Nathal Severijns
advertisement
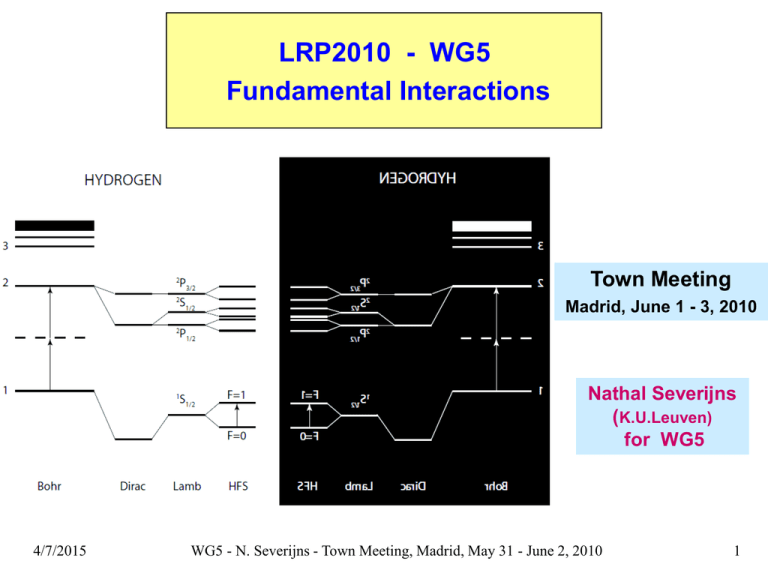
LRP2010 - WG5 Fundamental Interactions Town Meeting Madrid, June 1 - 3, 2010 Nathal Severijns (K.U.Leuven) for WG5 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 1 WG5 members R. Calabrese (Italy) G. Drexlin (Germany) D. Horvath (Hungary) K. Kirch (Switzerland) K. Pachucki (Poland) F. Piquemal (France) S. Schoenert (Germany) N. Severijns (Belgium) R. Timmermans (The Netherlands) C. Volpe (France) C. Weinheimer (Germany) O. Zimmer (France) K. Jungmann (The Netherlands) E. Widmann (Austria) thanks to colleagues who contributed as non-WG5 member 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 2 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 3 Key questions - Which fundamental symmetries are conserved in nature? - What is the origin of the matter dominance in the universe? - Are there new sources of CP violation? - What are the properties of antimatter? - What are the properties of the neutrino? - Are there other forces than the four known ones? - Are there new particles and what is their role in the universe? - What are the precise values of the fundamental constants? 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 4 Key issues 1. Fundamental Fermions - Neutrino oscillations and the neutrino mixing matrix Neutrino masses (direct measurements and double beta decay exps.) Quark mixing matrix and unitarity New (time reversal invariant) interactions in nuclear and muon β-decays 2. Discrete symmetries - Parity violation - Time reversal and CP violation in the quark sector (e.g. EDM’s) - CPT and Lorentz invariance 3 Properties of known basic interactions - QED and fundamental constants (e.g. g-2, α, anti-H, H-like ions, … ) - QCD (exotic atoms) - Gravity (e.g. matter vs. antimatter behavior, … ) 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 5 Future directions - overview 1. Fundamental Symmetries - Time reversal and CP violation - Parity non-conservation in atoms and ions - CPT conservation and Lorentz invariance 2. Neutrinos - Nature and mass of neutrinos - Neutrino mixing parameters and the CP violating phases 3. Electroweak interactions - Precision measurements in beta decay - Precise QED studies within the Standard Model Recommendations - overview 1. Support of small-sized laboratory and university groups 2. Support for and from theory 3. Facilities 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 6 1. Fundamental symmetries a. Time reversal and CP violation in the quark sector Neutrons QCD a nonzero particle EDM violates P, T and, assuming CPT conservation, also CP Leptons Nuclei Schiff Moment some current EDM constraints : Paramagnetic atoms: Tl, Cs, Fr Molecules atomic theory investigate different systems, providing complementary information on different sources of CP violation Diamagnetic atoms: Hg, Xe, Rn nuclear theory e.g. permanent EDM‘s matter – anti-matter asymmetry quark EDM quark chromo!EDM lepton EDM PbO, YbF, TlF FUNDAMENTAL THEORY - for p, d EDM exps. good prospects with ring (e.g. plans for COSY) - R- and D-corr. in decay (nTRV @ PSI) 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 7 1. Fundamental symmetries b. Parity non-conservation in atoms and ions e.g. APV: test of the SM through measurements of the Weinberg angle Future measurements: - trapped atoms and ions with enhanced APV effect, in casu Fr, Ba+, Ra+ - measurements on series of isotopes APV is complementary to parity-violating electron scattering (APV in graph) for determining effective weak couplings of quarks and search for new physics beyond SM Note: experiments at low energy very clean since radiative corrections are minimal 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 8 1. Fundamental symmetries c. CPT conservation and Lorentz invariance CPT: e.g. spectroscopy of (AD-CERN) - antiprotonic atoms (pbar-p, pbar-He) - antihydrogen (i.e. e+-pbar atom) AD-CERN Need for future facilities: ELENA, FLAIR Lorentz violation: test frame dependence of observables close interaction with theorists is essential 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 9 2. Neutrino masses, oscillations and mixing matrix Neutrino masses hierarchy Dirac or Majorana particle ?? - direct measurements: KATRIN spectrometer, sensitivity = 0.2 eV MARE calorimeters, phase-II sensit. = 0.2 eV - 0 decay: needs: 4/7/2015 CUORE (130Te), SuperNEMO (150Nd or 82Se), GERDA (76Ge): sensitivity ≈ 0.05 – 0.3 eV - enrichment of isotopes - experiments to support matrix elements calculations WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 10 2. Neutrino masses, oscillations and mixing matrix flavor eigenstates Neutrino mixing matrix: atmospheric 23 (45 4) mass eigenstates reactor solar 13 12 (?) 12 (33.7 1.3) oscillation experiments (e.g. Double Chooz) determine size of 13 if 13 large search for CP violation in lepton sector (phase ) superbeams, neutrino factories, beta-beams (esp. if 13 < 0.02) 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 11 3. Electroweak interactions a. Precision measurements in decay A. CKM quark mixing matrix (masses, theory, …) decays from K decays strong limits on physics beyond Standard Model e.g. 0.97425(22) 0.22534(93) 0.00393(36) 1.04(6) 0.0412(11) 0.230(11) 0.18 0.0387(23) 0.77 0.24 0.0081(6) - scalar currents - right-handed crts. 0.99995(61) Future: - improve precision (spectroscopy, mass measurements) - neutron lifetime issue ! - new transitions (e.g. superallowed, T = 1/2 mirror) 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 12 B. Correlation measurements in decay search for non-SM weak interactions: - S & T currents - new V, A interactions (e.g. V+A) - neutron decay a, A, B, R, … correlations with aSPECT, PERKEO, nTRV, … reliable value for lifetime n needed ! n = 885.7(8) s An PERKEO 4/7/2015 J n = 878.5(8) s WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 13 B. Correlation measurements in decay - nuclear beta decay a, A, … correlations - particle traps (@ GANIL, ISOLDE, KVI, … ) - simulation codes - needs for field - higher yields (nuclei & UCN) - polarized samples in traps ( tensor, right-handed currents, …) - precise determination of nuclear polarization - improved simulation codes - long beam times 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 14 3. Electroweak interactions b. Precise QED studies within the SM Accurate QED predictions required for improved determinations of fundamental constants (e.g. α, me, …) Precisions @ 10-13 level reached - g-2 measurements: electron α muon test standard model - light hydrogenic ions, muonic & pionic hydrogen, … e.g. me from L/ c for C5+ - light few-body atoms: He, Li, pbar-He, … - highly charged ions e.g. QED in strong E-fields, magnetic moments, … - many-electron atoms theory: electron correlations, … 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 15 QCD and Gravitaiton QCD - pionic atoms (e.g. DIRAC exp, PSI) - kaonic atoms & kaonic nuclear bound states e.g. SIDDHARTA, AMADEUS, AD, FLAIR - pbar-atoms (ELENA@AD, FLAIR) Gravitation - gravitational interaction of antimatter e.g. gravitational mass of anti-H with AEGIS@AD - searches for non-Newtonian gravity e.g. test law of gravity at small distances (GRANIT, qBounce, ..) 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 16 Future directions - overview 1. Fundamental Symmetries - Time reversal and CP violation - Parity non-conservation in atoms and ions - CPT conservation and Lorentz invariance 2. Neutrinos - Nature and mass of neutrinos - Neutrino mixing parameters and the CP violating phases 3. Electroweak interactions - Precision measurements in beta decay - Precise QED studies within the Standard Model Recommendations - overview 1. Support of small-sized laboratory and university groups 2. Support for and from theory 3. Facilities 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 17 Recommendations - 1 • Support of small-sized laboratories and university groups - training of young people - development of new techniques - detectors - to improve/extend possibilities of traps • Support for theory and from theory • Facilities 1. for precise QED studies with low-energy antiprotons ELENA @ CERN, later FLAIR@GSI 2. underground laboratories (upgrades / new ones) 3. upgraded and new facilities 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 18 Recommendations - 2 • Support of small-sized laboratories and university groups • Support for and from theory • Facilities 1. for precise QED studies with low-energy antiprotons 2. underground laboratories 3. upgraded and new facilities (time-ordered approach) nuclei - HIE-ISOLDE - SPIRAL2 (DESIR) - EURISOL neutrons - UCN source @ FRM-II - European Spallation Source anti-p - modules 4 & 5 of FAIR (for QED & antiproton research) 4. regular access to beams & long continuous beam time periods: nuclei: ISOL@MYRRHA neutrons: high-intensity neutron sources QED: 4/7/2015 sources of coherent short-wavelength e.m. radiation WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 19 The MYRRHA concept (SCK•CEN, Mol, Belgium) www.sckcen.be/myrrha/ Sub-critical reactor Accelerator (600 MeV proton, 4 mA) ADS “Accelerator Driven System” Spallation source ( proton neutron ) Neutron multiplier Flexible irradiation facility Waste transmutation Material testing others: RI, NTD-Si,... Fast neutron source Lead-Bismuth coolant http://www.sckcen.be/myrrha/ Future directions 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 21 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 22 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 23 Recommendations 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 24 4/7/2015 WG5 - N. Severijns - Town Meeting, Madrid, May 31 - June 2, 2010 25