Protists - SciencePLC
advertisement

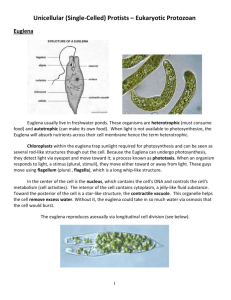
Video Introduction Kingdom Protista – The Protists Watch the following video on Discovery Education: http://player.discoveryeducation.com/index.cfm?guidAs setId=3D84751E-23C5-4538-9090-2725EE7B64D6 Set up Cornell Notes – p. ? Topic - Protists Definition Protists: (pro-tist) Eukaryote: (you-care-ee-oats) Euglena:____________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ (Draw and Label) Amoeba: _________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ (Draw and Label) Paramecium: ________________________ ____________________________________ ____________________________________ (Draw and Label) Volvox: __________________________________ _________________________________________ _________________________________________ (Draw and Label) All Protists are Eukaryotes Eukaryotes are organisms that have cells with a distinct membrane-bound nucleus and organelles. Most unicellular protists are microscopic, however, some multicellular protists grow more than 60 meters in a year. Today we will be discussing unicellular protists. Definitions: Protist: (pro-tist) Unicellular, multicellular or organisms in a colony with diverse nutritional and reproductive means. Eukaryotes: (you-care-ee-oats) Organisms that have cells with distinct membrane around nucleus and organelles. Euglena Euglena (you-glee-nuh) is a unicellular protist with characteristics of both plants and animals. It moves freely and feeds on other organisms, like an animal. Has the ability to make its own food, like a plant. Contains chloroplasts which are organelles that store chlorophyll and is a site to perform photosynthesis. Chloroplasts: (clor-oh-plasts) cell organelles in the Euglena Chlorophyll: (clor-oh-fil) green pigment that captures energy for photosynthesis from the sun. Photosynthesis: (fo-toe-sin-tha-sis) process which organisms use light energy to join carbon dioxide and water to make nutrients. Euglena: a unicellular protist with a reddish eyespot and a single flagellum, found in stagnant waters. Euglena Diagram Chloroplasts (with chlorophyll) Nucleus Flagellum Contractile vacuole Eyespot Amoeba An Amoeba (uh-mee-buh) is a unicellular protist Animal-like because they feed on other organisms and are able to move freely. Feeds and moves by using structures called pseudopods. (false feet) Surrounds another protist and takes it into its cytoplasm and digests it. Amoeba: a unicellular protist which is able to change shape because of the movements of pseudopods. They live in fresh water or soil or as parasites in man and animals. Amoeba Paramecium Paramecium (pair-uh-mee-see-um) is unicellular protist found in ponds and slow moving streams. This cell is covered with cilia, which are tiny hairs and are used for movement. Feeds through its oral groove as it moves through water. Eats bacteria, algae, and other small organisms. Could be described as animal-like because of how it feeds and moves. Excess water is pumped out of the cell by the contractile vacuole to prevent the cell from bursting. Has 2 nuclei; one needed for cell processes, the other is used only for sexual reproduction. Paramecium: a unicellular protist covered in cilia. The cilia is used for mobility and the Paramecium feeds through its specialized cell structure, its oral groove. Paramecium Macronucleus Micronucleus Contractile vacuole Oral Groove Volvox Volvox (vol-vox) is also a unicellular protist. Has chloroplasts to carry out photosynthesis for its food source. Volvox is unique because it lives in a group of cells called a colony. Each cell close to the surface propels the colony through water with their two small flagella. Volvox: a unicellular protist which lives in a colony and moves through the water with flagella. (freshwater algae) Volvox Protists Groups and Features Draw Table below on Page ? Protist Euglena Amoeba Paramecium Volvex Structure Locomotion (Movement) Food source (Energy) Specialized Cell Structure Protists Groups and Features Protist Structure Locomotion (Movement) Unicellular Flagellum Feeds on other organisms; can make nutrients Unicellular Pseudopods Feeds on other organisms Unicellular Cilia Feeds on other organisms Unicellular (lives in colonies) Flagella Euglena Amoeba Paramecium Volvex Food source (Energy) Makes nutrients Specialized Cell Structure Eyespot Oral groove and contractile vacuole Quick Check Quiz 1. Which protist is covered with cilia? a. Euglena b. Amoeba c. Paramecium d. Volvox 2. Which protist moves by forming pseudopods? a. Euglena b. Amoeba c. Paramecium d. Volvox 3. Which two protists share a feature with plant cells? a. Amoeba and Paramecium b. Euglena and Volvox c. Amoeba and Euglena d. Paramecium and Volvex 4. Which protists have a unicellualar structure? a. Euglena b. Paramecium c. Amoeba d. All the above