Microscope PPT
advertisement

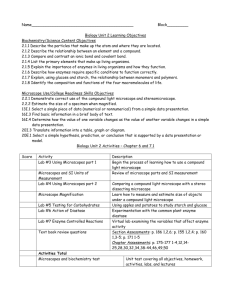
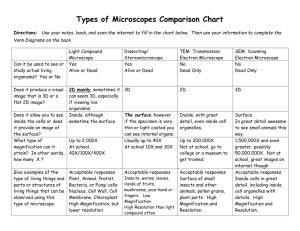
Created by J. Cook The Compound Microscope The Compound Microscope Preparing a wet mount slide What are the steps? 1.Place one or two drops on slide. 2.Cover with slip at 45○ angle. 3.Gently press down to remove air bubbles. Sketches List the 6 components of a sketch. 1.Name the object 2.Write the total magnification. 3.Complete a detailed sketch. Use pencil. 4.Label important parts. 5.Show the measurement (size of object). 6.Make detailed written observations of things that can’t be shown in sketch: descriptions of movement/behavior etc. . What is the benefit of each power? LOW: Scanning. Finding objects. Viewing a large area of the slide. MEDIUM: Greater detail than low, but can still see a fairly large area of slide. Easier to follow moving organisms than on high power. HIGH: Greatest magnification to see the most detail. Using High Power 1. Get object in sharp focus on low, then medium power before going to high. 2. The object must be centered. 3. Once on high power only small adjustments should be needed.Use only the fine adjustment knob. 4. Often requires more light than low or medium power. 5. Objects at slightly different levels will not all be in focus at the same time. 6. If you “lose” an object on high power you will have to go back to medium or low to find it again. Trouble Shooting How do you focus an object? 1.Always start on low power 2.Use Coarse adjustment first. 3.Then use fine adjustment What if no light is coming through? 1.Turn on the microscope and all power strips. 2.Adjust the diaphragm 3.Clean the lenses 4.Make sure the nose piece is “clicked” into place. Actual Field Diameters of Our Microscopes Write these numbers down in a safe place. You will need to know them all year long! POWER MAGNIFICATION FIELD DIAMETER Low 40X 100X 4500 µm 1800 µm 400X 450 µm Medium High Measuring under a microscope How is total magnification calculated? The objective lens multiplied by the eye piece What is the “field diameter”? The distance across the lighted circle you see when looking through the microscope. What is the general formula used to determine the size of an object? The field diameter divided by how many of that object you estimate would fit across the diameter. The Dissecting Microscope Comparing and Contrasting the microscopes List some similarities for both microscopes. State some differences for the Compound microscope. State some differences for the Dissecting microscope. (Include purpose, type of object to view, appearance of objects etc.)