12.3 TRANSCRIPTION NAME___________________HR___ LET`S
advertisement

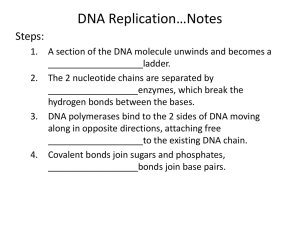
12.3 TRANSCRIPTION NAME___________________HR___ LET’S REVIEW: NUCLEOTIDES are the basic structure of the DNA molecule REPLICATION is how DNA makes copies of itself QUESTION: How are structures created by DNA? DNA in human cells are stuck in the nucleus. They are like a recipe in a cook book full of other recipes. What if you wanted to share a cookie recipe with your friend? You’d have to give them the entire book! What else could you do instead of giving them the entire book? You could write the recipe down which is the same method DNA uses to get the information out. DNA cannot actually write it down, but a copy can be made that is small enough to exit the nucleus and then used to make proteins in the proper place. This is a job for messenger RNA (Ribonucleic acid), or mRNA. DIFFERENCES between DNA & mRNA—allows mRNA to do things DNA cannot DIFFERENCES: DNA mRNA Type of sugar Nitrogen bases Shape/length Location Deoxyribonucleic acid Thymine-T (bonds w/adenine) Double-stranded/long Nucleus Ribonucleic acid Uracil-U (bonds w/adenine) Single-stranded/short Able to LEAVE the nucleus SIMILARITIES between DNA & mRNA—allow exchange of information for overall goal of protein production SIMILARITIES: DNA mRNA Phosphate & sugar “Backbone” of DNA “Backbone” of mRNA Nitrogen bases Adenine-A/Guanine-G/Cytosine-C Adenine-A/Guanine-G/Cytosine-C DNA never leaves the nucleus so protein production relies on mRNA to deliver the directions, or code, to the place outside of the nucleus in the cytoplasm. The process of making an mRNA copy from a DNA molecule inside the nucleus is called TRANSCRIPTION. TRANSCRIPTION: ►The enzyme—RNA polymerase-- “unzips” a strip of DNA to expose the N-bases ►Complimentary mRNA nucleotides are connected to the exposed DNA N-bases by weak hydrogen bonds “zipping” the mRNA strand to the DNA ►mRNA strand is released by the enzyme ►mRNA leaves the nucleus enters the cytoplasm ►The DNA strand is then “zipped” back together with RNA polymerase PRACTICE TRANSCRIPTION: Write complementary N-bases for mRNA using DNA strand below— REMEMBER—use U now instead of T COMPLETE: DNA vs mRNA Venn diagram DNA Complimentary mRNA A-C-G-T-A-T-Now that the recipe is copied and out of the cookbook (nucleus)… …where do we make our cookies (proteins)? INTERPRET the analogy of “MAKING PROTEINS” to “BAKING COOKIES” by completing the cookie diagram