Meiosis
• Mitosis Review animation
Asexual (vegetative) Reproduction• one parent produces an offspring
– Uses only mitosis
– Produces genetically identical offspring (each
offspring is an exact copy of the original organism)
•
Rapid- no need to find mates
– No mechanism for genetic diversity- works well in
a stable, unchanging environment.
Sexual Reproduction• the formation of a new individual by a
combination of two haploid sex cells
– Uses Meiosis- a specialized type of cell division which
halves the # of chromosomes in a gamete
• Female Gamete
– egg (ovum)
• Male Gamete
– sperm
– Requires Fertilization• the union of a sperm and an egg
• (N + N = 2N)
– Makes a zygote• the product of fertilization (has two sets of chromosomes)
– Causes changes in the genetic information
• in order to increase the diversity in the offspring.
How are the Goals of MEIOSIS Different
from the Goals of MITOSIS?
MITOSIS
MEIOSIS
1) Produces identical
daughter cells
(genetically)
1) Produces cells that
are NOT genetically
identical
2) Produces daughter
cells with the same
number of chromosomes as mother cell
2) Cuts chromosome
number of mother cell
in half
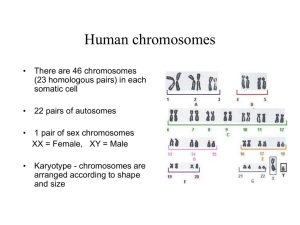
Homologous
chromosomes DO NOT
interact
Homologous
chromosomes pair up,
align and separate
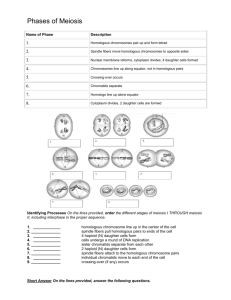
How Meiosis Works:
Animation
A few more Vocabulary Words:
• Germ Cells– Cells that give rise to the gametes of
organisms
– They are in the process of or have the
potential to undergo meiosis.
• Somatic Cells– cells that do not have the potential to form
gametes
• Synapsis– The pairing of homologous chromosomes
during prophase of meiosis I
• Tetrad– a unit of 4 chromatids formed by a
synapsed pair of homologous
chromosomes, each of which has
two chromatids
• Crossing Over– The process by which homologues
exchange segments with each other.
• Genetic Recombination– the reshuffling of genes on a
chromosome. Caused by breakage
of DNA and its reunion with the DNA
of a homologous chromosome.
Meiosis
• animation
How does the process of meiosis accomplish
the previously mentioned goals?
• two meiotic divisions
without DNA
replication in between
them.
• Independent
assortment and
crossing over
MEIOSIS I
– Prophase 1:
• Homologous sister chromatids find
each other. Crossing Over can occur
during the latter part of this stage.
– Metaphase 1:
• Homologous chromosomes align at
the equatorial plate. Independent
assortment happens here.
– Anaphase 1:
• Homologous pairs separate with
sister chromatids remaining
together.
– Telophase 1:
• Two daughter cells are formed with
each daughter containing only one
chromosome of the homologous
pair.
Meiosis II
– Prophase 2:
• DNA does not replicate.
Sister Chromatids prep for
division
– Metaphase 2:
• Sister chromatids align at
the equatorial plate.
– Anaphase 2:
• Centromeres divide and
sister chromatids migrate
separately to each pole.
– Telophase 2:
• Cell division is complete.
Four haploid daughter cells
are obtained.
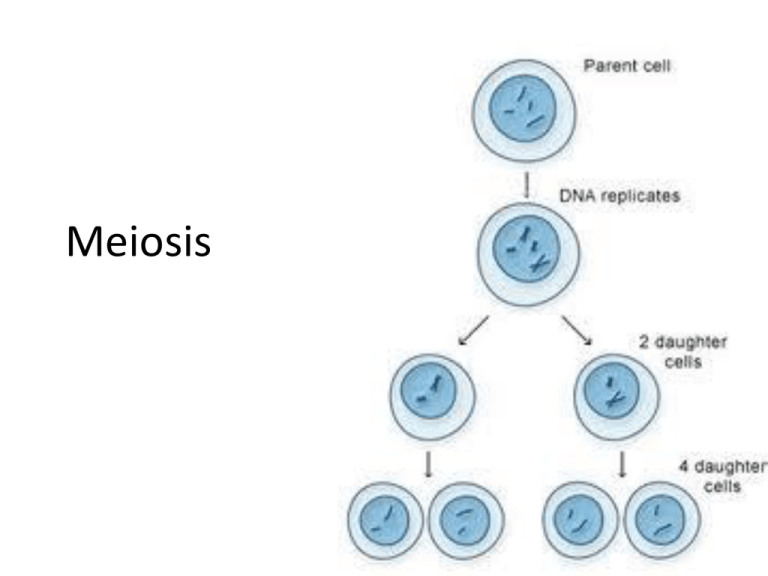
Summary
• One parent cell produces four daughter cells.
– Daughter cells have half the number of chromosomes
found in the original parent cell and with crossing over,
are genetically different.
• Meiosis differs from mitosis primarily because
there are two cell divisions in meiosis, resulting in
cells with a haploid number of chromosomes.
Meiosis Square Dance
• animation
• Independent Assortment– The process of random segregation
and assortment of chromosomes
during anaphase I of meiosis
resulting in the production of
genetically unique gametes.
• Chiasmata– A cross-shaped structure commonly
observed between homologous
chromosomes during meiosis; the
site of crossing-over.
• Random Fertilization– A mating system in which there is an equal
opportunity for all male and female gametes to join in
fertilization
– This means that an egg cell representing one of eight million different
genetic possibilities will be fertilized by a sperm cell representing one of
eight million genetic possibilities and the resulting zygote can have any of
the possible 64 trillion diploid combinations of genes.
Making Gametes
• Oogenesis– The process of ovum
formation in female animals
• Spermatogenesis– The process of sperm
formation in male animals