Meiosis
biology
Sexual Reproduction
Slide
1 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
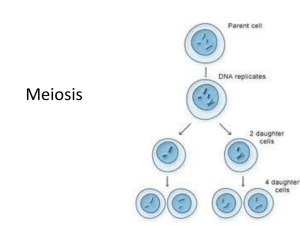
11-4 Meiosis
Phases of Meiosis
What happens during the process of
meiosis?
Sperm and ova (egg)
are created!
Sperm and ova are haploid
Slide
2 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Chromosome Number
Chromosome Number
All organisms have
different numbers of
chromosomes.
Human = 46
Carrot = 18
Dog = 78
Goldfish = 94
Slide
4 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Chromosome Number
*These two sets
of chromosomes
are
homologous.
One
chromosome
from mom and
one chromosome
from dad.
Slide
5 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
Homologous Chromosomes
•*Def: Pair of chromosomes
that contain the same alleles
for traits and phenotypes
•EX: chromosome with eye
color allele from mom is
homologous to chromosome
with eye color allele from dad
Mom
(1,3)
Dad
(2,4)
Chromosome Number QUIZ
How many
chromosomes
are in the
picture?
46
How many
homologous
chromosomes
are in the
picture?
23
11-4 Meiosis
Phases of Meiosis I
Meiosis I
Interphase I
Meiosis I
Prophase I
Metaphase I
Anaphase I
Telophase I
and
Cytokinesis
Slide
8 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Interphase I
centrioles
DNA copies itself
nucleus
Slide
9 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Prophase I
Nuclear membrane
disappears.
Homologous
chromosomes pair
up to form a tetrad.
Tetrad = 4 sister chromatids
Crossing over
occurs
Slide
10 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
Which pair up to make
homologous chromosomes?
Pink with pink;
yellow with yellow;
blue with blue
How many pairs
of homologous
chromosomes
are shown?
3
How many
chromosomes
are shown?
6
CROSSING OVER
1. *Homologous chromosomes pair up
2. One sister chromatid breaks off and
exchanges itself with a sister chromatid from
the other homologous chromosome.
Results in variation! Nature likes this
because some will be more fit than others.
Occurs randomly at different spots on
sister chromatid each time of meiosis.
That is why you don’t look exactly like your
siblings.
11-4 Meiosis
Crossing over
•When homologous chromosomes form tetrads in meiosis I, they
exchange portions of their chromatids in a process called crossing
over.
•Crossing-over produces new combinations of
alleles.
Does crossing over always occur at the
same allele?
NO! It is
random
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
Slide
13 of 35
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Metaphase I
Homologous
chromosomes line
up in middle of cell
Spindle fibers attach
to the chromosomes.
Slide
14 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Anaphase I
The fibers pull
the homologous
chromosomes
apart toward
opposite ends of
the cell.
Slide
15 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Telophase I
Nuclear membranes
form.
The cell
separates into
two cells.
Slide
16 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Phases of Meiosis
Meiosis involves two divisions
*meiosis I
*meiosis II
Slide
17 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Phases of Meiosis II
Meiosis II
Telophase I and
Cytokinesis I
Meiosis II
Prophase II
Metaphase II
Anaphase II Telophase II
and
Cytokinesis
Slide
18 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Prophase II
Nuclear
membrane
disappears.
Slide
19 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Metaphase II
Individual
chromosome
s line up in
the middle of
cell.
Slide
20 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Anaphase II
The sister
chromatids
separate and
move toward
opposite ends
of the cell.
Slide
21 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Telophase II
Meiosis II results
in four nonidentical haploid
cells.
Slide
22 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
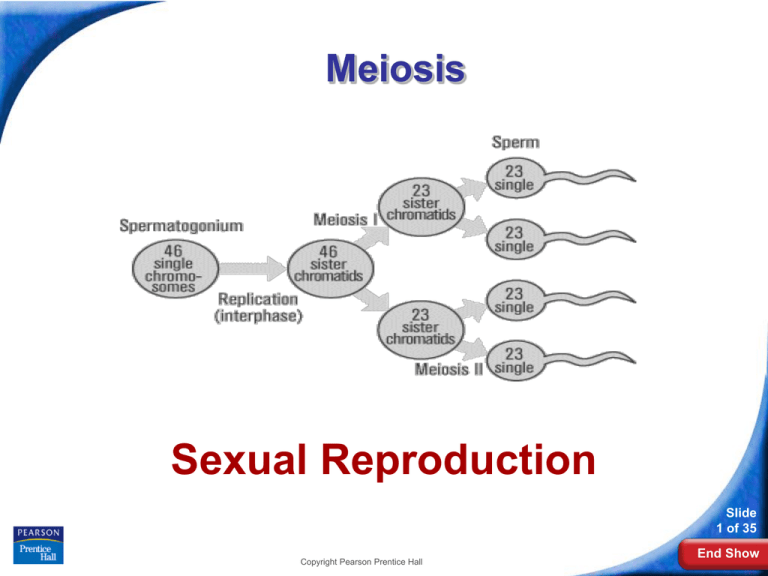
Gamete Formation
Gamete Formation
In male animals, meiosis results in four equal-sized
gametes called sperm.
Slide
23 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Gamete Formation
In many female animals, only one egg results from
meiosis. The other three cells, called polar bodies,
are usually not involved in reproduction.
Slide
24 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show
11-4 Meiosis
Meiosis
Why is meiosis important?
• Creates gametes that are HAPLOID.
• Due to crossing over, meiosis also creates
variation.
Slide
25 of 35
Copyright Pearson Prentice Hall
End Show