Cells and Tissues
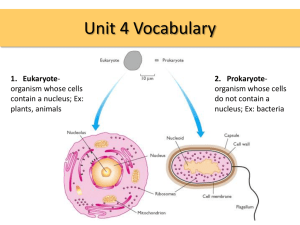
Mitochondria
Rough
Endoplasmic
Reticulum
Nuclear
Membrane
Chromatin
Cell Membrane
Golgi
Apparatus
Nucleolus
Centrosome/
Centriole
Lysosome
Ribosomes (red dots)
Peroxisome
Cytoplasm
Smooth
Endoplasmic
Reticulum
Flagella
Nucleus
Microtubule
Chromatin
Nuclear Envelope
Ribosome
Nucleolus
Cell Membrane
Rough ER
Centriole
Mitochondria
Smooth ER
Microvilli
Cilia
Golgi Apparatus
Microtubule
Microtubule
Lysosome
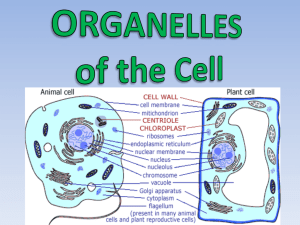
Organelle Functions
Organelle
Location
Function
Cell Membrane
External boundary of the cell
Confines cell contents; regulates entry and exit of
materials
Lysosome
Throughout cytoplasm
Digests and breaks down old organelles
Peroxisome
Throughout cytoplasm
Breaks down toxic materials in the cell (alcohol)
Mitochondria
Scattered throughout cell
Energy powerhouse of the cell (ATP)
Golgi Apparatus
Within cytoplasm
Process lipids/proteins for export out of the cell
Centrioles
2 rod-shaped bodies near the nucleus made of microtubules
Controls the spindle fibers during mitosis
Centrosome
Consists of the 2 centrioles and a mass of proteins near nucleus
Form the spindle fibers during mitosis that pulls
chromosomes apart
Smooth ER
Within cytoplasm
Synthesize lipids
Rough ER
Flattened sacs near nucleus
Synthesize proteins
Ribosomes
Attached to Rough ER
Synthesize proteins
Cilia
Hair like structures on surface of cell membrane
Movement
Microvilli
Hair like structures on surface of cell membrane (smaller than
cilia)
Increase surface area of the cell; involved in secretion
and absorption
Microtubules
Throughout cytoplasm; part of cytoskeleton; thick proteins
Moves organelles inside the cell; form the spindles
during mitosis; compose cilia, flagella, and centrioles
Microfilaments
Throughout cytoplasm; part of the cytoskeleton; thin stringy
proteins
Moves organelles inside the cell; also involved in muscle
contraction
Nucleolus
Within the nucleus
Synthesis of ribosomes
Nucleus
Near the center of the cell
Contains the genetic information
Nuclear Envelope w/ pores
External boundary of the nucleus
Allows materials into and out of the nucleus
Knowing functions are not required on the lab, but are helpful when clues are given in the question
Movements through the membrane:
Diffusion
Movement of molecules
from a high
concentration to a low
concentration
No energy required
Movements through the membrane:
Filtration
As blood flows through the capillary, smaller
molecules are filtered out through tiny openings
and larger molecules stay inside
Testing Solutions
Water
Glucose
Sucrose
Benedict’s Test
(test for glucose)
Iodine Test
(test for starch)
Color change from blue to orange
Color change from orange to dark purple
• Type of cell:
RBC
• Type of solution: Isotonic
• Water is diffusing: Into and out of RBC equally
• Type of cell:
Crenated RBC
• Type of solution: Hypertonic
• Water is diffusing: out of RBC faster
• Type of cell:
Lysed RBC
• Type of solution: Hypotonic
• Water is diffusing: Into RBC faster
Mitosis
• Phase:
Interphase
• What is occurring: Nuclear envelope is visible
DNA replication
Cell performs its normal job
Mitosis
• Phase:
Prophase
• What is occurring: Nuclear envelope is
disappearing
Chromosomes forming
Mitosis
• Phase:
Metaphase
• What is occurring: Chromosomes line up along
the center of the cell
Mitosis
• Phase:
Anaphase
• What is occurring: _______ are separating
Mitosis
• Phase:
Telophase
Cytokinesis
• What is occurring: Nuclear membrane reforms
Cell membrane forms
Tissues
Simple Squamous
• Location:
Lungs, endothelium of
capillaries
• Body Function:
Diffusion, osmosis
Simple Cuboidal
• Location:
Kidney tubules, glands,
ovaries
• Body Function:
Secretion, absorption
Simple Columnar
• Location:
GI tract, uterus
Secretion, absorption, move
• Body Function:
sperm
Pseudostratified Columnar
• Location:
Trachea
• Function:
Movement of fluids
(mucous)
Stratified Squamous
• Location:
Skin, mouth, anal
canal, esophagus
• Body Function:
Protection water
loss, abrasion
etc….
Transitional
• Location:
bladder
• Body Function: Stretch
Connective Tissues
Loose Connective Tissue
(Areolar)
Collagen Fibers
Reticular Fibers
Elastic Fibers
Fibroblasts
Fat (adipose)
Adipocyte
Nucleus
Reticular
Reticular Fibers
Dense Regular
Nuclei of Fibroblasts
Collagen Fibers
Hyaline cartilage
Chondrocytes
Lacuna (space occupied by cell)
Matrix
Elastic Cartilage
Fibrocartilage
Chondrocytes
Collagen
Fibers
Bone
Osteocytes
Central Canal
Blood
WBC
RBC
Platelets
Skeletal Muscle
• Location:
Attached to
Skeleton
• Body Function:
Voluntary
movement
Cardiac Muscle
• Location:
Intercalated Discs
• Body Function:
Heart
Heart muscle contraction
Smooth Muscle
• Location:
Blood vessels, GI tract
• Body Function:
Involuntary movement
Nervous tissue
• Location:
CNS, PNS
• Body Function:
Conduct nerve impulses