. Plant develops with one cotyledon _____ b. Plant has net-like veins. _____ c. Plant has vascular bundles arranged in circles. _____ d. Plant has flower petals arranged in multiples of three. 3. Describe three functions of fruit with respect to plant survival. (3 marks) - provides nutrients - provides protection - enhances dispersal Page 10 of 11 BCLN BIOLOGY 11 – Rev July 2014 4. Label the diagram below with the following terms. Please provide a brief explanation the function of each structure. Please be neat. (14 marks) o o o o o sepal stigma filament petal anther o o style ovary Sepal = protects budding flower Stigma = receives pollen during fertilization filament = holds anther up Petal = attracts pollinators Anther = contains pollen/male reproductive cells style = tube leading to ovary where pollen enters ovary = female reproductive organ 5. What is the dominant stage in the angiosperm life cycle? Is this stage diploid or haploid? (2 marks) - sporophyte (2n) = diploid Page 11 of 11