2.1.4: Relative sizes
advertisement
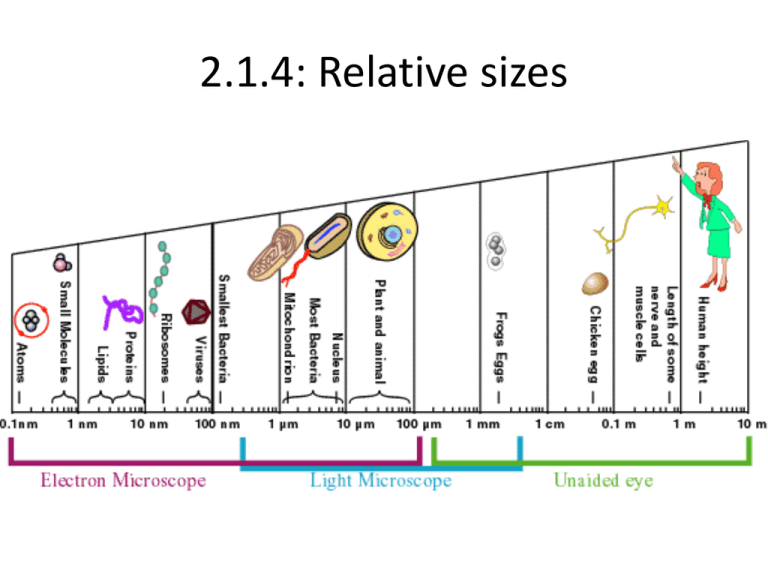
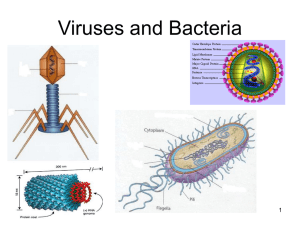
2.1.4: Relative sizes CONVERTING UNITS mm x 1,000 ÷ 1,000 µm x 1,000 ÷ 1,000 nm Compare the relative sizes of molecules, cell membrane thickness, viruses, bacteria, organelles and cells, using the appropriate SI unit. A molecule 1nm http://mendosa.com/glucose_molecule.jpg Glucose (1nm) A molecule 10nm http://www.biolibogy.com/images/structure_of_plasma_membrane.JPG A virus – the T bacteriophage 100nm 10nm http://oceanworld.tamu.edu/resources/oceanography-book/Images/BacteriophageCartoon.jpg Bacteriophage (virus) E.coli (bacteria cell) 100nm 0.1µm 1000nm 1µm http://bio1903.nicerweb.com/doc/class/bio1903/Locked/media/ch18/18_01T4PhageEColi_LP.jpg Bacteria (1µm) Cell ( up to 100µm) http://www.cic-caracas.org/departments/science/images/08eukaryote.jpg Organelle (10µm) 1mm = 1,000 µm 1 µm = ___1 mm 1,000 1 µm = 1,000 nm 1 nm = ___1 µm 1,000 1 nm 10 nm 100 nm 1 µm (up to) 10 µm (up to) 100 µm molecules membrane thickness virus Molly Met Virgil bacteria organelles cells But Organised Cells IB Question: State the typical size of (i) a bacterium [1] (ii) An average eukaryotic cell [1] (i) (approximately) 1μm [1] Accept any value between .5μm and 1.0μm. (ii) (approximately) 10μmto 100μm [1] Accept any value within this range. 2.1.5: Scale bar 15 µm 2.1.6: Surface area : volume 2.1.6: Surface area : volumeLets look at Surface areas and volumes……… • Fill in the table below: a Size of side (a) a a Surface area of the box (a x a x 6) Volume of Surface the box area to (a x a x a) volume ratio 1 6 1 2 24 8 3 54 27 4 96 64 5 150 125 6 216 216 7 294 343 6:1 2.1.6: Surface area:volume IB Question: Explain the importance of the surface area to volume ratio as a factor limiting cell size. [7] as size increases both surface area and volume increase, but volume increases more / ratio of surface area to volume decreases as size of cell increases; rate of metabolism is a function of its mass to volume ratio; surface area limits/affects the rate at which substances can enter (or leave) the cell; volume determines the rate at which material is produced/used; oxygen/nutrients/substances will take too long to diffuse into/out of the centre of the cell if it is too big; excretory products would take too long to be eliminated; heat will take too long to be eliminated; example of cell adaptation to increase the ratio of surface area:volume e.g. root hair cell; [7 max]