Genetic Code
advertisement

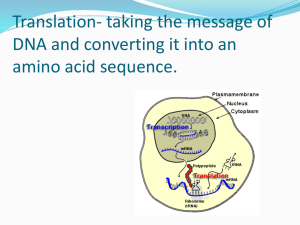
Nucleic Acids RNA and Transcription The Genetic Code Protein Synthesis Mutations 1 Types of RNA • Messenger RNA (mRNA) Carries genetic information for protein synthesis from DNA in nucleus to the ribosomes • Transfer RNA (tRNA) Small molecules of 20 types that recognize and transfer amino acids for protein synthesis • Ribosomal RNA (rRNA) Makes up 2/3 of ribosomes (1/3 protein) where protein synthesis takes place 2 Transcription • Genetic information contained in nucleus • One strand of DNA is copied • Complementary bases build mRNA DNA(1 strand) mRNA • In mRNA uracil (U) complements A (DNA) • New mRNA moves out of nucleus to ribosomes in cytoplasm 3 Genetic Code • Needed to build a particular protein • The sequence of amino acids is coded by the mRNA • Each triplet of bases along mRNA codes for an amino acid • The triplet are called codons • Codons are known for all 20 amino acids • Some codons signal the “start” and “end” of a polypeptide chain 4 Codons and Amino Acids Suppose that a section of a mRNA has the following series of bases. CCU–AGC –GGA –CUU Use a codon reference to determine the order of amino acids CCU = Proline AGC = Serine GGA = Glycine CUU = Leucine The mRNA codes for the peptide chain of Pro –Ser –Gly –Leu 5 Learning Check G1 What is the order of amino acids coded for by a section of RNA with the base sequence GCC –GUA –GAC ? GGC = Glycine GAC = Aspartic acid CUC = Leucine GUA =Valine GCC = Alanine CGC = Arginine 6 Solution G1 GGC = Glycine GAC = Aspartic acid CUC = Leucine GUA =Valine GCC = Alanine CGC = Arginine GCC –GUA –GAC Ala – Val – Asp 7 Activation of tRNA Each tRNA binds to its specific amino acid Pro Pro GGG GGG 8 Anticodons on tRNA • A three-base sequence on each tRNA • Complements a triplet on mRNA Pro anticodon GGG CCC codon on mRNA 9 Initiation and Elongation • mRNA attaches to a ribosome • tRNA with anticodon UAC binds to first codon (AUG) to initiate synthesis • The second codon picks up a tRNA with the proper anticodon. • A peptide bond forms between the amino acids at the first and second codons. • The first tRNA detaches and the ribosome shifts to the next codon on the mRNA 10 Peptide Formation Peptide starts to form Met Met Ser UAC AGA • •• • •• AUG UCU CUC Ser Leu AGA GAG • • • •• • UCU CUC UUU 11 Termination • Protein grows as tRNAs bring amino acids to the codons on the mRNA • When all amino acids for a protein are linked the next codon is “stop” • There is no tRNA for the “stop” codon • Protein synthesis ends • Protein released from ribosome 12 Learning Check G2 A. B. C. D. Match the following processes in protein synthesis with the statements: (1) Activation (2) Initiation (3) Elongation (4) Termination Ribosome moves along mRNA to add new amino acids to a growing peptide chain Completed peptide chain released A tRNA attaches to its specific amino acid tRNA binds to the AUG codon of the mRNA on the ribosome 13 Solution G2 A. B. C. D. Match the following processes in protein synthesis with the statements: (1) Activation (2) Initiation (3) Elongation (4) Termination (3) Ribosome moves along mRNA to add new amino acids to a growing peptide chain (4) Completed peptide chain released (1) A tRNA attaches to its specific amino acid (2) tRNA binds to the AUG codon of the mRNA on the ribosome 14 Learning Check G3 The following section of DNA is used to build a mRNA for a protein. GAA-CCC-TTT A. What is the corresponding base sequence on mRNA? B. What are the anticodons for the tRNAs? C. What is the amino acid order in the peptide? 15 Solution G3 GAA-CCC-TTT A. What is the corresponding base sequence on mRNA? CUU-GGG-AAA B. What are the anticodons for the tRNAs? GAA CCC UUU C. What is the amino acid order in the peptide? Leu-Gly-Lys 16 Mutations • Caused by mutagens such as radiation and chemicals • Alter the nucleotide sequence of DNA • Produce an incorrect series of codons in the mRNA from the altered DNA • A different codon binds with a different tRNA • The protein has one or more wrong amino acids in the peptide sequence • Can result in a defective protein or enzyme 17 Examples of Genetic Diseases Galactosemia Cystic fibrosis Downs syndrome Muscular dystrophy Huntington’s disease Sickle-cell anemia Hemophilia Tay-Sachs disease 18