Document 5780417

Milestone Minutes
Genetics
Week 3
Write notes in your Milestone Journal and answer the practice questions.
Genetics
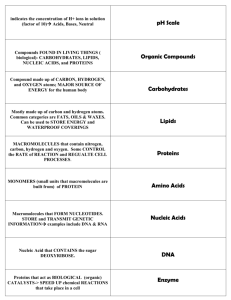
DNA and RNA are molecules essential for the transmission of genetic information.
DNA is a double stranded helix, contains the sugar deoxyribose, A-T & G-C
RNA is single stranded, contains the sugar ribose, A-U & G-C, produces proteins
DNA replication (copying)occurs prior to mitosis during the cell cycle
Mitosis stages: prophase, metaphase, anaphase, telophase
Mitosis results in two genetically identical daughter cells, occurs in autosomal cells, diploid (asexual)
Meiosis results in four genetically different gametes (egg & sperm), haploid (sexual)
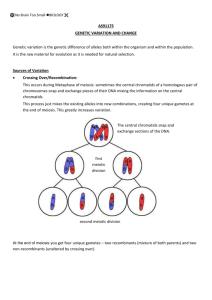
Recombination of genetic material (crossing over) occurs during anaphase 1 & 2 of meiosis
Mendel was the father of genetics and put forth laws concerning heredity.
Law of Dominance -dominate alleles (capital letter) suppress recessive alleles
(lowercase letter)
Law of Segregation -during fertilization gametes randomly pair to produce four sets of alleles (monohyrid)
TT=homozygous dominant, Tt=heterozygous, tt=homozygous recessive
Genotype is the combination of alleles, Phenotype is the physical expression of alleles
Law of Independent Assortment -genes for traits are inherited independently of each other (dihybrid)
Segregation & Independent Assortment allow only one allele a gene to be present in the gametes
Alterations (mutations) can occur during meiosis and change the genetic code.
Some environmental factors are mutagenic (sunlight, chemical waste, radiation, toxins)
Insertion-addition of one or more nucleic bases in the genetic sequence, changes reading frame
Deletion-removal of one or more nucleic bases in the sequence, changes reading frame
Substitution-switch of one or more nucleic bases in the genetic sequence, no change to reading frame
Nondisjunction- failure of homologous chromosomes to separate during anaphase of meiosis
Trisomy- condition of having an extra chromosome (Down Syndrome)
DNA technology can change the genetic makeup of an organism.
Recombination -moving genes from one organism to another
(crosspollination/Hybrids)
Genetic Engineeringusing organisms for beneficial purposes
(insulin production, fighting viruses)