Economic growth
advertisement

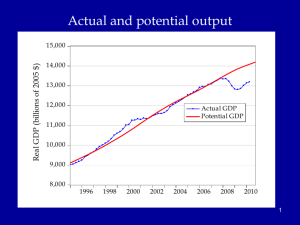
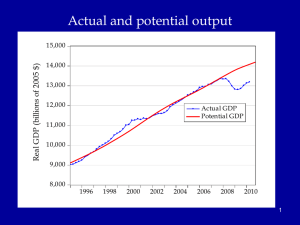
Economic growth Olduvai stone chopping tool, 1.8 – 2 million years BP 1 Actual and potential output Billions of 2005$ 16,000 14,000 12,000 Actual GDP Economic growth: 10,000 Studies growth of potential output Potential GDP 8,000 6,000 1980 1985 1990 1995 2000 2005 2010 2015 2020 2 Congressional Budget Office, Sept 2012, cbo.gov. Agenda • • • • • • Introductory background Essential aspects of economic growth Aggregate production functions Neoclassical growth model Simulation of increased saving experiment Then in the last week: deficits, debt, and economic growth 3 Historical Trends in Economic Growth in the US since 1800 1. Strong growth in Y 2. Strong growth in productivity (both Y/L and TFP) 3. Steady “capital deepening” (increase in K/L) 4. Strong growth in real wages since early 19th C; g(w/p) ~ g(X/L) 5. Real interest rate and profit rate basically trendless 4 Notes on the readings Chapters 4 and 5 are core and consensus economics Chapter 6 is controversial and one point of view. 5 Capital deepening in agriculture Food for Commons Morocco, 2002 6 Mining in rich and poor countries D.R. Congo Canada 7 Review of aggregate production function Yt = At F(Kt, Lt) Kt = capital services (like rentals as apartment-years) Lt = labor services (hours worked) At = level of technology gx = growth rate of x = (1/xt) dxt/dt = Δ xt/xt-1 = d[ln(xt))]/dt gA = growth of technology = rate of technological change = Δ At/At-1 Constant returns to scale: λYt = At F(λKt, λLt), or all inputs increased by λ means output increased by λ Perfect competition in factor and product markets (for p = 1): MPK = ∂Y/∂K = R = rental price of capital; ∂Y/∂L = w = wage rate Exhaustion of product with CRTS: MPK x K + MPL x L = RK + wL = Y Alternative measures of productivity: Labor productivity = Yt/Lt Total factor productivity (TFP) = At = Yt /F(Kt, Lt) 8 Review: Cobb-Douglas aggregate production function Remember Cobb-Douglas production function: or Yt = At Kt α Lt 1-α ln(Yt)= ln(At) + α ln(Kt) +(1-α) ln(Lt) Here α = ∂ln(Yt)/∂ln(Kt) = elasticity of output w.r.t. capital; (1-α ) = elasticity of output w.r.t. labor MPK = Rt = α At Kt α-1 Lt 1-α = α Yt/Kt Share of capital in national income = Rt Kt /Yt = α = constant. Ditto for share of labor. 9 The MIT School of Economics Robert Solow (1924 - ) Paul Samuelson (1915-2009) 10 Basic neoclassical growth model Major assumptions: 1. Basic setup: - full employment - flexible wages and prices - perfect competition - closed economy 2. Capital accumulation: ΔK = sY – δK; s = investment rate = constant 3. Labor supply: Δ L/L = n = exogenous 4. Production function - constant returns to scale - two factors (K, L) - single output used for both C and I: Y = C + I - no technological change to begin with - in next model, labor-augmenting technological change 5. Change of variable to transform to one-equation model: k = K/L = capital-labor ratio Y = F(K, L) = LF(K/L,1) y = Y/L = F(K/L,1) = f(k), where f(k) is per capita production fn. 11 Major variables: Y = output (GDP) L = labor inputs K = capital stock or services I = gross investment w = real wage rate r = real rate of return on capital (rate of profit) E = efficiency units = level of labor-augmenting technology (growth of E is technological change = ΔE/E) ~ ~ L = efficiency labor inputs = EL = similarly for other variables with “ ”notation) Further notational conventions Δ x = dx/dt gx = growth rate of x = (1/x) dx/dt = Δxt/xt-1=dln(xt)/dt s = I/Y = savings and investment rate k = capital-labor ratio = K/L c = consumption per capita = C/L i = investment per worker = I/L δ = depreciation rate on capital y = output per worker = Y/L n = rate of growth of population (or labor force) = gL = Δ L/L v = capital-output ratio = K/Y h = rate of labor-augmenting technological change 12 We want to derive “laws of motion” of the economy. To do this, start with (math on next slide): 5. Δ k/k = Δ K/K - Δ L/L With some algebra,* this becomes: 5’. Δ k/k = Δ K/K - n Y Δ k = sf(k) - (n + δ) k which in steady state is: 6. sf(k*) = (n + δ) k* In steady state, y, k, w, and r are constant. No growth in real wages, real incomes, per capita output, etc. *The algebra of the derivation: ΔK/K = (sY – δK)/K = s(Y/L)(L/K) – δ Δk/k = ΔK/K – n = s(Y/L)(L/K) – δ – n Δk = k [ s(Y/L)(L/K) – δ – n] = sy – (δ + n)k = sf(k) – (δ + n)k 13 Mathematical note We will use the following math fact: Define z = y/x Then (1) (Growth rate of z) = (growth rate of y) – (growth rate of x) Or gz = gy - gx Proof: Using logs: ln(zt) = ln(yt )– ln(xt) Taking time derivative: [dzt/dt]/zt = [dyt/dt]/yt - [dxt/dt]/xt which is the desired result. Note that we sometimes use the discrete version of (1), as we did in the last slide. This has a small error that is in the order of the size of the time step or the growth rates. For example, if gy = 5 % and gx = 3 %, then by the formula gz = 2 %, while the exact calculation is that gz = 1.9417 %. This is close enough for expository purposes. 14 y = Y/L y* y = f(k) (n+δ)k i = sf(k) i* = (I/Y)* k* k 15 Results of neoclassical model without TC y = Y/L Predictions of basic model: – “Steady state” – constant y, w, k, and r – gY = n Uniqueness and stability of equilibrium. – Equilibrium is unique – Equilibrium is stable (meaning k → k* as t → ∞ for all initial k0). y* y = f(k) (n+δ)k i = sf(k) i* = (I/Y)* k* k 26 But does not have growth predictions of historical record, so need further work (next lecture). 16 Economic growth (II) World fastest supercomputer, 2012 (IBM Sequoia at 16.2 petaflops) 17 Agenda - Continue analysis of NGM Discuss problem sets and ground rules Savings experiment On Monday, do economics of technological change and real business cycle model - On Wednesday, pset 1 due at the beginning of class. 18 Review from last time • • • • • • • Neoclassical growth model: classical + dynamics Growth involves potential output (not business cycles) Key assumptions: fixed s, labor growth at n Law of motion of economy: Δ k/k = sf(k) - (n + δ) k Unique and stable equilibrium: sf(k*) = (n + δ) k* Alas, does not capture major trends. Concluded need to include technological change (TC). • Economic growth involves: - increase in quantity (number of cars) - improved quality (safer cars) - new goods and services (computer replaces typewriter) 19 Growth trend, US, 1948-2008 2.0 ln(K) ln(Y) ln(hours) 1.6 1.2 0.8 0.4 0.0 50 55 60 65 70 75 80 85 90 95 00 05 20 Near-constancy of labor’s share of national income 80% Labor share of national income in US 70% 60% - Slow increase over most of century - Tiny decline in recent years as profits rose - Big rise in fringe benefit share (and decline in wage share) 50% 40% 30% Share of compensation Share of wages 20% 10% 0% 1929 1939 1949 1959 1969 1979 1989 1999 2009 21 What are the contributors to growth? Growth Accounting Growth accounting is a widely used technique used to separate out the sources of growth in a country; it relies on the neoclassical growth model Derivation Start with production function and competitive assumptions. For simplicity, assume a Cobb-Douglas production function with technological change: (1) Yt = At Kt α Lt 1-α Take logarithms: (2) ln(Yt) = ln(At )+ α ln(Kt) + (1 - α) ln(Lt ) Now take the time derivative. Note that ∂ln(x)/∂x=1/x and use chain rule: (3) ∂ln(Yt)/∂t= g[Yt] = g[At] + α g[Kt] + (1 - α) g[Lt ] In the C-D production function, α is the competitive share of K, sh(K); and (1 - α) the competitive share of labor, sh(L). (4) g[Yt] = g[At] + sh(K) g[Kt] + (1 – sh(L)) g[Lt ] From this, we estimate the rate of T.C. as: (5) g[At] = g[Yt] –sh(K) g[Kt] - sh(L) g[Lt ]} 22 Apply to U.S. private non-farm business, 1987-2011 g[Yt] = g[At] + sh(K) g[Kt] + sh(L) g[Lt ] We have data on everything but g[At]. According to U.S. Bureau of Labor Statistics: g[Yt] = 2.8 % p.y.; sh(K) = ¼; g[Kt] =3.6%; g[Lt ] = 1.1% So contribution to growth is K: 0.9% per year L: 0.8 % per year g[At]: 1.1 % per year So technology contributes 55% and capital 45% to growth in output per hour. Source: BLS, multifactor productivity page. 23 Added after class (correct the mistake) What are the contributions to per capita output growth? g[Y/L] = g(y) = g[A] + sh(K) g[K] + sh(L) g[L ] –g[L] = g[A] + sh(K) g[K] - sh(K) g[L ] = g[A] + sh(K) (g[K] - g[L ]) = g[A] + sh(K) (g[k]) Since g[y] = 1.7 % p.y.; sh(K) = ¼; g[k] =2.5% So contribution to growth is Of A: 1.1%, or 65% of total Of k: ¼ x 2.5, or 35% of total This is the very surprising results that technology contributes most of the rise in per capita output over the period. Similar in other countries/periods. 24 Introducing technological change First model omits technological change (TC). What is TC? • New processes that increase TFP (assembly line, fiber optics) • Improvements in quality of goods (plasma TV) • New goods and services (automobile, telephone, iPod) Analytically, TC is - Shift in production function. y = Y/L n ew f(k ) o ld f(k ) k k* 25 Technological change in medicine Scan for lung cancer African medicine man 26 Disappearance of polio: A benefit of growth that is not captured in the GDP statistics! The greatest technological change in history Abacus master, 1945 (.03 flops) IBM 1620, circa 1960 (104 flops) Sony Laptop, 2010 (1010 flops) IBM Sequoia, top supercomputer, 2012 (16x 1015 flops), 2x 2011 tops [flop = floating point operations per second, e.g., 1011011011001001/0010110100010101] Introducing technological change We take specific form which is “labor-augmenting technological change” at rate h. For this, we need new variable called “efficiency labor units” denoted as E ~ where E = efficiency units of labor and indicates efficiency units. L=EL New production function is then y = Y/L n ew f(k ) Y F K , EL F (K , L ) F K,L L f ( k ), y o ld f(k ) L F K /L , 1 w here k K / L k k* Y / L f (k) Note: Redefining labor units in efficiency terms is a specific way of representing TC that makes everything work out easily. Other forms of TC will give slightly different results. 29 The math with technological change is this: y Y / L f (k ) k = K /L k = s f (k ) (n h ) k T est th e lo n g -ru n eq u ilib riu m o f k 0 : s f (k ) = (n h ) k The equilibrium is unique and globally stable. It has exactly the same properties as earlier one, except: • Note that the growth term includes h (rate of tech. change). • All natural variables are growing at h: wage rates, per capita output, capital-labor ratio etc. are growing at h rather than 0. 30 T.C. for the Cobb-Douglas In C-D case, labor-augmenting TC is very simple: S et A 0 E 0 1 fo r sim p licity . Y t K t ( e ht L t ) 1 yt Y t/ Lt K yt Kt L t t ( e ht L t ) 1 / L t K t L 1 t /L t = kt 31 Results of neoclassical model with labor-augmenting TC For C-D case, s k * ( n h ) k * k * s / (n h ) 1 /( 1 ) /( 1 ) y * f ( k *) s / ( n h ) Unique and stable equilibrium under standard assumptions: Predictions of basic model: – – – – Steady state: constant y , w , k , a n d r Here output per capita, capital per capita, and wage rate grow at h. Labor’s share of output is constant. Hence, captures the basic trends! 32 y Y/L Impact with labor-augmenting TC y f (k) y* (n )k i*=I*/Y* i sf ( k ) k* k = K33/ L ln (Y), etc. Time profiles of major variables with TC ln (Y); gY = n+h ln (K); gK = n+h ln ( L ); g L n h ln (L) ); gL = n time 34 Sources of TC Technological change is in some deep sense “endogenous.” The underlying theory will be discussed on Monday. 35 Several “comparative dynamics” experiments • Change growth in labor force (immigration or retirement policy) • Change in rate of TC • Change in national savings and investment rate (tax changes, savings changes, demographic changes) Here we will investigate only a change in the national savings rate. 36