Big Bang - AbergavennyAS.org.uk
advertisement

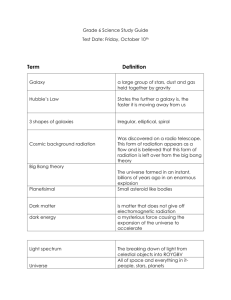
The Big Bang Theory John Mallett The 'Big Bang' Theory? Why do we think there was a 'Big Bang'? History of the discoveries Measurement of velocity and distance Current view of the origin of universe Latest information. Using history to explain the slow growth of understanding of the universe. The 'Big Bang' will emerge as a theory. There are many key discoveries to determine distance and velocity. Some history of 'Big Bang' theory Cepheid Variable Stars 1784 The term Cepheid originates from Delta Cephei in the constellation of Cepheus identified by John Goodricke in 1784. A periodic yellow super giant (F6-K2) Classical Very regular period order of days to months 4 - 20 times the mass of the Sun 100,000 times more luminous. Type II Period of between 1 and 50 days Half the mass of the Sun Several sub groups 1- 4 days BL Her 10 - 20 days W Virginis > 20 days RV Tauri Friedrich Bessel 1838 Parallax First used to measure 61 Cygni Only useful for quite close objects where parallax can be measured. Close stars in our galaxy Proxima Centauri - has a parallax of 0.7687 ± 0.0003 arcsec Henrietta Levitt 1908– Cepheid Variables The discovery that there was a relationship between the log of the period and the luminosity Made on 1777 variable stars from Harvard photographic plates. She received almost no recognition in her lifetime. Ejnar Hertzprung 1913 Determined the accurate distance of several Cepheids in the Milky Way by using parallax. The scale of Cepheid distance could now be used for any Cepheid. Harlow Shapley – 1915 Used Cepheid 'Levitt's Law' to measure the Milky Way Edwin Hubble – 1924 Used 'Levitt's Law' to show that Andromeda was a galaxy like our own Milky Way but more distant. Settled the 'Island Universe Debate' Shapley – Curtis debate – were Andromeda and other nebular within our galaxy? Albert Einstein 1917 – Cosmological constant A term in the General relativity to allow for a static universe. At this time the universe was still considered static. Einstein eventually said that this was the greatest mistake in his life! Edwin Hubble & Milton Humason – 1929 Used the 'red shift' of distant galaxy spectra to identify velocity Proposed from General Relativity by George Lemaitre -1927 Red Shift Splitting light up into it's spectrum can show characteristic absorption lines for elements. Similar to the Doppler effect reducing the frequency of a car as it goes away from you. Edwin Hubble discovered that all distant galaxies were moving away from us. Hubble Constant – H0 Estimated as 68km/s per Mpc 1 Mpc = 3,260,000 Light Years Faber - Jackson relation 1976 Related to elliptical Galaxies Luminosity is proportional to (velocity dispersion)4 Calibrated by distance 'standard candles' Tully – Fisher relation 1977 Related to spiral Galaxies Uses the width or shift of the absorption line to estimate luminosity The use the inverse square law to arrive at distance. This relationship was calibrated using the other distance 'standard candles' Globular clusters All the stars form at the same time Serving as a cosmic clock... Globular clusters Globular clusters The oldest observed globular clusters only contain stars less than 0.7 solar masses. So, much dimmer than our Sun There are a number of uncertainties: Difficulty in determining exact distance to globular clusters Some uncertainty of brightness and mass. The finer details of stellar evolution are still unclear. So the best estimates of age of oldest clusters is 11- 18 Billion years The Universe must be at least as old as the oldest cluster.. Saul Perlmutter and Adam Riess of the US and Brian Schmidt of Australia 2011 Used white dwarf supernova type 1a in distant galaxies to measure distance. Type 1a supernova are always the same brightness Slight difference in the colour (spectra) can indicate velocity They discovered that the expansion of the universe is accelerating! They got a Nobel Prize for Physics in 2011 Image of M101 – Hewelsfield Observatory – 28/3/2012 Type 1a Supernova So where are we so far? Evidence of expansion and acceleration of the universe Quantification of rate of expansion Some really valuable and validated distance tools All based on some key assumptions: Isotropic – Universe the same at all distances and directions Laws remain the same throughout the universe Some supporting observations. Cosmic Microwave Background CMB Distribution of Galaxies Discovered in 1964 by Arno Penzias & Robert Wilson 1978 Nobel Prize The radiation from the 'Big Bang' The expansion of space causes the wavelength to increase The peak of this is now at 1.873mm wavelength Frequency of 160.2 GHz (2.725K) Isotropic to 1 part in 100,000 WMAP Image of the CMB Wilkinson Microwave Anisotropy Probe Our Galaxy Galaxy distribution For 'Big Bang' to be valid distribution of matter should have been symmetrical and Isotropic. Current Problems with the 'Big Bang' Theory Flatness problem WMAP has determined the geometry of the universe to be nearly flat. Under 'Big Bang' cosmology curvature grows with time. To be nearly flat would be a very big coincidence (like balancing a pencil on its point) Horizon problem Calculating the distance of objects at the edge of our horizon are so far apart that assuming universe is Isotropic that they can never have originated at the same point. Monopole problem (plasma physics particle with only one magnetic pole!) Cosmology predicts a large number of heavy stable 'magnetic Monopoles' We have not yet seen any. Orange curve – Closed high density universe that will ultimately collapse back to singularity Green – Flat critical density universe that will slow down and settle at 3-4 times the current size Red – Current thinking, Large fraction of matter is dark and universe is accelerating. Inflation to fix the problems! A theoretical solution to the problems! Developed as a theory by Alan Guth, Andrei Linde, Paul Steinhardt & Andy Albrecht Provides a solution to all three problems and some other more subtle problems What is it? A period of very rapid exponential growth prior to the more gradual expansion 'Inflation' It is an extension to 'Big Bang' theory