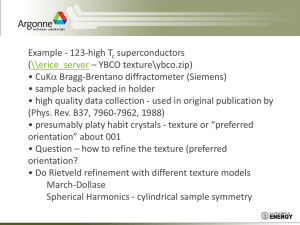
texture methods
advertisement

Texture Analysis for the evaluation of human irises reproduction in ocular prostheses and colored contact lenses Jorge Herrera, Meritxell Vilaseca, Montserrat Arjona, Jochen Düll, Jaume Pujol. Centre for Sensors, Instruments and Systems Development (CD6). Optics and Optometry Department, Technical University of Catalonia (UPC) OUTLINE • INTRODUCTION • PREVIOUS WORK: – EXPERIMENTAL SETUP AND SAMPLES – AVERAGE COLOR STUDY • TEXTURE METHODS • RESULTS • CONCLUSIONS 2 INTRODUCTION • Motivation: - Increase the knowledge of color distribution in human irises through the use of a CCD camera and multispectral techniques. - Study of human irises reproduction made by ocular prostheses and colored contact lenses • Objectives: - Implement the different tools necessary to assess the texture of human irises. - Compare textural features among human irises, ocular prostheses and contact lenses. 3 PREVIOUS WORK: Experimental setup Relative Spectral Sensitivity RGB ACQUISITION R Channel G Channel B Channel 1.0 0.8 0.6 0.4 0.2 0.0 400 450 500 550 600 650 700 Wavelength (nm) Collaboration with La Universidad de Granada, M. Melgosa and R. Huer and F. Imai from Samsung Company Vilaseca et.al. Applied Optics, 2008. 4 PREVIOUS WORK: samples and pixelwise conversion from raw digital levels to color data. Samples: 106 Irises, 68 Prostheses and 17 colored contact Lenses. Human irises 0.35 RGB Acquisition Spectral Reconstruction: Pseudo-inverse (PSE) Spectral reflectance 0.30 0.25 0.20 0.15 0.10 0.05 0.00 400 440 480 520 560 600 640 680 720 Wavelength (nm) Illuminant Tristimuli values XYZ CIE L*a*b* Coordinates 5 760 PREVIOUS WORK: average color assessment 6 PREVIOUS WORK: average color assessment 7 TEXTURE METHODS: image segmentation process • The segmentation process is divided in four main steps: 1.Pupil 4.Detection 2.3.Occlusion Border detection ofdetection detection specular from Iris reflections between -Variable eyelashes and sclera thresholding. Similar and eyelids zone procedure to -Blob -one Onanalysis. border the-Kirsch used edge point in -Eccentricity enhancement pupil detection and solidity and detection filtering line like measurements -Ellipse Hough drawing transform Screen shot of the application in Matlab 50 100 150 200 250 300 350 400 450 500 550 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 8 TEXTURE METHODS: Statistical approach to texture description and CIEDE2000 Color difference images First order texture measures are statistics calculated from the original image values, like variance, and do not consider pixel neighbour relationships. Second order measures consider the relationship between groups of two pixels in the original image. Third and higher order textures (considering the relationships among three or more pixels) L* 50 100 150 50 200 250 100 a* 50 300 100 350 150 150 200 400 200 450 250 250 b* 50 500 300 100 550 350 100 200 300 400 500 600 150 700 400 200 Mean L*a*b* 300 350 400 450 250 450 500 300 550 500 350 100 200 300 400 400 500 600 CIEDE2000 700 550 450 100 500 550 100 200 300 400 500 600 700 200 300 400 500 600 9 700 TEXTURE METHODS: First-order statistics • First-order statistics from the image histogram Pi Entropy N 1 Ep Pi log 2 Pi i 0 Energy N 1 En Pi 2 i 0 1 . . . . . i . . . . . . N 3rd central moment N 1 3 i m Pi i 0 3 N 1 m iPi i 0 10 TEXTURE METHODS: Co-occurrence matrices Co-occurrence matrices (equivalently secondorder statistics, Haralick’s descriptors) This matrix is a tabulation of how often different combinations of pixel brightness values (grey levels) occur in an image. Parameters: Levels(matrix size), distance and angle 1 . . N 1 Entropy Energy Contrast Ep Pi , j log2 Pi , j i , j 0 En C N 1 N 1 2 i, j P i j i , j 0 i, j . . . . N 1 . . i P i , j 0 . j . . 2 N 11 TEXTURE METHODS: test of classification • Linear discriminant analysis -Discriminat functions are the linear combinations of variables that better separates the groups. RESULTS TEXTURE ANALYSIS WITH FIRST-ORDER STATISTICS. Linear discriminant analysis based on the first-order statistics (Classification of samples according to texture) Correct irises (%) Correct prostheses (%) Correct C. Lenses (%) 68.4 43.3 64.7 11 RESULTS TEXTURE ANALYSIS WITH SECOND ORDER STATISTICS. Linear discriminant analysis based on the second-order statistics (Classification of samples according to texture) Correct irises (%) Correct prostheses (%) Correct C. Lenses (%) 88.4 82.1 100.0 12 CONCLUSIONS - Different tools from statistics and image processing were implemented for the analysis of the texture of the samples - It was shown that there exist differences in texture between samples, so that classification is possible to distinguish them according to their textural features. • These results may be helpful for companies that produce prostheses and colored contact lenses. 13 Acknowlegments This work was supported by the Ministry of Science and Innovation through the Project DPI2008-06455C02-01. Jorge Herrera gratefully acknowledges the support of the Commissioner for Universities and Research of the Department of Innovation, Universities and Enterprise of the Generalitat of Catalonia and the European Social Fund 15 ¡Thanks for your attention! 16