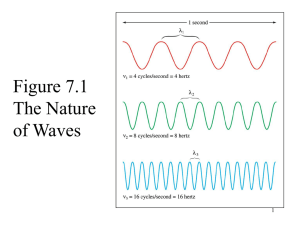
Electrons can only occupy so-called atomic
advertisement

Shape of orbitals s-orbital p-orbitals Electrons can only occupy so-called atomic orbitals with well defined energy levels corresponding to the principal quantum number, n. The lowest level will have n = 1, the next n = 2, and so on. Electrons must always enter the first available orbital of lowest energy. The first element, hydrogen, only has one electron, and so this electron must enter the 1s orbital. The electronic configuration of hydrogen in the ground state must therefore be: H 1s1. Boron 1s2 2s2 2p1 Atomic number 5 Carbon 1s2 2s2 2p2 Atomic number 6 According to Hund’s rule, fill a set of similar energy orbitals with as many unpaired electrons as possible (as in the p or d orbitals). The successive ionization energies of sodium [Ar] 3s1 • • • • Electron removed Ionization energy/KJmol-1 orbital 1st 496 3s1 2nd 4565 3rd 691 4th 9544 5th 13 352 6th 16 611 7th 20 115 8th 25 491 9th 28 934 10th 141 367 1s2 11th 159 079 1s1 2p6, 2p2 One electron furthest away from nucleus easiest to remove (3S1) Eight nearer to nucleus, harder to remove (2p6, 2p2) Two very close to the nucleus and most difficult to remove (1s2) Proves numbers of electrons in each shell is 2,8,1 First ionisation energies (IE) of elements in periods 2 to 4/KJmol-1 IEs increase across period (nuclear charge increasing, shielding the same) Li, 520 Be, 900 B, 801 C, 1086 N, 1402 O, 1314 F, 1681 Ne, 2081 Na, 495 Mg, 735 Al, 580 Si, 780 P, 1060 S, 1005 Cl, 1255 Ar, 1527 K, 419 Ca, 590 Ga, 579 Ge, 762 As, 947 Se, 941 Br, 1140 Kr, 1351 IEs decrease down a group (distance of outer electrons from nucleus increasing) First ionisation energies (IE) of elements in periods 2 to 4/KJmol-1 1. 2. Look at group II and group III: the first electron for Al is a 3P1 electron and is less tightly held than 3S electron as it is further away from nucleus Look at group V and group VI: a paired electron is easier to remove than an unpaired electron and the configuration for sulfur is 3P4, so it has a paired electron Li, 520 Be, 900 B, 801 C, 1086 N, 1402 O, 1314 F, 1681 Ne, 2081 Na, 495 Mg, 735 Al, 580 Si, 780 P, 1060 S, 1005 Cl, 1255 Ar, 1527 K, 419 Ca, 590 Ga, 579 Ge, 762 As, 947 Se, 941 Br, 1140 Kr, 1351 The Ionization Energies for elements in Period 3 Element I1 I2 I3 I4 I5 I6 I7 Na 495 4560 Mg 735 1445 7730 Al 580 1815 2740 11600 Si 780 1575 3220 4350 16100 P 1060 1890 2905 4950 6270 21200 S 1005 2260 3375 4565 6950 8490 27000 [Ne]3S23P4 Cl 1255 2295 3850 5160 6560 9360 11000 [Ne]3S23P5 Ar 1527 2665 3945 5770 7230 8780 12000 [Ne]3S23P6 configuration [Ne]3S1 [Ne]3S2 I1 = first ionization energy; A(g) I2 = second ionization energy; A+(g) I3 etc. [Ne]3S23P1 [Ne]3S23P2 A+(g) + eA2+(g) + e- [Ne]3S23P3