AQA Biology AS Level

AQA Biology AS Level
Unit 2
Meiosis, Mitosis and the Cell Cycle
Outcomes:
• Know that cell division by meiosis results in the formation of gametes .
• Can describe the importance of meiosis in creating variation by independent assortment of chromosomes and crossing over .
• Know that cell division by mitosis results in an increase in number of identical cells for growth and repair .
• Identify and name the stages of mitosis in diagrams and photomicrographs.
• Describe the cell cycle and relate it to an understanding of cancer and its treatment.
Replication of chromosomes occurs prior to division
Homologous chromosomes centromere chromatids chromosome
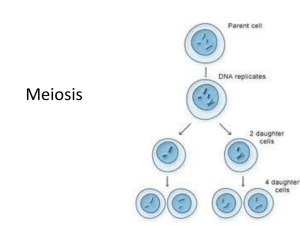
Meiosis consists of two divisions
Meiosis 1 Meiosis 2
Gametes are formed by meiosis:
Homologous chromosomes associate
Outcomes:
• Know that cell division by meiosis results in the formation of gametes .
• Describe the importance of meiosis in creating variation by independent assortment of chromosomes and crossing over .
• Know that cell division by mitosis results in an increase in number of identical cells for growth and repair .
• Identify and name the stages of mitosis in diagrams and photomicrographs.
• Describe the cell cycle and relate it to an understanding of cancer and its treatment.
Independent segregation increases variation paternal maternal
Random assortment in meiosis I
Random assortment in meiosis II
maternal paternal
or
Random assortment in meiosis I
Random assortment in meiosis II
Crossing over increases variation
recombinant chromosome chiasma
In the first division of meiosis the homologous chromosomes associate
Crossing over increases variation
B B b b
G g G g
B, G B, g b, G b, g
All gametes have a different combination of alleles on the chromosomes
Outcomes:
• Know that cell division by meiosis results in the formation of gametes .
• Can describe the importance of meiosis in creating variation by independent assortment of chromosomes and crossing over .
• Know that cell division by mitosis results in an increase in number of identical cells for growth and repair .
• Identify and name the stages of mitosis in diagrams and photomicrographs.
• Describe the cell cycle and relate it to an understanding of cancer and its treatment.
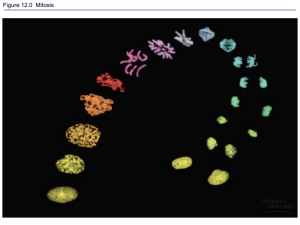
Mitosis produces two identical daughter cells.
metaphase prophase anaphase interphase cytoplasmic division (cytokinesis) telophase
M
I
T
O
S
I
S interphase prophase metaphase anaphase telophase cytokinesis
Stages of mitosis
Chromosomes appear, nucleus disappears
Chromatids pulled to poles
Chromosomes invisible; DNA replicates
Cytoplasmic division
Chromosomes at equator, spindle forms
Chromatids at poles, nucleus reforms
Outcomes:
• Know that cell division by meiosis results in the formation of gametes .
• Can describe the importance of meiosis in creating variation by independent assortment of chromosomes and crossing over .
• Know that cell division by mitosis results in an increase in number of identical cells for growth and repair .
• Identify and name the stages of mitosis in diagrams and photomicrographs.
• Describe the cell cycle and relate it to an understanding of cancer and its treatment.
The cell cycle
interphase nuclear division anaphase
G1:
Growth of daughter cell
Duplication of organelles other than nucleus
G2:
Cell checks
DNA and makes any repairs. Cell prepares for division
S:
Replication of DNA
Cancer
Summary
• Meoisis produces haploid gametes that are genetically different.
Variation is further increased by independent segregation of chromosomes and crossing over forming recombinant chromosomes.
• Mitosis is the nuclear division which produces 2 genetically identical, diploid cells. It consists of prophase, metaphase, anaphase and telophase.
• Cell cycle consists of interphase, nuclear division (mitosis or meiosis) and cytplasmic division (cytokinesis).
• Cancer is caused by mutation of genes that regulate the cell cycle and treatment is designed to inhibit cell division.