Endocrine Glands and Hormones that
are Associated with Male Reproductive
System and Their Function.
Following endocrine glands and hormones are associated with
male reproductive system:
1. Hypothalamus: Secretes Gonadotropin-releasing Hormone
(GnRH) to stimulate pituitary for the secretion of FSH & LH.
2. Pituitary gland: Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH):
Function: a) Stimulate the growth of the seminiferous tubules.
b) Control spermatogenesis, synthesis and release of
testosterone hormone.
Luteinizing hormone:
Function: Synthesis and release of testosterone in the
presence of FSH.
Endocrine Glands and Hormones that
are Associated with Male
Reproductive System and Their
Function.
• Testis: Secretes Testosterone from its Interstitial (Leydig
cell of the testis) cells.
Function of testosterone hormone: a) Maintain normal
sexual behavior of animals.
b)Maintenance of the function of male accessory genital
gland.
c) Control of spermatogenesis together with FSH.
d) Prenatal maintenance of Wolffian duct and its
differentiation into epididymis and ductus deferens.
• Prostate gland: Secrete relaxin which helps in motility
of spermatozoa in semen.
Endocrine Glands and Hormones that
are Associated with Male
Reproductive System and Their
Function.
• Inhibin: Secretes from Sustentacular cells of
the testis and blocks the secretion of pituitaryFSH and control spermatogenesis.
• Sustentacular cells produces large quantity of
estrogen hormone in pathological condition
(tumor) leading to feminization of animals.
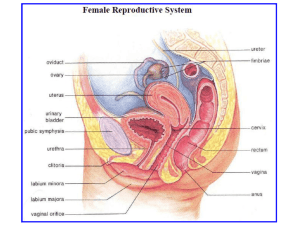
Endocrine Glands and Hormones
that are Associated with Female
Reproductive System and Their
Function.
• Following endocrine glands are associated with female
reproduction:
1. Pituitary gland
2. Ovary
3. Corpus luteum (temporary gland)
4. Placenta (temporary gland)
5. Uterus, and
6. Pineal gland.
Endocrine Gland and their
Reproductive Function in Female
Hypothalamus: GnRH, function is similar to male.
Pituitary Gland:
1. Follicle Stimulating Hormone (FSH):
a) Growth and maturation of ovarian follicles.
b) Initiate estrogen (maintain all female sex character)
secretion from granulosa cells.
2. Luteinizing Hormone (LH):
a) Initiate ovulation
b) Initiate corpus luteum (CL) formation and secretion of
progesterone from CL.
3. Prolactin: In rat activates corpus luteum, and in Pigeon
causes production of crop milk.
Endocrine Gland and their
Reproductive Function in Female
Ovary:
Estrogen: Cause development of mammary
gland, external genitalia (vulva)
development, fat mobilization, axillary hair
development etc.
Endocrine Gland and their
Reproductive Function in Female
Corpus Luteum: Secretes,
1. Progesterone: Maintenance of pregnancy
(decrease tone of uterus, and inhibit FSH).
2. Estrogen: Function already described.
3. Relaxin: Relaxes the cervix, and soften pubic
symphysis and helps in parturition.
Endocrine Gland and their
Reproductive Function in Female
• Placenta:
Progesterone: Secrete by placenta at late
stage of pregnancy for its maintenance.
• Uterus:
Secretes Luteolytic factor PGF2α
In case of failure of pregnancy PGF2α cause
luteolysis means regression of corpus luteum.
• Pineal Gland:
Influence gonadotropic functions (like FSH and
LH).
Estrous Cycle
The estrous cycle is regulated by intrinsic
hypothalamo-hypophyseal-ovarian rhythm
that is modulated by environmental and
internal neuroendocrine factors. In domestic
animals this cycle is called “Estrous cycle”, and
in primates and human this cycle is called
“menstruation.”
Phases of Estrous Cycle
Total length of estrous cycle in the cow is 21
days.
1. Proestrus: is the period of follicular
maturation and endometrial proliferation
following failure of the corpus luteum of the
previous cycle. During this phase
progesterone level falls while FSH and
estrogen level rise for next estrus stage. This
stage ranges from 18-20 days of estrus cycle.
Phases of Estrous Cycle
2. Estrus: is the period of sexual receptiveness of
animals (female accept male). During this
period ovulation occurs in most animals
followed by increase secretion of LH hormone.
Estrogen hormone declines at the end of this
stage. This stage is at just 21 days of estrous
cycle.
Phases of Estrous Cycle
3. Metestrus: It is the stage of corpus luteum
development and initial phase of progesterone
secretion. This stage is from 1-3 days.
4. Diestrus: It is the phase of active corpus luteum
and action of progesterone on uterus and other
accessory sex gland, e.g. hyperplasia of the
uterine gland. However, if pregnancy fails corpus
luteum regress by the action of Luteolytic factor
PGF2α.
This is the longest period of the estrous cycle and
ranges from 4-17 days.
Anestrus
In some animal due to hormonal imbalances or
my be due to environmental factor or
neurological disorder or may be due to other
causes there may be prolonged sexual
inactivity and absence of estrous cycle. This
situation is called anestrous means absence
of estrous.
Length of Estrous Cycle in Animals
(indays)
Cow
Sow Bitch Primates
1. Proestrous 3
2-3
1- 2 wks
2. Estrus
½
1
9
3. Metestrus
3
3
45
4. Diestrus
14
12
45 Vary
---------------------------------------------------------------20.5 – 21d. 19d
2m>
5. Horse 21d, sheep 17d, Goat 19-21d, cat 1421d.
Length of Menstrual Cycle in Primates
and Human
There are four phases:
1. Menstruation Phase: The fluid contain dead cell, epithelial cell
debris of the uterus and mucus. Average length 3-7 days.
2. Follicular Phase: It starts from day 1 of menstruation. About 20
follicle develop but one oocyte become egg. This happen at day 10
of 28 day cycle.
3. Ovulation: Generally happens at mid cycle. Ovulation time is at 1415 day of 28 day cycle. The life span of typical egg is 24 hours, after
that it die unless meet a spermatozoa.
4. Luteal Phase: The rest of the days of cycle is luteal phase during this
time corpus luteum developed and persist if pregnancy happen or
regression occur if pregnancy not occur and uterus start to take
preparation for next cycle.
Time of Ovulation and duration of
estrus in Animals
Time of Ovulation
Cattle
Horse
Swine
Sheep
Goat
Dog
Duration of estrus
12(10-15) hrs. after end of estrus
4-24 hrs
24(10-15) hrs before end of the estrus
3-9 days
38-48 hrs. after the onset of estrus
2-3 days
18-20 hrs “ “
“
Near the end of estrus
1-2 days after onset of estrus
“
18-72 hrs
22-60 hrs
9 days
Age at Puberty in
Common Domestic Animals
Species
Cattle
Horse
Swine
Sheep
Goat
Dog
Cat
Age at Puberty
8-18 months
10-24 months
6-8 months
6 -15 months
4-8 months
6-20 months
5-12 months
Histological Changes of the Uterus
During Estrus Period in Animals
Proestrus: Under the influence of estrogen the mucosa
of the uterus becomes thickend, congested, and
edematous with mucin filled epithelium.
Estrus: Endometrial edema and hypermia are maximal.
Metestrus: Edema of the endometrium lessens,
breakdown occurs in some of the congested blood
vessels.
Diestrus: Under the influence of progesterone the
endometrium become secretory type. Glands of the
endometrium undergoes coiling, branching and
secretory type.
Histological Changes of the Vagina
During Estrus Period in Animals
In animals vaginal changes noticed during
estrus. At this stage the height of the vaginal
epithelium increased.
In other stages of the estrous cycle the height of
the vaginal epithelium decreased
comparatively.
Practical Class
Students should study:
1. Anterior Pituitary Gland.
2. Leydig cell of testis.
3. Sustentacular cells of the testis
4. Prostate gland.
5. Granulosa cell layer of ovary
6. Corpus luteum
7. Endometrium, and
8. Pineal Gland.