meiosis ii

11. 2 MEIOSIS
M R S . S T I P A N O V I C H
MEIOSIS
• Takes place only in the reproductive cells
• Sperm Cells
• A male child does not have sperm cells until puberty
• Egg Cells
• A female child is born with all of the eggs she will ever need
MEIOSIS
• Homologous Chromosomes
• 1 from Dad
• 1 from Mom
Somatic Cells (body cells) contain two identical sets of chromosomes
(copies).
They are called diploid.
MEIOSIS
• 2N-A diploid cell can be represented by
“2n”
Example: Fruit flies have 8 chromosomes, so we say 2N=8
MEIOSIS
• Gamete cells (reproductive) contain only one set of chromosomes. They are called haploid.
Example: A fruit fly’s sex cells would be represented by “N”.
If 2N=8, then N=4
MEIOSIS
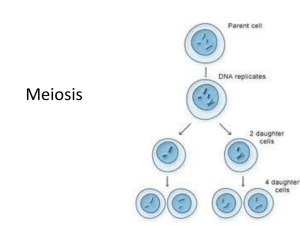
• We all start out as diploid cells
(fertilized egg cells). How do we make haploid cells from diploid cells?
• Answer: Meiosis!
• Meiosis-the process of reduction division in which the number of chromosomes in a cell is cut in half.
Only takes place in germ cells.
plasma membrane newly forming microtubules in the cytoplasm spindle equator
(midway between the two poles) one pair of homologous chromosomes
PROPHASE I
MEIOSIS I
METAPHASE I ANAPHASE I TELOPHASE I
Fig. 9.4a p. 142
MEIOSIS 1
• Interphase 1: Gamete cells follow normal path—replicating DNA and forming more organelles
• Prophase 1: Each replicated chromosome finds its homologous pair.
• Crossing-over: The homologous pairs wrap around each other and pass genetic information back and forth.
MEIOSIS 1
• Metaphase 1:
• Homologous pairs line up next to each other in the middle of the cell
• Spindle fibers attach to each pair of chromatids
MEIOSIS 1
• Anaphase 1:
• Spindle Fibers pull the paired
chromatids apart from each other
• Pull pairs toward opposite ends of the cell
MEIOSIS 1
• Telophase 1 and Cytokinesis:
• Nuclear membrane forms
• Cell separates into two new cells
MEIOSIS 1
• We end up with 2 new cells with very different genetic information from it’s parent cell (due to crossing over)
• This is why you do not look exactly like your mother or exactly like your father.
• This is also why you might look like an extended relative, such as a grandfather or aunt
MEIOSIS II
• Now, we need to split the cells one more time.
there is no DNA replication between the two divisions
PROPHASE II
MEIOSIS II
METAPHASE II ANAPHASE II TELOPHASE II
MEIOSIS II
• Interphase: NOTHING
MEIOSIS II
• Prophase II:
• Spindle re-emerges
MEIOSIS II
• Metaphase II
• Sister chromatids line up in the middle of the cells (like Mitosis)
• Spindle fibers attach
MEIOSIS II
• Anaphase II
• Each CHROMATID is pulled to a separate pole (opposite ends)
MEIOSIS II
• Telophase II
• Nuclear membrane re-forms
Cytokinesis Occurs
We have 4 haploid cells
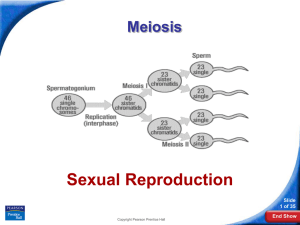
SPERM
• Spermatogenesis
• Spermatocyte to 4 spermatids
EGGS
• Oogenesis
• Oocyte to 3 polar bodies and 1 ovum
2n n gametes
2n germ cell germ cell each chromosome duplicated during interphase
MEIOSIS I separation of homologues
MEIOSIS II separation of sister chromatids diploid number restored at fertilization gametes zygote