ppt slides
advertisement

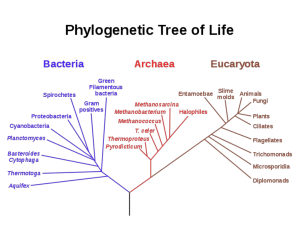
Protists 1. Ancestor of eukaryotes. Chromosomes Plasma membrane 2. Infoldings of membrane. 3. Eukaryotic cell. Nucleus Endoplasmic reticulum Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic cells endosymbiosis Eukaryotic vs. Prokaryotic cells Protist Diversity Bacteria Archaea EUKARYA This icon shows the overall tree of life. The highlighted branch indicates which lineage is shown in more detail below Bacteria Archaea EUKARYA Paraphyletic group Fungi Animals All eukaryotes are protists (orange branches) except for the fungi, animals, and land plants Common ancestor of all eukaryotes Land plants Unikonta vs bikonta Bacteria Archaea AMOEBOZOA Lobose amoebae 7 lineages of protists Cellular slime molds OPISTHOKONTA UNIKONTA Plasmodial slime molds Fungi Choanoflagellates EUKARYOTES All eukaryotes are protists except for the fungi, animals, and land plants Animals EXCAVATA Parabasilids Diplomonads Euglenids Kinetoplastids PLANTAE Glaucophyte algae Red algae Green algae Green plants RHIZARIA Foraminifera Chlorarachniophytes ALVEOLATA Ciliates Apicomplexa STRAMENOPILA Oomycetes Diatoms Brown algae CHROMALVEOLATA Dinoflagellates BIKONTA Land plants pseudopodium Adaptations for obtaining energy - ingestion AMOEBOZOA OPISTHOKONTA Primary vs secondary endosymbiosis EXCAVATA Parabasilids EUKARYOTES Diplomonads Euglenids Kinetoplastids PLANTAE Glaucophyte algae Red algae Primary (initial) endosymbiosis: occurred here Green algae Land plants RHIZARIA Secondary endosymbiosis: Red algal and green algal chloroplasts were transferred to other protists Foraminifera Chlorarachniophytes ALVEOLATA Ciliates Apicomplexa STRAMENOPILA Oomycetes Diatoms Brown algae CHROMALVEOLATA Dinoflagellates Adaptations for movement Alternation of Generations