Types of cells and organelles

Introduction to Cells
Cells are the basic units of organisms
C ells can only be observed under microscope
Basic types of cells:
Animal Cell Plant Cell
Number of Cells
Organisms may be:
• Unicellular – composed of one cell
• Multicellularcomposed of many cells that may organize
2
Cells May be Prokaryotic or
Eukaryotic
Prokaryotes: include bacteria & lack a nucleus or membrane-bound structures called organelles
Eukaryotes: include most other cells & have a nucleus and membrane-bound organelles (plants, fungi, & animals)
3
Prokaryote vs Eukaryote
• Two structural types of cells are recognized:
– Prokaryotic
– Archaea and bacteria
– Eukaryotic: plants, algae, fungi, protists, and animals (variety)
• Comparing prokaryotic and eukaryotic cells
– Prokaryote comes from the Greek words for prenucleus.
– Eukaryote comes from the Greek words for true nucleus.
Prokaryote
• Contains plasma membrane
• Simpler internal structure
• Absence of nucleus
• One circular chromosome, not in a membrane
• No membrane enclosed organelles
• Peptidoglycan cell walls
• Binary fission for cell division
• Smaller
Eukaryote
• Contains plasma membrane
• Contain nucleus
• Paired chromosomes, in nuclear membrane
• Membrane enclosed organelles
• Simple
(polysaccharide) cell walls
• Cell division by mitosis or meiosis
• Larger
Structure of Prokaryotic vs. Eukaryotic cell
Prokaryotes – The first Cells
• Cells that lack a nucleus or membrane-bound organelles
• Includes bacteria
• Simplest type of cell
• Single, circular chromosome copyright cmassengale 7
Prokaryotes
• Nucleoid region
(center) contains the DNA
• Surrounded by cell membrane & cell wall (peptidoglycan)
• Contain ribosomes
(no membrane) in their cytoplasm to make proteins copyright cmassengale 8
Eukaryotes
• Cells that HAVE a nucleus and membranebound organelles
• Includes protists, fungi, plants, and animals
• More complex type of cells copyright cmassengale 9
Differences b/w the 2 types of cells
Eukaryotic
• Larger
• Contains membrane bound organelles
• Contains a nucleus
Prokaryotic
• Smaller
• Does not contain membrane bound organelles
• No nucleus
All cells have a:
And are grouped into two broad categories:
Which are mainly:
Cell walls
Which contains unique structures such as:
Words you can use:
• Animals
• bacteria
• chloroplasts
• Eukaryotes
• a large central vacuole
• plants
• plasma membrane
• prokaryotes
Some contain yeast and algae
All cells have a:
Plasma membrane
And are grouped into two broad categories:
Words you can use:
• Animals
• bacteria
• chloroplasts
• Eukaryotes
• a large central vacuole
• plants
• plasma membrane
• prokaryotes eukaryotic prokaryote s
Which are mainly: bacteria
Cell walls plants
Which contains unique structures such as: animals chloroplasts
Some contain yeast and algae
A large central vacuole
Viruses
• Non cellular
• Obligate intracellular parasites
– They must live inside another cell to survive
• Have only one type of nucleic acid
– DNA or RNA (never both)
– Single or Double stranded
• Protein coat (no plasma membrane)
• Few to no enzymes
– Takes enzymes and use host cell metabolic machinery
• No metabolic activity
• They require a host cell to exhibit the characteristics of life.
• Virus diversity
– Different viruses have different hosts
– Only some viruses cause disease
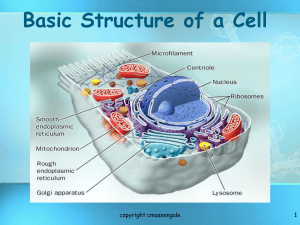
Structure & Organelles
VOCABULARY
• Organelle
• Plasma Membrane
• Cytoskeleton
• Nucleus
• Nucleolus
• Golgi Apparatus
• Endoplasmic
Reticulum
• Chloroplast
• Mitochondria
• Lysosome
• Vacuole
• Vesicle
• Cell wall
• Ribosome
• Cytosol
• Cytoplasm
Organelles
• Very small (Microscopic) “little organs” that carry out specific functions within each cell
• Perform various functions for a cell
• Found in the cytoplasm
• May or may not be membrane- bound
15
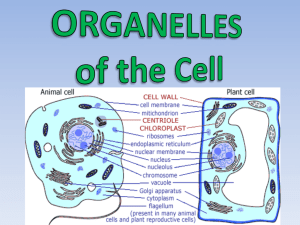
Eukaryotic: Animal Cell
Eukaryotic: Plant Cell
Prokaryotic Cell
Plasma Membrane (AKA cell membrane
• Function: A flexible boundary that controls the movement of substances in and out of the cell.
• Key word:
Selective permeability.
• Cell Type: All cells
• Analogy:
__________
Cell Membrane in Plants
Cell membrane
• Lies immediately against the cell wall in plant cells
• Pushes out against the cell wall to maintain cell shape
Cell Wall
• Nonliving layer
• Found in plants, fungi, & bacteria
• Made of cellulose in plants
• Made of peptidoglycan in bacteria
• Made of chitin in Fungi
• Cell Type: Plants
• Analogy:____________
_________________
Cell wall
Cell Wall
• Supports and protects cell
• Found outside of the cell membrane
22
More on Cytoplasm
cytoplasm
• Contains organelles to carry out specific jobs
• Collective term for cytosol plus the organelles suspended within the cytosol
• Found in ALL cells
• Analogy:__________
____________
Cytosol
• The fluid surrounding the cytoplasm’s organelles, internal membranes, and cytoskeleton fibers
• Analogy:_________
______________ copyright cmassengale 24
Cytoskeleton
• Helps cell maintain cell shape and supporting structure
• Also help move organelles around
• Made of proteins
• Microfilaments are threadlike & made of ACTIN
• Microtubules are tubelike & made of TUBULIN
• Analogy:________________
____________
25
Cellular Support
• Cytoskeleton is made of microtubules thin, hollow cylinders made of protein,
& microfilaments thin solid protein fibers
Cytoskeleton
MICROTUBULES
MICROFILAMENTS copyright cmassengale 28
Nucleus
• Function: The nucleus contains the cells DNA, stores information used to make proteins
– For cell growth, function & reproduction.
• Key Word: Control
Center
• Cell Type: All
Eukaryotic Cells
• Analogy:
____________
Nucleolus
• Inside nucleus
• Cell may have 1 to
3 nucleoli
• Disappears when cell divides
• Makes ribosomes that make proteins
• Analogy:________
____________ copyright cmassengale 30
Endoplasmic Reticulum - ER
• Network of hollow membrane tubules
• Connects to nuclear envelope & cell membrane
• Functions in Synthesis of cell products &
Transport
Analogy?_______
_____________
_____________
31
Rough Endoplasmic Reticulum (Rough
ER)
• Has ribosomes on its surface
• Makes membrane proteins and proteins for
EXPORT out of cell copyright cmassengale 32
Smooth Endoplasmic Reticulum
• Smooth ER lacks ribosomes on its surface
• Is attached to the ends of rough ER
• Makes cell products that are USED
INSIDE the cell copyright cmassengale 33
Functions of the Smooth ER
• Makes membrane lipids (steroids)
• Regulates calcium
(muscle cells)
• Destroys toxic substances
(Liver) copyright cmassengale 34
Ribosomes
• “
Protein factories” for cell
• Small particles of RNA and protein found throughout the cytoplasm. Produce proteins by following coded instructions that come from the nucleus .
• Join amino acids to make proteins
• Process called protein synthesis
• Analogy:________
copyright cmassengale 35
Golgi Apparatus
• Function: It’s a flattened stack of membranes that modifies, sorts & packages proteins into sacs.
• Key Word: Packing
& Sorting
• Cell Type: All
Eukaryotic Cells
• Analogy:
____________
Golgi Bodies
Look like a stack of pancakes
Modify, sort, & package molecules from ER for storage OR transport out of cell copyright cmassengale 37
Golgi
copyright cmassengale 38
Vesicles
-small saclike organelles that store and transport materials around the inside of cells copyright cmassengale 39
Chloroplasts
• Function: Capture light energy & convert it into chemical energy through photosynthesis.
• Key Word:
Producer of energy
• Cell Type: Euk.
Plant cell
• Analogy:
____________
Vacuoles
• Fluid filled sacks for storage
• Small or absent in animal cells
• Plant cells have a large Central
Vacuole
• No vacuoles in
bacterial cells
• Analogy:_____
__________ copyright cmassengale 41
Vacuoles
• In plants, they store
Cell Sap
• Includes storage of sugars, proteins, minerals, lipids, wastes, salts, water, and enzymes copyright cmassengale 42
Mitochondria
• Function: It converts fuel particles (mainly sugar) into usable energy.
• Key Word:
Powerhouse
• Cell Type: All
Eukaryotic Cells
• Analogy:
____________
MITOCHONDRIA CONT
Surrounded by a DOUBLE membrane
Has its own DNA
Folded inner membrane called CRISTAE
(increases surface area for more chemical
Reactions)
Interior called MATRIX copyright cmassengale 44
Interesting Fact ---
• Mitochondria
Come from cytoplasm in the
EGG cell during fertilization
Therefore … copyright cmassengale
• You inherit your mitochondria from your mother
!
45
Lysosomes
• Function:
Processes enzymes that digest excess or worn out organelles, wastes.
• Key Word: Gets rid of waste
• Cell Type: Euk.
Animal Cells
• Analogy:
____________
Similarities between plant cells and animal cells
Both have a cell membrane surrounding the cytoplasm
Both have a nucleus
Both contain mitochondria
Differences between plant cells and animal cells
Animal cells Plant cells
Relatively smaller in size
Irregular shape
No cell wall
Relatively larger in size
Regular shape
Cell wall present
Differences between Plant
Cells and Animal Cells
Animal cells Plant cells
Vacuole small or absent
Glycogen as food storage
Nucleus at the center
Large central vacuole
Starch as food storage
Nucleus near cell wall
Cell Movement with Cilia &
Flagella copyright cmassengale 50
Cilia & Flagella
• Cilia short, numerous, hair-like projections that move in a wavelike motion
• Flagella larger projections that move w/ a whip-like motion
Cilia & Flagella
• Cilia are shorter and more numerous on cells
• Flagella are longer and fewer (usually
1-3) on cells copyright cmassengale 53
Cilia Moving Away Dust Particles from the Lungs
Respiratory System copyright cmassengale 54
Cell Size
Question:
Are the cells in an elephant bigger, smaller, or about the same size as those in a mouse?
copyright cmassengale 55
Cell Size
Question:
Are the cells in an elephant bigger, smaller, or about the same size as those in a mouse?
About the same size, but …
The elephant has MANY MORE cells than a mouse!
copyright cmassengale 56