Cell Structure and Functioning
advertisement

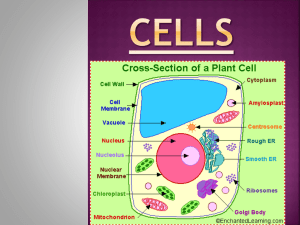
Patterns in Nature Topic 4: Cell Structure and Functioning Part of the Patterns in Nature Module Biology in Focus, Preliminary Course Glenda Childrawi and Stephanie Hollis Introduction: Levels of Organisation Most living organisms that are seen every day consist of many cells and are termed multicellular. englishexercises.org Introduction: Levels of Organisation Some living things however consist of only 1 cell that carries out all of its life functions. These are called unicellular organisms. microscopy-uk.org.uk Introduction: Levels of Organisation The term ‘cell’ is used to describe the basic unit of any organism, whether its only one unit or consisting of many units. wakeup-world.com DOT Point Identify cell organelles seen with current light and electron microscopes science.kukuchew.com microscope-microscope.org The structure of cells (as seen with a light microscope) The general contents of cells can be studied using the light microscope. Electron microscopes can provide us with greater details. historyforkids.org The structure of cells (as seen with a light microscope) Cells vary greatly in shape, size, structure and function. There is no ‘typical’ cell. To allow a general understanding of the structure and functioning of cells, a hypothetical cell of plants and animals is often studied. The structure of cells (as seen with a light microscope) Cells that are found in plants and animals have the same basic features with some variations. Over the next few slides we are going to explore the parts that are visible with a light microscope. cccmkc.edu.hk The structure of cells (as seen with a light microscope) Protoplasm The part of the cell which functions essential to life are carried out. This includes the inside of the nucleus and all of the cytoplasm leavingbio.net The structure of cells (as seen with a light microscope) Cytoplasm: This is the part of the protoplasm that is outside the nucleus. It consists of a liquid based background (cytosol) in which there are dissolved chemical substances, suspended organelles and insoluble granules. ajweinmann.wordpress.com 90% of the cytoplasm is water which is the medium in which all cell chemicals are dissolved or suspended. The structure of cells (as seen with a light microscope) Nucleus The large, spherical, oval or sometimes elongate structure in the cytoplasm. It is colourless, transparent and slightly more jelly like than the rest of the cell. rocklin.k12.ca.us It is the control centre of the cell The structure of cells (as seen with a light microscope) Cell Membrane Surrounds the cell contents in all cells and separates the cell contents from its surroundings. course1.winona.edu It controls the passage of water and other chemical substances into and out of the cell Plant Cells Plant cells have some additional structures which can be viewed under a light microscope. ipm.ncsu.edu These structures are exclusive to plant cells and therefore not usually found in animal cells. Plant Cells Chloroplasts Organelles that are green in colour due to the presence of a pigment called chlorophyll. Under a light microscope they appear as green, disc shaped structures, smaller than the nucleus. rocklin.k12.ca.us Chloroplasts are responsible for photosynthesis (the manufacture of sugar in plants, using the energy from the sun) Plant Cells Vacuole In plant cells are large, permanent, fluid-filled sacs in the cytoplasm of mature cells. Each vacuole consists of a watery solution called cell sap, surrounded by a single membrane, the tonoplast. biologycorner.com Vacuoles are used for storage but also play an important role in providing the plant with support. Comparing Plant and Animal Cells To compare two things, both similarities and differences must be examined. A good way to compare plant and animal cells is using a diagram. bbc.co.uk Homework Answer the following questions in your notebook. Be prepared to discuss next lesson. Identify organelles only seen with a light microscope Hand out Observing Plant and Animal Cells PRAC and discuss for next lesson.