Parasite 寄生虫
advertisement

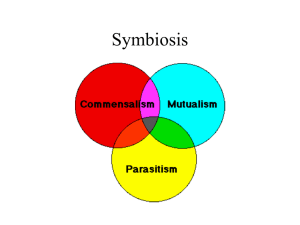
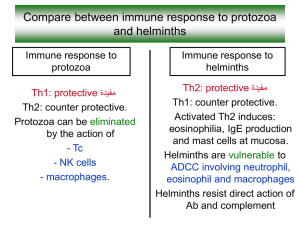
Human Parasitology For 8-year medical students 人体寄生虫学 Wu Zhongdao, Ph.D Professor Department of Parasitology QQ: 1151917403 2014-10-9 Prof Lv Fangli(吕芳丽) Prof Li Xiurong(李学荣) Prof Fung Mingchiu(冯明钊), Ph.D, (Hong Kong Chinese University) Associate Prof Wang Xuelan(汪雪兰) 林炳亮教授 科 职 擅 室: 中山三院感染性疾病科 称: 主任医师 教授 长: 乙肝,丙肝的抗病毒治疗 ,肝硬化,肝 衰竭的救治,自身免疫性肝病及寄生虫病的诊治 执业经历: 医学博士,研究生导师,1991年从中山 医科大学毕业后一直在现单位从事感染性疾病的临床 和研究工作。美国西北大学访问学者,广东医学会感 染病学分会秘书,广东医学会肝脏病分会病毒性肝炎 组常委,广东寄生虫病学会常务理事,主要研究病毒 性肝炎防治 ,肝硬化的诊治 ,肝衰竭和肝再生机制, 干细胞治疗终末期肝病的临床应用。 教学进度表请上360云盘下载: http://yunpan.cn/cgfGGzPYfK6HZ 访问密码 5229 Curriculum of Human Parasitology 2014 1. Lecture: 9 Nov~15 Jan 2 hr each week Total 32 hr 2. Practice in Laboratory:19 Nov ~3 Jan 3 hr each week Total 24 hr 3. TBL & learning by yourself 4. Test: homework, final test 学习内容 寄生虫学(parasitology)总论 吸虫 (trematode) 绦虫 (cestode) 线虫 (nematode) 原虫 (protozoa) 医学节肢动物(arthropoda) Textbook and reading books: Textbook of Medical Parasitology, Edition by Wu Zhongdao, Lv Fangli and Zheng Xiaoying.The book can be ordered at the Department of Parasitology 《人体寄生虫学》(詹希美教授主编)人民卫生出版社 (第二版) Parasite online http://www.msu.edu/course/zol/316/ PARASITOLOGY online textbook: http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/book/parasit-sta.htm http://202.116.102.10/BIOLOGY/news/home.aspx http://pathmicro.med.sc.edu/book/parasit-sta.htm Parasite online http://www.msu.edu/course/zol/316/ http://www.cdc.gov/parasites/az/index.html http://apps.who.int/tdr/ 利用网上工具如Youtube搜寻视频学习资料 考试形式:100分 1、理论考试: 8年制及检验:笔试(期终):80分 五年制临床及医学相关:笔试(期终:80分) 2、实验考试:辩认虫卵或虫体标本(20个标本,15分) 实验课平时作业:5分) 2. 学习竞赛活动--人体寄生虫学课程学习创意比赛 ① 人体寄生虫学生活史模式图; ② 人体寄生虫学学习内容的相关歌曲或微视频; ③ 人体寄生虫虫体或虫卵手机照片。 我们将通过老师和学生评分相结合的形式,各评出优 秀奖6名,三等奖4名,三等奖2名,1等奖1名。 请各位同学将自己的作品发送到:刘记收, 1224989703@qq.com。 Lesson one 寄生虫学概述 Introduction of Parasitology Parasite(寄生虫) Host(宿主) Parasitism(寄生关系) Parasitize (寄生) Parasitic disease (寄生虫病) What is Parasite(寄生虫) ? Parasitic diseases (寄生虫病)? Parasitology (寄生虫学)? Parasitic helminth eggs(400×) 1. unfertilized egg of A.lumbricoides (未受精蛔虫卵) 2-4. fertilized egg of A.lumbricoides (受精蛔虫卵) 5-7. hookworm eggs (钩虫) 8. egg of Trichuris trichiura (鞭虫虫卵) 9-10. eggs of Enterobius vermicularis (蛲虫虫卵) 11-12. eggs of tapeworm (绦虫虫卵) 13. egg of Hymenolpis nana (微小膜壳绦 虫虫卵) 14. egg of Clonorchis sinensis (华支睾吸虫 虫卵) 15. egg of Schistosoma japonicum(日本血 吸虫虫卵) 16. egg of Paragonimus westermani (卫氏 并殖吸虫虫卵) 17. egg of Fasciolopsis buski(布氏姜片虫 虫卵) egg of Schistosoma japonicum 日本血吸虫 hookworm eggs 钩虫 egg of Schistosoma mansoni 曼氏血吸虫 egg of Schistosoma haematobium 埃及血吸虫 bancrofti microfilariae 斑氏丝虫微丝蚴 malayi microfilariae 马来丝虫微丝蚴 larve of Strongyloides stercoralis 粪类圆线虫 larve of Angiostrongylus cantonensis 广州管圆线虫 larvae cyst of Trichinella spiralis 旋毛虫 cysticercus of Taenia saginata 牛带绦虫囊尾蚴 Sparganum of Spirometra mansoni 曼氏迭宫绦虫裂头蚴 cysticercus of Taenia solium 猪带绦虫囊尾蚴 Trophozoite of Entamoeba histolytica 溶组织阿米巴滋养体 Trophozoites of Giardia lamblis 蓝氏贾第鞭虫滋养体 cyst of Entamoeba histolytica 溶组织阿米巴包囊 cysts of Giardia lamblis 包囊 trophozoite of Plasmodium vivax 间日疟原虫滋养体 schizont of Plasmodium vivax 间日疟原裂殖体(裂殖子schizozoite) Female gametocyte of P. vivax male gametocyte & trophozoite of P. vivax 间日疟原虫雌配子体 间日疟原虫雄配子体 Biology of Parasites • • • • • • Symbiosis (共生现象) Parasitism (寄生现象) Parasite (寄生虫) Host (宿主/寄主) Life cycle Parasite-host interaction Symbiosis (共生) 1.Commensalism (共栖) 2.Mutualism (互利共生) 3. Parasitism Parasite Definitive host Intermediate host Reservoir host (寄生) Host Paratenic or transport host Symbiosis (共生) both members of different species living together Including: • Commensalisms • Mutualism • parasitism Commensalism (共栖): The word was from Latin for “eating at same table”, denoting an association which is beneficial to one partner and at least not disadvantageous to the other. The two partners can survive independently. Mutualism (互利共生) an association in which the mutualist and the host depend on each other physiologically, and such an association is beneficial to both organisms (partners). Bifidobacterium Parasitism (寄生) another type of symbiotic relationship between two organisms: a parasite (寄生), usually the smaller of the two, and a host (宿主), upon which the parasite is physiologically dependent. A parasite (寄生虫) : an organism that lives on or in a host organism (宿主) and gets its food from or at the expense of its host. 寄生物(parasite): virus, bacterium, protozoa, helminths one cell or multicellular organism Survive Manner : • Obligate parasite (专性寄生虫): cannot survive in any other manner, such as most human parasites • Facultative parasite (兼性寄生虫): exist in a free-living state or as a commensal state, such as Strongyloides stercoralis • Temporary parasite (偶然寄生虫): somrtime invide into human (animal parasite) Living in body or on the surface: • Endoparasite (体内寄生虫) • Ectoparasite (体外寄生虫) There are three main classes of parasites that can cause disease in humans, medical/human parasites: 1. Medical Protozoa(原虫) 2. Medical Helminths(蠕虫) 3. Ectoparasites/Medical arthropods(体外寄生虫或医 学节肢动物). Helminths: Trematode(吸虫) Tapeworm/cestode (绦虫) Nematode (线虫) How to name parasite? Phylum(门)、Class(纲)、Order(目)、 Family(科)、Genus(属)、Species(种) Each parasite has two names: a Genus(属名) and a Species name(种名) Schistosoma japonicum 属名 种名 Protozoa(原虫) Blood Intestine Lung Other organ Plasmodium Leishmania Toxoplasma Entamoeba Cryptosporidium Giardia Pneumocystis Trichomonas 疟原虫 利什曼原虫 弓形虫 阿米巴 隐孢子虫 贾第虫 肺孢子虫 毛滴虫 Trematode(吸虫) Blood Schistosome spp 血吸虫 intestine Clonorchis sinensis 肝吸虫 Fasciolopsis buski 姜片虫 Lung & other Paragonimus westermani organs 肺吸虫 Tapeworm(绦虫) Intestine Taenia solium 猪带绦虫 intestine Taenia saginata 牛带绦虫 Liver & other organs Brain & other organ Echinocococus granulosus(larva) Spirometra mansoni(larva) 细粒棘球绦虫 曼氏迭宫绦虫 Nematode(线虫) Ascris 蛔虫 pinworm 蛲虫 whipworm 鞭虫 hookworm 钩虫 Lymphatic system filaria 丝虫 Intestine & muscle Trichnella 旋毛虫 intestine Medical arthropod(医学节肢动物) Class Arachnid Tick, mite 蜱、螨 Class Insecta 蚊、蝇、白蛉、 蚤、虱、蟑螂 Mosquito,fly, sandfly,flea, louse, cockroach What is Parasitology? Parasitology (寄生虫学): the study of parasites and their relationships to their hosts. Medical parasites The morphology, life cycle Relationship with hosts and environment How to control Medical Parasitology Human parasitology Medical protozoology(原虫学) Medical helminthology(蠕虫学) Medical arthropodology(节肢 动物学)/entomology(昆虫学) What is Parasitology? Parasite 寄生虫 pathogen Host 宿主 humans/animals Relationship of parasitism Control of parasitic disease Basic subject of medicine Life cycle(生活史): The period of time that it takes for an organism to live its entire life. Some animals, such as parasite and insects, change their shape several times during their life cycle. Host: definitive host intermediate host reservoir host paratenic host. Host(宿主) : an organism that harbours the parasite and provides the nourishment and shelter. Definitive host (终宿主) : harbour the adult parasites and most highly developed form of the parasite or in which the parasite replicates sexually. Intermediate host (中间终主) : harbour the larval stages of parasite development or the asexual forms of the parasite . Reservoir host (保虫宿主) : harbours the parasites and serves as an important source of infection to other susceptible hosts Host? Parasite? The stage of life cycle? The stage of infection(invading) Parasitic site? Which stage of parasite can be detected? Paratenic host or transport host (转续宿主) The larva of some parasites can invade a non-normal host, but can not grow, and only lives in the larva stage. If the larva enters a normal definitive host, it can continue to grow into an adult worm. The non-normal host is called paratenic host or transport host. It functions as a transport or carrier host. Reservoir host Paratenic host or transport host Zoonosis Zoonosis(人兽共患病) : means the diseases of animals which are transmissible to man. These are the infections which are naturally transmitted between the vertebrate animals and man. Animal human TRANSMISSION OF PARASITES(传播) Source of infection (传染源) Oral route Inoculation by an arthropod Penetration of vector the skin and mucous Sexual contact membrane Susceptible individual (易感者) Parasite-host interaction Parasite’s ability to breach host barriers and to evade destruction by innate local and tissue host defenses Parasitism is the result of evolution. free living parasitism Parasite have the ability to fit the environment of host Commensalism 共栖 Parasitism 寄生 互利 共生 Mutualism Host impact on parasite Innate immunity Acquired immunity parasite Changes of structure IMMUNOEVASION Parasite impact on host damages Direct damage loss nutrition toxins & hypersensitivity Parasitic infection and Parasitic diseases Parasite infection individual Infective individual without symptoms Acute Chronic advanced Parasites are still common pathogenic organisms of human • Targeted diseases in China: HB, HIV,TB, SARS, Schistosoma japonicum • Most of target diseases in TDR/WHO New public health problems Co-infection, Imported infection, emerging infection, opportunistic infection , Worm world! Accoding to WHO statistics , parasites are the cause of more human deaths than anything else apart from HIV/AIDS and TB, one living person in ten suffers from one or more of eight major tropical diseases: malaria, schistosomiasis, lymphatic filariasis, onchocerciasis, leprosy, sleeping sickness,Chagas disease,and leishmaniasis <<Parasitology Today>> http://www.who.int TDR focuses on infectious diseases √ African trypanosomiasis(非洲锥虫病) √ Chagas disease(恰加斯病或美洲锥虫病) Dengue(登革热) √ Leishmaniasis(利什曼病) Leprosy(麻疯病) √ Lymphatic filariasis(淋巴丝虫病) √ Malaria(疟疾) √ Onchocerciasis(盘尾丝虫病或河盲症) √ Schistosomiasis(血吸虫病) Tuberculosis(结核病) 在发达国家也面临寄生虫病的问题: 国际旅行-境外感染-疟疾等 新现的寄生虫-如Cyclosporiasis(环孢子虫病) http://www.cdc.gov/ Outbreak Investigations — United States, 2014 2014年美国环孢子虫病发病人数统计 (Cyclosporiasis) 提出了一个观点:进一步审视“寄生现象”,进一步 探索利用“寄生虫”感染诱导TH2为主优势免疫应答 的特性,发展新型生物治疗方法和虫源性药物 http://infect.dxy.cn/article/80806(丁香园) 许多寄生虫抗原对抗原递呈细胞的成熟和分化起抑 制作用 我们课题组的工作 rSj16 induce more Treg T cells in vitro * + IL-12p40,IFN-r,IL-17 rSj16 induce more Treg T cells in vivo IL-10,IL-4 Why should you study Parasitology? To be a doctor , Basic subject of medicine: relation to immunology and pathology How to study ? Morphology, Life cycle, Pathogenesis and clinical manifestation Diagnosis, Epidemiology and control Key points: life cycle(生活史) How many stages of the life cycle? Which stage is infective stage? And how? Which stage inhabit humans? And where? Which stage is primary cause of the disease? Which stage was detected for diagnosis?