Unit I: Computer Basics
advertisement
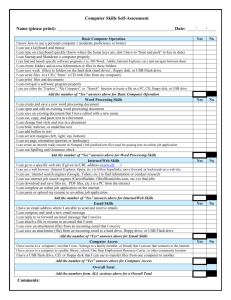
Understand Computer Fundamentals What Is A Computer? An electronic device that receives, processes, and store data, and produces a result (output). Classified by size, speed and application Uses hardware and software What Is A Computer? An electronic device that receives, processes, and store data, and produces a result (output). Classified by size, speed and application Uses hardware and software Types of Personal Computers Desktop computer: Laptop computer: designed to be used on a desktop. designed to be small enough and light enough to be used on your lap. Notebook/Tablet computer: but still small enough to be portable. designed to be used on a desktop Hardware vs. Software Has to be one or the other (not both) Everything has to fall into a category What is the difference? Hardware The tangible, physical equipment that can be seen and touched such as: “the equipment of the computer that you can see and touch” PARTS OF A COMPUTER SYSTEM Monitor Speaker Keyboard Computer Case (Processor inside) CD-ROM/DVD Drive Mouse Printer Floppy Disk Drive The Parts A of Computer CPU (Central Processing Unit) The “brains” of the computer housed on a tiny silicon chip inside the computer case. • Floppy Disk Drive CD-ROM/DVD Drive Monitor Keyboard Mouse Speakers Printer Scanner Hardware Let’s view some hardware! Computer Parts Video Input vs. Output Input: Information goes into the computer though it Output: Information comes out of the computer to it Input Devices Keyboard Mouse/Trackball Joystick Light Pen Pointing Stick Touchpad Touch Screen Bar Code Reader Scanner Microphone Graphics Tablet Digital Cameras Output Devices Monitor: screen that displays information such as text, numbers, and Printer: gives you information pictures. • • • Softcopy from the computer in printed form. Hardcopy Speakers: allow you to hear voice, music, and other sounds from your computer. Processing Device Central Processing Unit (CPU) – known as the heart or “brain” of the computer and is responsible for processing the information that has been entered into the computer Storage Devices Internal Storage: Allows you to store information inside of the computer Hard Drive: Allows the fastest access to information RAM (Random Access Memory) – temporary ROM (Read Only Memory) long-term memory External Storage: Allows you to use devices to store information outside of the computer Floppy Disks CD-ROMs (Compact Disc Read Only Memory) CD-RW (Compact Disc (Read and Write) DVDs (Digital Video Disc) USB/Jump Drives Storage Devices Hard Disk Drive: used to store data inside of the computer. • Magnetic platter that holds a large amount of information in a form the computer can understand. • Floppy Disk: flat circles of iron oxide-coated plastic enclosed in a hard plastic case. • Most are 3 ½ inches and have a capacity to hold 1.44 MB or more of data. CD ROM Drive: a compact disk that reads only memory. CD-RW: a device that allows you to read and write to a compact disk Which Storage Device Holds The Most Information? FLOPPY DISKS CD-ROM DISC 1.44 MB 640 MB HARD DRIVES DVD DISC 17 GB 80 and above GB Storage Capacity 1. 2. 3. 4. 5. 6. Floppy Disk Zip Disk CD DVD Jump Drive*** (could be smaller) Hard Drive Input vs. Output vs. Storage vs. Processing Mouse Scanner “Jump Drive”/USB Drive Floppy Disk Intel Processor Microphone Speaker CD Hard Drive Printer Keyboard Zip Drive Software The intangible set of instructions that tells the computer what to do; known as programs or software programs. Types of Software Operating System Software • Sets the rules for how computer hardware and application software work together, controls the operation of the computer. • Example: Windows XP Application Software • Lets you accomplish specific tasks based on your needs. • Examples: MS Word, Excel, Access, Explorer Operating System Software Tasks Boots (starts up) the computer Formats disks Creates folders Saves and retrieves files Moves and copies files Every Computer Has ONE Operating System Software! Types of Application Software Word Processing • Program that allows you to create, edit, and print text documents • Spreadsheet • Numbered Rows and Lettered Columns • Intersection of a row and column is a cell • Report, flyer, memo Grade book, financial info Database • • Lets you set up an electronic filing system Enter text and numbers • Find, search, and print info in different ways • Address book, Card Catalog Operating or Application? Microsoft XP Microsoft Word Explorer Microsoft 2000 MicroType MAC OS Novell (what you log into when you first get here) The Information Cycle What Happens During The IPOS Cycle? INPUT – when information is entered into the computer; the computer receives information PROCESSING – when the computer processes the information that has been entered OUTPUT – when information leaves the computer STORAGE – when information is stored to be used later. Computer Terms What Is A Computer? An electronic device that receives data, processes data, stores data, and produces a result (output). A collection of electronic circuits, which can be on or off (open or closed). • These two states of the circuit are represented by two digits, 0 and 1. • Called the binary system Types of Computers Supercomputer: most powerful • Used to do things like predict hurricanes and navigate satellites Mainframes and minicomputers: used by business and government to process large amounts of information Personal computers: smaller and less powerful than the other types of computers Additional Types of Computers PDAs (Personal Digital Assistants): a handheld device that is often used in conjunction with a desktop or other PC. • May have a special keyboard, some use a pen or stylus for entering data - Data can be transferred to a desktop or laptop computer Data Communications The technology that enables computers to communicate The transmission of text, numeric, voice or video data from one machine to another. Popular examples: • Internet, electronic messages (e-mail), faxes, and electronic or online banking Four components: • • • • Sender: the computer that is sending the message. Receiver: the computer receiving the message. Channel: the media that carries or transports the message. (telephone wire, coaxial cable, microwave signal, or fiber optic) Protocol: the rules that govern the orderly transfer of the data sent. Data Communications Network: when computers are connected to other computers • • They can share information and sometimes hardware (printers) Local Area Networks (LAN): computers connected together in a relatively close location such as in the same building or department. • • The data and software for these computers are stored on a central computer called the file server. Wide Area Networks (WAN): when local area networks are expanded to include several local area networks within a city, state, region, territory, country, continent, or the world. System Components Central Processing Unit (CPU): the microprocessor, the brains of the computer. • • Housed on a tiny silicon chip CPU has two primary sections: • • Arithmetic/logic unit Control unit Arithmetic/logic unit (ALU): performs arithmetic computations and logical operations; by combining these two operations the ALU can execute complex tasks. Control Unit: is the “boss” and coordinates all of the CPU’s activities. • Uses programming instructions, it controls the flow of information through the processor by controlling what happens inside the processor. System Components Memory: found on the motherboard; short term and long term. • Random Access Memory (RAM): memory on the motherboard that is short term. • When the computer is turned off or if there is loss of power, what ever is stored in RAM disappears. • The computer can read from and write to RAM. • Read-Only Memory (ROM): that is long term. memory on the motherboard • This memory is nonvolatile and your computer can only read from a ROM chip. • The instructions remain on the chip regardless if the power is turned on or off. System Components Basic Controllers: on the motherboard, a device that controls the transfer of data from the computer to a peripheral device and vice versa. • Examples: keyboards, mouse, monitors, and printers. • Generally stored on one single chip. Serial and Parallel Ports: used to connect our peripheral devices to the computer; usually one serial and one parallel port on a computer. • Serial devices transmit data one bit at a time. • A modem may be connected to this port. • A printer may be connected to this port. • Parallel devices transfer several bits at a time. System Components Universal Serial Bus (USB): a new standard that supports data transfer rates of up to 12 million bits per second. • • A single USB port can be used to connect up to 127 peripheral devices Expected to replace serial and parallel ports in the near future. Expansion Slots: an opening on the motherboard where a circuit board or expansion board can be inserted. • Examples: Additional Memory, video cards, modem cards, and sound cards. Data Representation ASCII (American Standard Code for Information Interchange): the most popular and widely used standardized coding system Byte: eight bits or combinations of ones and zeros represent a character. • MB-Megabyte or roughly 1 million bytes • GB-Gigabyte or roughly one billion bytes Three Types of Printers Dot Matrix • Gives a printed image in a pattern (matrix) of tiny ink dots. • Less expensive and not as clear Inkjet Printer • Better quality of printed document • Machine uses an ink cartridge and a printing element to print a finer image on the paper. Laser • Best quality of printed documents • Laser beam • More expensive • Quick Systems Software A group of programs that coordinate and control the resources and operations of a computer system. • Operating System (OS): provide an interface between the user or application program and the computer hardware. • • Enables all components of the computer system to communicate. Win 95/98/2000 Mac System 6/7 GUI (graphical user interface): graphical symbols (icons) represent files, disks, programs, and other objects. Systems Software – DOS Prompt/GUI Things To Note Hardware vs. Software (including types of Hardware and Software) Input vas Output Types of Storage System Components • Central Processing Unit (CPU) • Arithmetic/logic unit (ALU) • Control Unit: • Memory: • Random Access Memory (RAM): Short Term • Read-Only Memory (ROM): Long Term • Serial/Parallel Ports/USB: used to connect our peripheral devices Pick A Part & Define (26 Total) Desktop Data Laptop Mainframes/Minicomputers Network USB PC case CPU Memory Expansion Slots Byte Hardware Web TV Software Computer PDAs ALU Serial and Parallel Ports LAN/WAN Motherboard Control Unit RAM ASCII Notebook Supercomputer ROM