file6
advertisement

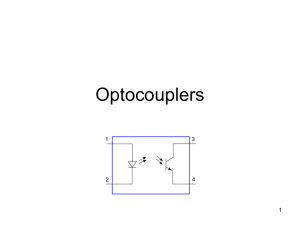
Optocuploare Amplificatoare-Izolatoare Aplicaţii Transformer Ground Isolation Optocoupler Block Schematic Tuning transmitter / receiver wavelengths Texas Instruments first optocoupler Analog optocouplers Phototransistor / Photo-Darlington Optocouplers Optocouplers using other photo-detectors in the output circuit : a. a photo-FET, b. a Light-Activated SCR ( Silicon Controlled Rectifier) , and c. a Light-Activated -Triac The Schottky Transistor Typical digital optocoupler ( first manufactured by Hewlett-Packard ) Interfacing two logic circuits through optocouplers provides ground isolation Dual Analog Optocoupler Free-space light barrier to detect obstacles Confocal lens system increases detection resolution Position transducer or /and tachometer using an optocoupler Reflection Optocoupler Checking the leaking current i.e. the isolation resistance Path of the common mode in an optocoupler Measuring the common mode rejection Neutralizing parasitic capacitance Neutralizing both common-mode capacitances in a dual link Optocoupler’s CTR − Current Transfer Ratio Measuring the D.C. CTR (statically ) Phototransistor turned into a controlled current generator to accurately determine CTR Dark Current Measurement Circuit Current vs. Voltage Characteristic of the Optocoupler Input LED Determining the saturation voltage of the output phototransistor Optocoupler Switching Mode Operation Recommended circuit for measuring the optocoupler switching times Optocoupler Transfer Characteristic in Frequency Domain Optocoupler Pass-band Determination Experimental result Desensitivation of the Optocoupler Phototransistor Faster Response Using a cascode also speeds-up the circuit Faster Turn-On by Using the Classical Peaking Capacitor in the Base-Circuit of the LED Driver The Effect of the Peaking Capacitor on the Forward Current Shortening the Switching Times by Prebiasing the LED Practical Circuit for LED Pre-bias Strong peaking Typical Digital Optocoupler Large Miller Capacitance of the Output Phototransistor Can Change the Output Characteristics Replacing the Phototransistor with a PD + Regular BJT Combination Corrects the Previous Behavior Open-Circuit on behalf of the not-connected transistor hurts ( it is better to short its legs) Like That ! Draining the charge out of the junction shortens optocoupler turn off Coupling the discharge circuits is detrimental Isolation Amplifiers Ground Isolation Means Infinite Impedance Between the Meant Circuits Isolation Amplifier Circuit Symbol Controlled-Gain Amplifier Provides Optically-Isolated Control Circuit Same function, different circuit Basic Isolation Amplifier with Negative Feedback in the Receiver Feedback Parallel-Series Topology Turns the Photodiode into a Current Generator Feedback circuit loading effect upon the basic amplifier Equivalent Schematic of the Feedback Amplifier Showing the Loading Effects Compensating for optocoupler non-linearity by using a matching-device in the feedback loop Nonlinearity compensation through negative feedback in the transmitter LEDs ‘True’ Control Classical Compensated Isolation Amplifier Differential Isolation Amplifier Switch-Mode Amplifier FM Modulation Used for Linear Signal Transfer Over a Light Barrier PWM − Pulse-Width Modulation over Light Barrier Principle of PWM Manufacturer’s Recommended Circuit to Experimentally Obtain the Transfer Characteristic in the Frequency Domain Isolation-Amplifier Transfer Characteristic Different Configuration – Same Transfer Characteristic Envisaged Isolation-Amplifier Gain vs. Frequency Characteristic, as Given in Data Sheet Din capitolul Fotodioda, urmatoarele două aplicaţii pot fi considerate amplificatoare izolatoare cu optocuploare Densimeter Intrusion Detector