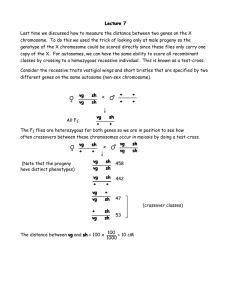
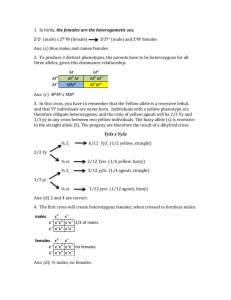
Gene Linkage and Crossing Over
advertisement

Gene Linkage and Crossing Over Gene Linkage & Crossing Over • Genes that are found on the same chromosome are said to be LINKED genes • Linked genes are inherited TOGETHER. • Genes will NOT separate during meiosis… • unless...CROSSING OVER occurs Linked Genes • Chromosome “13” (first copy): ------a----b-------------c------------d • Chromosome “13” (second copy): ------A----B------------C------------D • When separated during meiosis: – One cell gets a,b,c,d – One cell gets A,B,C,D • What happens if cross over occurs between B and C? – One cell gets a,b,C,D (recombinant) – One cell gets A,B,c,d (recombinant) • Finding freq of recombinants indicates amount of crossing over Gene Mapping • • A chromosome map a linear map of genes on the chromosome. It contains: 1. The order in which specific genes occur on a chromosome 2. The distances between the genes A Map is derived from crossover frequencies. Mapping Chromosomes • The closer genes are together on a chromosome the fewer the crossovers that occur. • Genes farther apart (more map units apart) affected by more crossovers (higher crossover frequency) • For eg. Crossover value of – 1% = 1 map unit apart - genes are close together; – 12% = 12 map units apart - genes are further apart Cross over frequency = Map distance Chromosome Map 96 Mapping Chromosomes: An Analogy The Houses on Main Street • Arnold lives 12 doors away from Beth • Carlos lives 11 doors away from Deanna • Beth lives 3 doors away from Carlos • Arnold lives 4 doors away from Deanna and 15 away from Carlos • In what order are the houses on the street? • T. H. Morgan collected the following COF’s from data with Dros. Fruit flies • B = bar shaped eyes. • C = carnation eyes. • FV = fused veins. • S = scalloped winged. • They are all on the same chromosome FV/B FV/C B/C FV/S C/S = 2.5% = 3% = 5.5% = 8% = 11% Use the crossover frequencies to plot a gene map How did Mendel calculate crossover frequencies? Crossover % = number of recombinations total number of offspring X 100 EXAMPLE: Drosophila melanogaster (fruit fly) • E = normal body color e = ebony • N = straight wings n = curved wings • In a cross between EENN and eenn, what genotype and phenotype would you expect? F1: • Genotype • Phenotype EeNn normal/straight 100% 100% But let’s say an actual cross resulted in: • 282 wild/straight E_N_ • 9 black/straight eeN_ • 9 wild/curled E_nn Crossover % = new combinations Total number = 18 300 Crossover frequency= 6% Example: • Assume the crossover frequency between gene A and B is 12%, between B and C is 7%, and between A and C is 5%. Draw the chromosome.