Chapter 3, part A
Chapter 3a
Compartmentation:
Cells and Tissues
About this Chapter
• Body compartments
• Biological membranes
• Intracellular compartments
• Tissue types and characteristics
• Tissue remodeling
• Organs
Three Major Body Cavities
POSTERIOR ANTERIOR
Cranial cavity
Pleural sac
Pericardial sac
Thoracic cavity
Diaphragm
Abdominal cavity
Abdominopelvic cavity
Pelvic cavity
Figure 3-1
Body Cavities
Lumens of Hollow Organs
• Hollow organs
• Heart
• Lungs
• Blood vessels
• Intestines
• Lumen
• Not the internal environment
Functional Compartments
1. Outside Body
2. Extracellular fluid
• Plasma
• Interstitial fluid
3. Intracellular fluid
4. Organelles and vacuoles
Body Fluid Compartments
Capillary wall Cell membrane
Blood cells
Blood vessel
Plasma
ECF
Interstitial fluid Intracellular fluid
Cell membrane
ICF
Figure 3-2
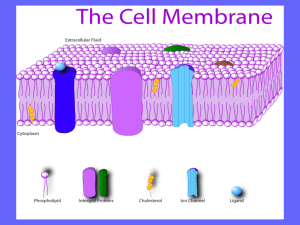
Cell Membrane: Overview
• Membranes in the body
Pericardial membrane
Loose connective tissue
Heart
Cell
The pericardial membrane is a tissue that surrounds the heart.
Seen magnified, the pericardial membrane is a layer of flattened epithelial cells supported by connective tissue.
Each cell of the pericardial membrane has a cell membrane surrounding it.
The cell membrane is a phospholipid bilayer.
Figure 3-3
Cell Membrane: Functions
• Physical barrier
• Gateway for exchange
• Communication
• Cell structure
Cell Membrane: Structure
• The fluid mosaic model of a biological membrane
Carbohydrate group of glycoprotein
Carbohydrate group of glycolipid
Extracellular surface of membrane
Membrane splits into layers in freeze-fracture electron microscopy.
Proteins
Intracellular surface of membrane
Cholesterol molecules insert themselves into the lipid layer.
Lipid tails form the interior layer of the membrane.
Phospholipid heads face the aqueous intracellular and extracellular compartments.
Figure 3-4
Cell Membrane: Composition
• Lipids
• Phospholipids
• Sphingolipids
• Cholesterol
• Proteins
• Integral
• Peripheral
• Lipid-anchored
Cell Membrane: Composition
Table 3-1
Cell Membrane: Structure and Formation
• Phospholipids have polar and non-polar regions
(a) Phospholipid molecules have polar heads and nonpolar tails.
The “R” group is a variable polar group.
Structural model
Polar head
(hydrophilic)
Nonpolar fatty acid tail
(hydrophobic)
Molecular models Stylized model
Figure 3-5a
Cell Membrane: Formation
• Membrane phospholipids form bilayers, micelles, or liposomes
Phospholipids arrange themselves so that their nonpolar tails are not in contact with aqueous solutions such as extracellular fluid.
(b)
Phospholipid bilayer forms a sheet.
Tails
Micelles are droplets of phospholipids.
Liposomes have an aqueous center.
Figure 3-5b
Cell Membrane: Proteins
• The three types of membrane proteins: integral, peripheral, and lipid-anchored
Integral
(transmembrane) protein
Glycoprotein
Peripheral protein
Peripheral protein
Cytoskeleton proteins
Lipid-anchored proteins
Cytoplasm
Figure 3-6
Cell Membrane: Lipid Rafts
• Sphingolipids and alkaline phosphatase
Figure 3-8
Cell Membrane Components
Cholesterol
CELL MEMBRANE consists of
Phospholipids, Sphingolipids Carbohydrates together form
Glycolipids together form
Glycoproteins together form
Lipid bilayer functions as
Selective barrier between cytosol and external environment
Structural stability whose functions include
Cell recognition
Immune response
Proteins
Figure 3-9
Intracellular Compartments
• Cytoplasm
• Cytosol
• Inclusions
• Organelles
• Nucleus
Cell Compartments
• A map for the study of cell structure
THE CELL is composed of
Cell membrane
Nucleus Cytoplasm
Cytosol
Membranous organelles
• Mitochondria
• Endoplasmic reticulum
• Golgi complex
• Lysosomes
• Peroxisomes
Inclusions
• Lipid droplets
• Glycogen granules
• Ribosomes
• Vaults
• Proteasomes
• Cytoskeleton
• Centrioles
• Centrosomes
• Cilia
• Flagella
Extracellular fluid
Figure 3-11
Inclusions Have No Membranes
• Ribosomes
• Free
• Fixed
• Polyribosomes
• Proteasomes
• Vaults
• RNA/protein
Cytoplasmic Proteins Fibers
• Actin (microfilaments)
• Intermediate
• Myosin
• Keratin
• Neurofilaments
• Microtubules
• Tubulin
• Centrioles, cilia, flagella
Microtubule function
• Centrioles
• Pull chromosomes
• Form core in cilia
• Cilia and flagella
• Fluid movement
Centrioles
Figure 3-13a –b
Cilia and Flagella
Figure 3-13c –d
Cytoskeleton: Function
• Cell shape
• Internal organization
• Intracellular transport
• Assembly of cells into tissues
• Movement
Cytoskeleton and Cytoplasmic Protein Fibers
(a)
Microvilli increase cell surface area.
They are supported by microfilaments.
Microfilaments form a network just inside the cell membrane.
Microtubules are the largest cytoskeleton fiber.
Intermediate filaments include myosin and keratin.
(b)
Figure 3-14
Cytoskeleton and Cytoplasmic Protein Fibers
• Motor proteins move on cytoskeletal fibers
Organelle
Motor protein
ATP
Direction of movement
Cytoskeletal fiber
Figure 3-15
Mitochondria
• Membrane-enclosed compartments
• Unique DNA
• Site of cellular ATP generation
Mitochondria
Matrix is the innermost compartment.
Inner membrane
Outer membrane
Cristae
The intermembrane space forms a compartment.
Cytosolic side of membrane
Matrix
Cytoplasm of cell
Figure 3-16
Endoplasmic Reticulum (ER)
• Smooth ER
• Synthesis of fatty acids, steroids, lipids
• Modified forms in liver, kidney, muscles
• Rough ER
• Rows of ribosomes
• Protein assembly and modification
Endoplasmic Reticulum
Ribosomes are attached to cytosolic side of rough endoplasmic reticulum.
Endoplasmic reticulum
Lumen of endoplasmic reticulum
Smooth endoplasmic reticulum
Figure 3-17