Our View of the Universe
advertisement

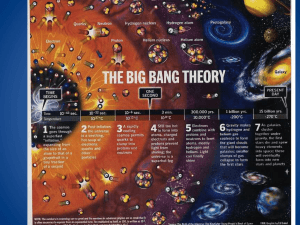
Our View of the Universe History The Big Bang The Anthropic Principle Physicists Find Elusive Particle Seen as Key to Universe “ASPEN, Colo. — Signaling a likely end to one of the longest, most expensive searches in the history of science, physicists said Wednesday that they had discovered a new subatomic particle that looks for all the world like the Higgs boson, a key to understanding why there is diversity and life in the universe.” - New York Times, July 4 2012 Integration of Science and Religion ? Worldview - 2012 Worldview – 1700 BCE Ptolemy – 150 AD Source - http://www.vikdhillon.staff.shef.ac.uk/ Copernicus – 1500 AD Heliocentric Model Galileo and Kepler – 1600s SN 1604 Elliptical orbits Phases of Venus 1610 Sir Isaac Newton (1642 – 1727) • Principia mathematica • Law of Universal Gravitation – Confirmed Kepler’s Laws of planetary motion Static Universe Model (Einstein’ s universe) Albert Einstein (1879 – 1955) • Newtonian mechanics did not reconcile with laws of electromagnetism • General Theory of Relativity (1916) E = mc 2 – Nobel Prize in Physics 1921 Led to Quantum Theory Georges Lemaitre, S.J. • Belgian priest and physicist • Applied general relativity to cosmology – derived equations describing universe of constant mass and expanding radius (1927). Theory of the Primordial Egg – Disputed by Einstein – Later known as Hubble’s Law – Pejoratively (Hoyle 1949) referred to as: » The Big Bang The Big Bang - Evidence • Edwin Hubble (1889 – 1953) – Hooker telescope at Mount Wilson CA Discovered galaxies beyond the Milky Way • Measured distances by “brightness” • Light from distant galaxies is “red shifted” Galaxies are all moving away • Hubble’s Law (1929) H = v/d Electromagnetic spectrum • Light behaves as both a particle (photon) and a wave • Shorter wavelengths/higher energy The Doppler Effect • Change in frequency of a wave (sound or light) for an observer moving relative to its source. • Applications – radar (police, weather), medical imaging The Big Bang - Evidence • Edwin Hubble (1929) – Assumes all galaxies emit similar light – Spectroscopically measured light from far off galaxies – Light from distant galaxies is “red shifted” , i.e. has longer wavelengths than light from nearby galaxies – Confirmation of Big bang theory. • Microwave Background Radiation (1964) – – – – Princeton and Bell Labs (New Jersey) New radio telescopes Found microwave “noise” everywhere Determined age of the universe (13.7 billion years) • Oldest galaxy – UDFy 38135539 (2011) – 13.07 billion light years away (600 MY after the big bang) But Why is There Anything at All ? • “The Laws of Nature” – mathematical relationships that describe what we observe. • The Law of Gravity • First and Second Law of Thermodynamics • Theory of Relativity ( E = mc2 ) • Each of these laws is defined by a constant which could (theoretcially) have different values than what we observe. The Fundamental Constants (Forces) • Strong nuclear force – holds subatomic particles together • Weak nuclear force – Causes radioactive decay – Higgs boson is part of this • Gravitational force • Electromagnetic force – Combines electricity and magnetism • Matter/anti-matter ratio • Expansion rate of the universe – H in Hubble’s Law If any of these were even slightly larger or smaller the universe as we know it would not exist!!! Let’s Play! Roulette – spaces 1-36, 0, 00 • Chance of hitting a 7? 1/38 • Let it ride! 1/38 x 1/38 = 1/1444 • How about 3 times ? 1/38 x 1/38 x 1/38 = 1/54,872 • Hitting 6 times 1 in 3 billion chance The Goldilocks Enigma Why is the universe “just right” for life? • Random chance – – We are winners of the cosmic lottery • Anthropic principle (AP) – Weak AP: universe must support our presence – Strong AP: “fine tuning” suggests there is an intentionality in universe’s creation • Multiverse hypothesis – There are many hostile universes, we just happen to be in one that isn’t hostile • Temporal Multiverse • Simultaneous Multiverses String Theory/M Theory The Theory of Everything (ToE) • All matter is composed of strings of infinitely small energy loops • Attempts to unify: – Quantum physics (behavior of very small things) – Relativity theory (behavior of very large things) • Is it testable?? • Advocates believe it will ultimately explain why the constants are what they are? Questions? • Why do YOU think the Big Bang should be accepted or not accepted? • Projects such as the Super Hadron Collider are VERY expensive – are they worth it? • Do you think a Theory of Everything will eventually be arrived at? What then? Day 2 - Schedule :00 9am :30 :45 10am Gather - Continental Breakfast Welcome/Updates The Big Bang :00 :45 Sauer/Ryscavage Sauer Sauer Questions/Discussion :00 11am :15 :30 Transition Small Groups 1-3/Lunch Groups 4-7 :00 12pm :15 :30 1pm 2pm 3pm 4pm 5pm Transition Lunch Groups 1-3/Small Groups 4-7 :00 :30 Religious Cosmology Dallavalle Questions/Discussion Reflection Period Small Groups Collins :00 :30 :00 :30 :00 :30 :00 :30 Large Group Report Out Depart