IB Biology
10 Genetics HL
10.1 Meiosis
All syllabus statements ©IBO 2007
All images CC or public domain or link to original material.
Shelly Fargo
Jason de Nys
http://www.flickr.com/photos/carolinabio/6241450806/
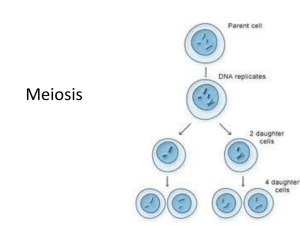
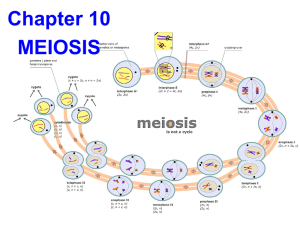
10.1.1 Describe the behaviour of the chromosomes in the phases of meiosis
The best way to see what happens in
this dynamic process is to view some
animations
There is a link to 3 Videos on PowerPoint 4.1!!!
We made a summary of
notes in class that is similar
(ours is more indepth) to
slide 2. You should practice
drawing this on your own.
10.1.2 Outline the formation of chiasmata in the process of crossing over
Hmmmm… chiasmata,
chiasmata,
chiasmata…
10.1.2 Outline the formation of chiasmata in the process of crossing over
Hmmmm… chiasmata,
chiasmata,
chiasmata…
Singular: chiasma….
You may have hear this word before in
another context
Ah yes!
The place where some of the optic nerves cross
over in the brain
Greek khīasma, cross-piece,
from khīazein, to mark with
an X, from khei, khī, chi
(from the letter's shape).
http://www.wordnik.com/words/chiasma
http://en.wikipedia.org/wiki/File:Gray773.png
Crossing over involves the swapping of segments of
DNA between chromatids on homologous pairs
The points at which the
chromatids cross are the
chiasmata
Chiasmata: evidence of
exchange between
chromatids
This micrograph shows a
pair of homologous
chromosomes, each with
two chromatids, during
prophase I of meiosis in a
salamander.
Two chiasmata are visible.
© 2008 Sinauer Associates Sadava, D. et al. Life: The Science of Biology, 8th ed.
(Sunderland, MA: Sinauer Associates and W. H. Freeman & Company), 198. Used
with permission. All rights reserved
10.1.3 Explain how meiosis results in an effectively infinite genetic variety in gametes through
crossing over in prophase I and random orientation in metaphase I
• Crossing over can occur on any part of a
chromosome.
• The size of the section swapped between
chromosomes can be almost any size.
• The number of chiasmata on each chromatid can
vary
These three points alone lead to innumerable
possibilities
You viewed this animation in
PowerPoint 4.1
From the animation on the previous page:
Number of possible orientations =
2 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑐ℎ𝑟𝑜𝑚𝑜𝑠𝑜𝑚𝑒 𝑝𝑎𝑖𝑟𝑠
Work it out for the human genome! (Hint…we did this in class
on our meiosis drawing)
One of the strange results
you get when you Google
“random orientation”
Number of possible orientations =
2 𝑛𝑢𝑚𝑏𝑒𝑟 𝑜𝑓 𝑐ℎ𝑟𝑜𝑚𝑜𝑠𝑜𝑚𝑒 𝑝𝑎𝑖𝑟𝑠
Work it out for the human genome!
2 23
= 8,388,608 possibilities!
10.1.4 State Mendel’s Law of independent assortment.
Each pair of alleles segregates into
gametes independently
Also… mmm…
http://www.flickr.com/photos/staipale/2580650017/
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Gregor_Mendel.png
An example of the independent
assortment of the gene for
colour (green [y] or yellow [Y])
and the gene for pod type
(smooth [R] or wrinkled [r])
In Italian for
your pleasure!
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:Independent_assortment_%26_segregation-it.svg
10.1.5 Explain the relationship between Mendel’s law of independent assortment and meiosis
Mendel
examining his
pea flowers
My
babies…
http://www.flickr.com/photos/kaptainkobold/356759039/
Mendel knew nothing of modern genetics, genes had not been
discovered. He was working from the traits he observed, the
phenotypes. He named the heritable factors alleles.
So his Law:
Each pair of alleles
segregates into gametes
independently.
…relates to the random
orientation of
homologous chromosomes
during meiosis in
metaphase I
http://commons.wikimedia.org/wiki/File:MetaphaseIF.jpg
How do I answer that one for the IB
Bio Test?
• The Law of Independent assortment states that each pair of
chromosomes orientate themselves on the metaphase
plate independently of other pairs of chromosomes during
meiosis (metaphase I).
– Don’t know which side of the metaphase plate the ‘mom’
chromosomes and the ‘dad’ chromosome will be on
• In meiosis I homologous chromosomes arranged randomly
at the equatorial plate during metaphase I
• In meiosis I homologous pairs of chromosomes segregate to
opposite poles of the cell during
anaphase I (Law of segregation)
• This is necessary for independent assortment of genes and
therefore alleles.
Further information:
Doo do do do do ,do doo do
do do do, do do do
Three of the best sites for
IB-specific Biology
information. The top link
takes you to the PPT by
Stephen Taylor