Document
advertisement
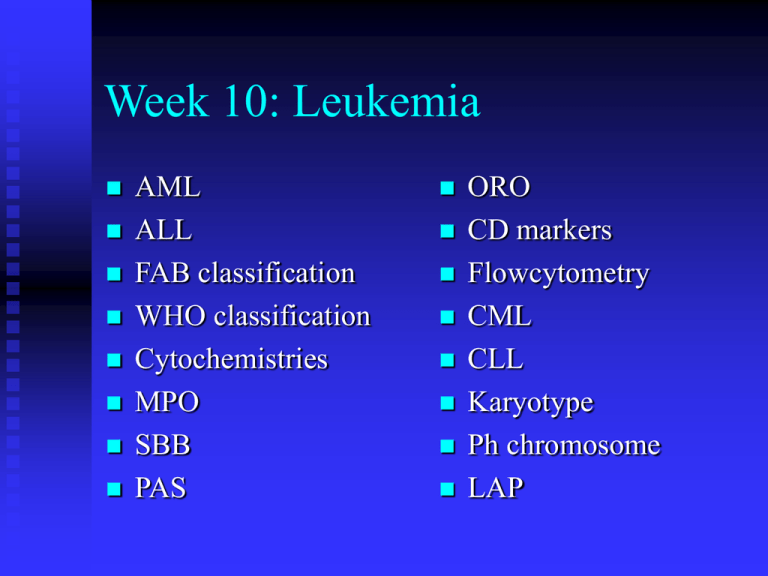
Week 10: Leukemia AML ALL FAB classification WHO classification Cytochemistries MPO SBB PAS ORO CD markers Flowcytometry CML CLL Karyotype Ph chromosome LAP Signs and Symptoms of AML Insidious nonspecific onset Pallor due to anemia Febrile due to ineffective WBC Petechiae due to thrombocytopenia Mucus membrane and gum bleed in M4 and M5 Bone pain Typical Labs of AML Leukocytosis Blastemia Leukemic hiatus Auer rods in M2, M3, M4 Thrombocytopenia Anemia >20% blasts in BM Other Findings CD 13 and CD 33 in flowcytometry Cytochemistries Myeloperoxidase Sudan black B Choloroacetate esterase (specific) Nonspecific esterase FAB (1976) Classification M0 -- Undifferentiated AML M1 -- AML without maturation M2 -- AML with maturation M3 -- Acute Promyelocytic Leukemia M4 -- Acute Meylomonocytic Leukemia M5 -- Acute Monocytic Leukemia M6 -- Erythroleukemia (DiGuglielmo’s) M7 -- Megakaryoblastic Leukemia M1 and M2 Myeloperoxidase (MPO) p-Phenylene diamine + Catecol + H2O2 MPO > Brown black deposits M3 M4 M5 Chloracetate (Specific) Esterase Myeloid Cell Line Naphthol-ASD-chloracetate CAE > Free naphthol compounds + Stable diazonium salt (eg, Fast Corinth) > Red deposit Non-Specific Esterase Monocytic Line Naphthyl acetate ANAE > Free naphthyl compounds +Stable diazonium salt (eg, Fast blue RR) > Brown deposits NSE with Fl inhibition Histiocyte Double Esterase in M4 FAB vs WHO Classifications of Hematologic Neoplasm FAB criteria Morphology Cytochemistry WHO criteria Morphology Immunophenotyping Genetic features Karyotyping Molecular testing Clinical features WHO Classification of AML AML with recurrent cytogenic translocations AML with multi-lineage dysplasia AML and myelodysplasia, therapy related AML, not otherwise categorized AML with Recurrent Cytogenetic Translocations (WHO 1995) t(8;21) -- some maturation of neutrophilic line; rare in older patients; AML1/ETO fusion protein; >90% FAB M2 t(15;17) -- APL (granular and microgranular variants); retinoic acid receptor (RAR) leukemias; middle aged adults; DIC inv(16) or t(16;16) -- monocytic and granulocytic; abnormal eosinophilic component 11q23 -- monocytic; children; most common is t(9;11) FAB Classification of ALL L1: Small homogeneous blasts; mostly in children L2: Large heterogeneous blasts; mostly in adults L3: “Burkitt” large basophilic B-cell blasts with vacuoles L2 L3 Periodic Acid Schiff Periodic acid + Glycogen oxidation > Aldehyde + Schiff reagent (para-rosaniline, Na metabisulfite) > Red deposit ALL Cytochemistries Oil Red O: stains L3 vacuoles Terminal deoxynucleotidyl transferase (Tdt): DNA polymerase in early lymphoblasts Cell surface markers (CD’s) Cytoplasmic and surface immunoglobulins: B-cell line T-cell receptor (TCR) WHO Classification of Lymphoproliferative Syndromes Precursor B Lymphoblastic Leukemia/Lymphoma (ALL/LBL) -- ALL in children (80-85% of childhood ALL); LBL in young adults and rare; FAB L1 or L2 blast morphology Precursor T ALL/LBL -- 15% of childhood ALL and 25% of adult ALL Burkitt Leukemia/Lymphoma (FAB L3) •Antigens •B-Lineage •T-Lineage •HLA Dr •Tdt •CD34 •+ •+ •+ •0 to + •+ •0 •CD19 •C 22 •CD10 •CD20 •Cyt- •SIg •+ •cALL and older •cALL and older •Pre-B and older •Pre-B and older •B-ALL •Pre-T •Pre-T •Pre-T •0 •0 •0 •CD7 •CD3 •CD5 •CD2 •CD1 •0 •0 •0 •0 •0 •+ •+ •+ •T-ALL •T-ALL Prognosis Indicators Favorable Poor WBC < 50,000/L 50,000/L Age 1 - 10 < 1 or 10 Gender Female Male Blast B-cell T-cell and mixed Karyotype Hyperploidy Trisomy 4, 10, 17 t(12;21) (TEL/AML1) Hypoploidy Trisomy 5 t(1;19 (E2A/PBX1) Mixed lineage leukemia T(9;22) (Ph) BM blast count Mkd reduction at day 7 during induction Mild reduction at day 7 Typical Labs in CML Leukocytosis with blastemia Thrombocytosis Basophilia Micro-megakaryocytes Low LAP score (intermediate if infected) About 10% blasts in BM Philadelphia chromosome CML Bone marrow aspirate and biopsy Pseudo-Gaucher’s cells in BM Leukocyte Alkaline Phosphatase (LAP) Naphthol AS-MX phosphate LAP at pH8.6 > Naphthol AS-MX + Diazonium salt (eg, Fast blue RR) > Insoluble pigment LAP Score Count 100 consecutive segs and bands Score: 0 = no granules 1+ = occasional diffuse granules 2+ = moderate number of granules 3+ = many strongly positive granules 4+ = confluent strongly positive granules 0 2+ 1+ 3+ 4+ LAP Score Example: 0 1+ 2+ 3+ 4+ x x x x x 35 cells 30 cells 20 cells 10 cells 5 cells = 0 = 30 = 40 = 30 = 20 120 LAP Score Philadelphia Chromosome 9 and 22 translocation almost specific to CML Karyotype to visualize Ph chromosome Produces BCR/c-abl fusion oncogene Gene product p190 is a hyperactive tyrosine kinase Ph chromosome seen in ALL produces p210 and chronic neutrophilic leukemia produces p230 Karyotype 46,XX,t(9;22)(q34;q11.2) -- Ph chromosome FISH showing the BCR (green), ABL (orange), and BCR-ABL fusion signals (arrow): A=positive (contains a residual ABL signal), B=normal FAB (1982) Classification of Myeloproliferative Disease (MPD) Chronic Myelocytic Leukemia (CML) Polycythemia Vera (PV) Essential Thrombocythemia (ET) Agnogenic Myeloid Metaplasia with or without Myelofibrosis (AMM) Benign Leukemoid Reaction WHO Classification of MPS (1997) CML becomes CML, Ph + t(9;22) BCR/ABL Chronic Neutrophilic Leukemia (CNL) Chronic Eosinophilic Leukemia and Hypereosinophilic Syndrome (CEL/HES) PV remains PV ET remains ET AMM becomes Chronic Idiopathic Myelofibrosis Myelofibrosis Myelofibrosis Chronic Lymphocytic Leukemia Exclusive in elderly Lyphocytosis unrelated to viral infection Hyper-mature lymphocytes with highly condensed nuclei Smudge cells: preventable with a drop of bovine albumin CLL PB and BM Bone Marrow WHO Lymphoid Neoplasms B cell neoplasms T/NK cell neoplasms Hodgkin lymphoma (disease) Mature B Cell Neoplasms B cell CLL/SLL B prolymphocytic leukemia Burkitt’s lymphoma / leukemia Splenic marginal zone B lymphoma Extranodal marginal B lymphoma Hairy cell leukemia Lymphoplasmocytic leukemia Mantle cell lymphoma Plasma cell myeloma / plasmacytoma Follicular lymphoma Diffuse large B lymphoma T/NK Cell Neoplasms T prolymphocytic leukemia T granular lymphocytic leukemia Aggressive NK cell leukemia Adult T lymphoma / leukemia Mycosis fungoides (Sezary syndrome) Anaplastic large cell lymphoma Hepatosplenic T lymphoma Peripheral T lymphoma Immunoblastic T lymphoma