Plant anatomy and growth
advertisement

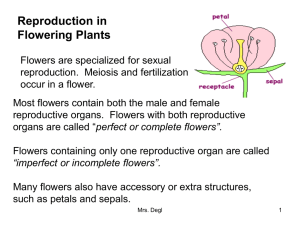
PLANT ANATOMY AND GROWTH STAGES OF PLANT GROWTH & DEVELOPMENT Seed germination Vegetative Reproduction GOOD SEED GERMINATION REQUIREMENTS Proper temperature Sufficient moisture Ample supply of oxygen TYPES OF SEEDS Vegetable seeds Flower seeds Examples: Celery, Cantaloupe, lettuce Examples: Foxglove, Gold Yarrow, Blue Flax Herbs seeds Examples: Peppermint, Cumin, Chives FUNCTIONS OF SEEDS Nourishment of the embryo Dispersal to a new location Dormancy during unfavorable conditions MONOCOTS Epicotyl Hypocotyl Radicle Cotyledon Coleoptile Endosperm Seed coat PARTS OF SEED DICOT Epicotyl Hpocotyl Radicle Cotyledons Seed coat PARTS OF SEED MONOCOT STAGES OF GERMINATION Absorption of water and oxygen into seed Seed coat ruptures and the primary root (radicle) begins to grow downward Epicotyl elongates, coleoptile piercing the soil as it grows upward Coleoptile unfolds DICOT STAGES OF GERMINATION Absorption of water and oxygen into seed Seed coat ruptures and the primary root (radicle) begins to grow downward Hypocotyl curves into a loop and pushes through the soil, pulling the cotyledons toward the soil surface Emergence of seedling occurs Cotyledons spread apart and the stem tip is exposed to air and sunlight PRIMARY PLANT PARTS Roots Stem Leaves flowers ROOTS Absorb water Anchor and support plants Stores food STEM Supports leaves, flowers, fruit, and seeds Conducts water, nutrients, and food Stores food FUNCTIONS OF PLANT PARTS LEAVES Manufacture food for the plant Necessary for transpiration Store food FLOWERS Serves as site of reproduction Store food FUNCTIONS OF PLANT PARTS TYPES OF ROOT SYSTEMS Tap root system-one root larger than the others Fibrous root systemall roots about the same size PARTS OF THE STEM Node Internode Terminal bud Lateral bud Leaf scar Vascular bundle scar TYPES OF STEMS Herbaceous stems Examples: Annual plants, and Vivacious plants Ligneous stems Examples: Trees, Shrubs, Bushes MONOCOTS Epidermis Pith Vascular bundles DICOTS TISSUE IN A STEM Epidermis Cortex Vascular bundles Pith STRUCTURE OF A LEAF A leaf is made up of many layers that are sandwiched between two layers of tough skin cells. They are called epidermis. These layers protect the leaf from insects, bacteria, and other pests. LEAF TYPES Simple leaf- consists of a single blade, not dissected into separate leaflets, but may have teeth or lobes. Compound leaf- Leaf dissected into many smaller leaf like structures; there is a lateral bud at the base of a compound leaf but not at the base of a leaflet. ABOVE GROUND STEM MODIFICATIONS Crown- appears just above or just below ground level from which modified stems grow. This type of growth is common in soil grains. Stolon- runners that grow along top of soils surface. This growth common in strawberry plants and clover Spur- appears laterally on branches of fruit trees and bears fruit BELOW GROUND STEM MODIFICATIONS Rhizome- underground stems that grow horizontally below soil surface commonin bluegrass, brome grass, quack grass, and canada thistle Tuber- enlarged fleshy parts found at tip of rhizome common to potatoes Corn- fleshy, short underground stems with very few buds common to timothy and gladiolus Bulb- short disc-shaped stem surrounded by leaflike scale structures common to onion and garlic VEGETATIVE GROWTH STAGES OF SMALL GRAINS Tillering Jointing Boot VEGETATIVE GROWTH STAGES OF CORN Two-leaf stage Six-leaf stage Ten-leaf stage Fourteen-leaf stage Two-leaf stage Six-leaf stage Ten-leaf stage Fourteen-leaf stage LIFE CYCLE OF FLOWERING PLANT Seed germination and seedling growth Vegetative growth Flower formation Pollination Fertilization Seed development PISTIL Female part where egg cell originates Stigma- upper part of pistil that catches pollen Style- supports stigma Ovary- produces ovules which develop into seeds STAMEN Male part of the flower Filament- supports anther Anther- bears the pollen PARTS OF A COMPLETE FLOWER Accessory Organs •Corolla- petals of the flower •Calyx- sepals of the flower •Pedicel- stalk of an individual flower PARTS OF A COMPLETE FLOWER TYPES OF FLOWERS Complete- has stamens, pistils, petals, and sepals on same flower common to dicots Incomplete- has stamens and pistils but no petals or sepals common to monocots Perfect- both stamens and pistils on the same flower Imperfect- either stamens or pistils but not both on the same flower Staminate- only male flower parts Pistillate- only female flower parts Monoecious- staminate and pistillate flowers found on the same plant (ex. Corn, cucumber, squash) Dioecious- staminate and pistillate flowers found on separate plants (ex. Holly, date, palm, spinach) GO FERTILIZATION! Pollen grain alights on the surface of stigma forms a pollen tube pollen tube grows down the style to the ovary penetrates the ovary and the male cell unite with the ovule Fertilization is the union of the male and female cells. The result is called a zygote. Cell division takes place and the zygote becomes the embryo of the seed. MERISTEM (MERISTEMATIC TISSUE) Comprised of actively dividing cells that develop and differentiate into other tissues and organs Cells have thin walls and dense protoplast PERMANENT Develops from meristems Non-dividing differentiated cells BASIC TYPES OF FERTILIZATION SHOOT MERISTEMS Found in tops of the shoots Responsible for producing new buds and leaves in a uniform pattern at the end of stem and laterally along stem APICAL MERISTEMS ROOT MERISTEMS Growing points for root system Found at various ends of the roots LATERAL MERISTEMS Account for girth and growth of woody stems Composed of cellulose and pectin Provide mechanical support for plant Vascular cambium- produces new xylem and phloem Cork cambium- produces bark (the protective covering of old stems and roots) Number of growth rings indicates tree’s age MERISTEMS TISSUE INTERCALARY MERISTEMS Active tissues that have been separated from the shoot terminal meristem by regions of more mature or developed tissue Found near the nodes of grasses Reason for continuous growth after mowing grasses Modified Leaves Colorful Poinsettia leaves become modified to create attention to the flower, and are then called ‘bracts’. Cactus leaves become modified as protective structures. Stem serves both leaf and stem functions Flowers Reproductive structures (sexual) Major parts include Pistil Stamen Ovaries Petals and sepals See diagram for additional parts and locations Perfect vs. Imperfect flowers Flowers Plants with both male and female flowers on the same plant are called monoecious (meaning ‘one house’) Squash, corn, birch Plants with male and female flowers on different plants are dioecious (male and female plants) Holly, Ginkgo biloba No fruit unless you have a female plant that receives proper pollen from the male plant flowers