REDUCED GENOME E.coli
advertisement

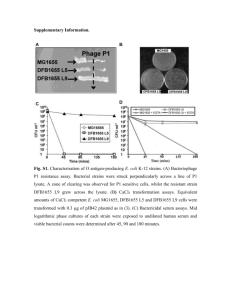
CLEAN GENOME E. COLI – MULTIPLE DELETION STRAINS Gulpreet Kaur Microbial Biotechnology, Fall 2011 A bit of history… Fredrick Blattner: 1997 - published complete genome of E.coli-K12 strain 2002 - engineered reduced E. coli genome -developed Scarab Genomics 2006 - emergent properties of reduced genome E. coli Why E.Coli K-12? Vast knowledge on its genomic organization Commonly used for research and metabolite production Popular strains – MG1655 and W3110 Why reduce the genome? Problems in using E. coli K-12 strains: Loss of desired gene over time Mutation of desired gene Low protein productivity Lack of purity in product Batch-to-batch variations High production costs What to delete? Backbone genome: 3.71Mb Total genome targeted to be deleted: 20% What to delete? Genes specific for some environments Potential pathogenicity genes DNA sequence repeats Mobile DNA elements that mediate recombination events Insertion Sequences Transposases, Integrases Defective phage remnants Outer Ring: E. coli K-12 Inner rings: (from center to outwards) 1-5: regions of E. coli K-12 absent in other genomes 1: RS218 2: CFT073 3: S. flexneri 2457T 4: O157:H7 EDL933 5: DH10B Ring 6: Deletion targets Red: MDS12 Yellow: MDS41 Green: MDS 42 Purple: MDS43 Ring 7: Native IS elements Ring 8: Confirmation of deletion in MDS43 Red: Genome present Green: Deletions Design and validation of MDS Comparison among strains TRANSFORMATION EFFICIENCIES Efficiencies of MDS42 were twice that of MG1655 Efficiencies of MDS42 were comparable to DH10B NO IS SEQUENCES! NO IS SEQUENCES! NO IS-MEDIATED MUTAGENESIS! Adaptation of MDS41 and MG1655 to Salicin/Minimal Medium ● : MG1655 ▼: MDS41 ONLY IS MUTAGENESIS NOT POSSIBLE! ONLY IS MUTAGENESIS NOT POSSIBLE! Induction of cycA mutations in MG1655 and MDS41 PLASMID STABILITY – pCTXVP60 PLASMID STABILITY – pT-ITR PLASMID STABILITY GROWTH RATES A. MDS41 in minimal growth medium ■ : optical density (left scale) ● : DCW (left scale) ▼: glucose concentration (right scale) B. CAT expression in MDS41 and MG1655 ■ : MG1655 ● and▼: MDS41 duplicates CONCLUSIONS The strains have the following: Enhanced transformation efficiency Reduced mutability Increased plasmid stability Normal growth rates Can me used as ‘chassis’ for metabolite production BIBLIOGRAPHY Posfai G. et. al., 2006. Emergent properties of reduced-genome Escherichia coli. Science 312, 1044-1046. Kolisnychenko V., Plunkett G. III, Herring C.D., Feher T. Posfai J., Blattner F.R., Posfai G. 2002. Engineering a reduced Escherichia coli genome. Genome Res. 12(4):640-7. Blattner F.R. et. al., 1997. The Complete Genome Sequence of Escherichia coli K-12. Science 277, 1453-1469. Pictures, Figures, Tables: S2: http://www.news.wisc.edu/newsphotos/perna.html S5: http://www.scarabgenomics.com/pdfs/cleangenome.pdf S7,8,9,12,14,18: Posfai G. et. al., 2006. Emergent properties of reducedgenome Escherichia coli. Science 312, 1044-1046 S11, 17: Posfai G. et. al., 2006. Emergent properties of reduced-genome Escherichia coli. Science 312, 1044-1046 (supporting online material) FURTHER READING… Sung BH, Lee CH, Yu BJ, Lee JH, Lee JY, Kim MS, Blattner FR, Kim SC. Development of a biofilm production-deficient Escherichia coli strain as a host for biotechnological applications. Appl Environ Microbiol. 2006 May;72(5):3336-42. Sharma SS, Blattner FR, Harcum SW. Recombinant protein production in an Escherichia coli reduced genome strain. Metab Eng. 2007 Mar;9(2):13341. Lee JH, Sung BH, Kim MS, Blattner FR, Yoon BH, Kim JH, Kim SC. Metabolic engineering of a reduced-genome strain of Escherichia coli for L-threonine production. Microb Cell Fact. 2009 Jan 7;8:2. Umenhoffer K, Fehér T, Balikó G, Ayaydin F, Pósfai J, Blattner FR, Pósfai G. Reduced evolvability of Escherichia coli MDS42, an IS-less cellular chassis for molecular and synthetic biology applications. Microb Cell Fact. 2010 May 21;9:38. QUESTIONS? Referencec : www.slideshare.com