Nucleus and Ribosomes
By: Ryan Thomas
Katie Thomas
Nicholas Weaver
Alexandra Farlow and
Patrick Wagner
Chromosomes
•
•
•
Rod-like structures that result when
chromatin condenses and coils
Each species has a particular number of
chromosomes that is passed on to the next
generation
Found in prokaryotes, eukaryotes, plant and
animal cells, fungi, and protists
Chromosome Analogy
•
•
•
•
The chromosome could be compared to a
computer using binary code
The computer uses 1's and 0's to code for
processes
The chromosome uses cytosine, guanine,
adenine, and thymine for cellular processes
The computer stores the code, just like a
chromosome
Function With Other Organelles
•
•
The Endoplasmic Reticulum synthesizes
proteins from the mRNA from chromosomes
Chromosomes also code for tRNA (to carry
amino acids) and rRNA (components of the
ribosome) which all have to do with protein
synthesis from the ER.
Some Diseases Caused by
Chromosome Malfunction
•
•
Down Syndrome (Caused by the presence of all or part
of a copy of the 21st chromosome)
Turner Syndrome (One female sex chromosome is
missing or abnormal)
•
Cystic Fibrosis (Mutation of the 7q chromosome)
•
Color Blindness (X chromosome mutation)
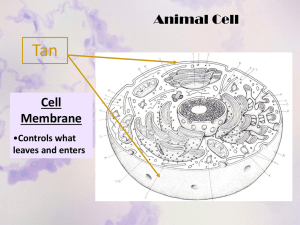
Nuclear Pore
•
•
•
The nuclear pore regulates the molecules going
between the nucleus and the cytoplasm of a cell.
One of the biggest protein complexes in the cell.
The nuclear pore is found in all eukaryotes
Nuclear Pore Malfunctions
•
As the nuclear pore ages it causes a loss of
integrity in the nucleus. This means that the
nuclear membrane does not function as well
as it could. The substances that pass
between the nucleus and the cytoplasm are
not as regulated as when the nuclear pore is
in its best shape.
Nuclear Pore Analogy
Nuclear Pore:Nucleus :: Pores:Skin
•
•
•
Both the nuclear pore and the pores on our skin are a
protective covering.
The nuclear pore regulate what goes in between the
cytoplasm and nucleus of a cell, while pores on the skin
also regulate the entrance and exit of bacteria and
bodily fluids.
When the nuclear pore grows old it does not function
well, just as the pores on our skin do when we get old
and our pores are clogged up.
How does the nuclear pore work
with other organelles?
•
•
The nuclear pore works with the nucleus to
ensure that all the right substances with
enter and exit the cell at the right time.
It also works with the cytoplasm in the same
way as it does with the nucleus.
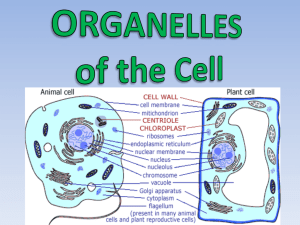
Ribosomes
Protein Synthesizers
Ribosomes
A ribosome is a particle that is composed of protein and RNA and is the
site of protein synthesis. It is composed of two subunits that work
together to make proteins according to the RNA.
They are found in both prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells. (plants animals
bacteria)
Diseases
-If one protein malfunctions it can send a wave of dramatic effects on the
body. One of these effects is mental retardation. The proteins are
responsible for making the DNA codes, and in the case of mental
retardation they have made a faulty enzyme in the code.
Another faulty code the proteins can produce can make a person albino.
Inside the Cells:
-Messages from the nucleus are sent into the endoplasmic reticulum where the
ribosomes are located.
The proteins are transferred to the golgi apparatus where the proteins are
modified.
Ribosomes work along with most of the organelles because they make the
proteins that they need to perform.
Ribosome:Construction
Workers
Ribosomes form proteins which act like the bricks to build a
house.
They take orders from the RNA and Nucleus just as workers have
to pay attention to the building plans and instructions from a
forman.
The proteins made by Ribosomes act as a barrier from diseases
just as a house is used to protect people from weather and
diseases.
Chromatin
The Source of All Knowledge in the Cell
Chromatin Structure and Function
Chromatin is composed of DNA, proteins called
histones and other assorted components
such as transcription factors. Chromatin
contains the genetic information that guides
the function of the cell and the creation of
proteins.
DNA- Stores the genetic information to produce
proteins.
Histones- Compacts the DNA into tight groups,
saving space.
Found Where?
Chromatin is found in animal, plant, fungi and
protist cells.
Chromatin is not found in prokaryotic cells.
DNA is 'naked' and not packaged with any
proteins, therefore classifying it as simply
DNA not chromatin.
Diseases
Chromatin is opened and closed by chromatin
remodeling ATPases. A misfunction of these
cause several diseases including:
- embryonic lethality
-cause mutations that lead to cancer
Chromatin is like...
Chromatin is like a staple holding a stack of
important documents together.
-It binds the DNA together to save space
-stores the important information.
-it helps keep the DNA organized and allows it
to function properly.
Chromatin works with...
Chromatin works with other nuclear organelles
by entering and exiting the nuclear
membrane through nuclear pores. Chromatin
also works with ribosomes by giving them
genetic info to produce.
The Assembler of Ribosomes in Eukaryotes
Nucleolus Function
•
•
Primary function of the nucleolus is to assemble
subunits which then come together to form the
organelle known as the ribosomes in a Eukaryotic cell.
Because the nucleolus assembles the ribosomes it
indirectly plays a large role in the synthesis of proteins.
Structure
•
•
•
•
Largest structure inside the boundaries of the nucleus.
The complex structural organization in cells has evolved
during the transition period from anamniotes to
amniotes.
Anamniotes are vertebrates which do not posses
amnion.
Amniotes are creatures that lay eggs and have adapted
themselves to the terrestrial environment.
Where it is found!
The Nucleolus is found in all types of
Eukaryotic cells such as plant, animal, protist
and fungi cells.
It is found at the heart of the cell, in the center
of the nucleolus.
Diseases should it malfunction...
A malfunctioning nucleolus is known to cause
neurodegenerative disorders such as
Huntington's and Alzheimer's, and could also
be a cause of Parkinson's disease as well.
A Nucleolus is like....
A nucleolus is like a manager of the cell which
acts as the factory.
The ribosomes are the factory workers that
constantly take orders from the nucleolus.
The nucleolus is constantly "hiring and training"
new ribosomes just like new factory workers.
Works with....
The nucleolus and its counter part the nucleus
work with the entirety of the cell, and all the
organelles present, however nucleolus mainly
works with the DNA and RNA brought into
the nucleus to make Ribosomes.
Bibliography
••
••
••
•
http://www.ks.uiuc.edu/Research/npc/
http://www.ndm.ox.ac.uk/erika-mancini-chromatin-remodelling
http://www.brighthub.com/science/genetics/articles/23710.aspx
http://www.alzforum.org/new/detail.asp?id=2023
http://www.buzzle.com/articles/nucleolus-function.html
http://www.els.net/WileyCDA/ElsArticle/refId-a0005975.html
http://www.psypost.org/2011/02/nucleoli-parkinsons-disease-brain-3930