HUMAN-GENETICS-COURSE-LF---Mendelian Gen
advertisement

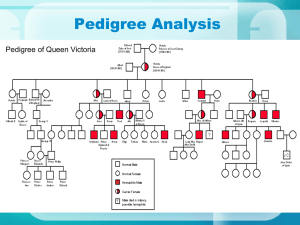
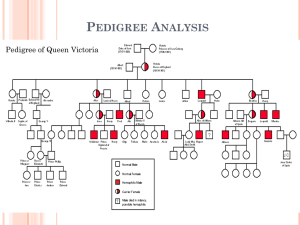
II. TRANSMISSION GENETICS Mendelian Inheritance • Known as single-gene inheritance/unifactorial trait • Gregor Mendel: “father of genetics” From 1857-1863 crossed and catalogued 24,034 pea plants • Why pea plants? Easy to grow Develop quickly Traits with easily distinguishing forms (green-yellow, tall-short, round-wrinkled) continuous vs. discontinuous traits Mendel’s Laws • Law of Dominance: 1 gene (dominant) can mask the appearance of another gene (recessive) • Law of Segregation: during formation of gametes alleles separate Aa A /a • Law of Independent Assortment: during formation of gametes genes randomly arrange themselves AaBb AB / Ab / aB / ab Inheritance of a gene on 1 chromosome does not influence inheritance of a gene on a different chromosome Exception: Linkage (red hair-freckles) Rules for Problem-Solving: • • • • Write down dominant and recessive genes Write down parents’ genes (P generation) Get parents’ gametes Do the cross on a punnett square (board for offspring possibilities – F1 generation) • Get results and label answer Types of Problems: • Simple 1 trait cross • Monohybrid Cross (Ff X Ff) Genotype: 1:2:1 Phenotype: 3:1 • Simple 2 trait cross • Dihybrid Cross (FfDd X FfDd) Phenotype: 9:3:3:1 • Incomplete Dominance (3 phenotypes present) Andalusian Fowl FF (black) ff (white) Ff (blue) Roan Cattle FF (brown/reddish) ff (white) Ff (brown with white) Four O’Clock Flowers FF (red) ff (white) Ff (pink) Pedigree Analysis • Displays familial relationships and depicts which have specific phenotypes and genotypes • Autosomal Dominant Trait: a trait can appear in either sex because an autosome carries the disease; do not skip generations Porphyria variegata: red urine, abdominal pain, coma, death Huntington Disease: progressive uncontrollable movements and personality change (begins in middle age) Polydactyly: extra fingers or toes Marfan Syndrome: long limbs, sunken chest, lens dislocation, weakened aorta • Autosomal Recessive Inheritance: can appear in either sex; Affected individuals with homozygous recessive genotype; can skip generations Cystic Fibrosis: lung infections and congestion Sickle Cell Anemia: joint pain, spleen damage Tay Sachs Disease: NS degeneration Phenylketonuria (PKU): fair skin, mental retardation Albinism: lack of melanin in skin, eyes, hair Pedigree Information: • Female = circle Male = square • Parents – connected by a single line Consanguineous: parents are related (shown by a double line) • • • • Siblings’ ages read from left to right (older to younger) Arabic numbers = siblings Roman numerals = generations Twins represented by diagonal lines Identical Twins (monozygotic): horizontal line Fraternal Twins (dizygotic): no line


![Biology Chapter 3 Study Guide Heredity [12/10/2015]](http://s3.studylib.net/store/data/006638861_1-0d9e410b8030ad1b7ef4ddd4e479e8f1-300x300.png)