Radar Basics lecture (ppt)
advertisement
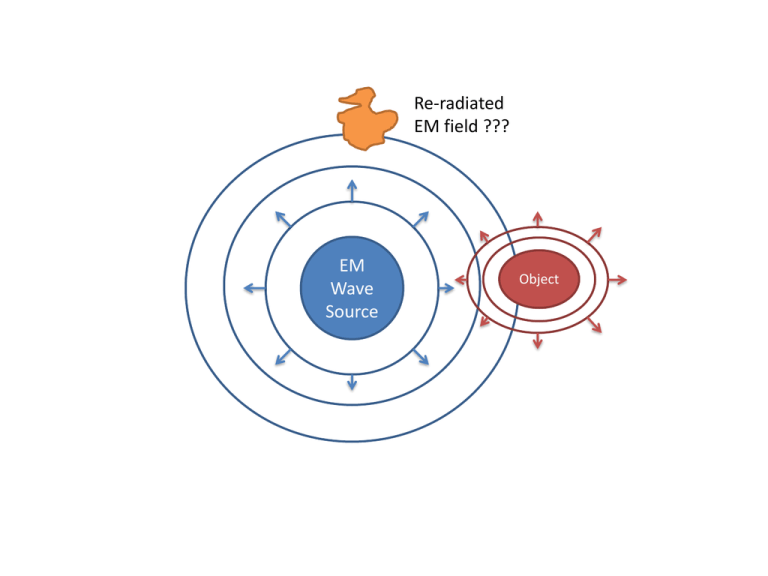
Re-radiated EM field ??? EM Wave Source Object uniform traveling wave reflected traveling wave Dipole Antenna Generator Transmission Line free space wave Continuous Energy Density (Standing Wave) Reflective Parabaloid Power Density decreased in this region due to reflection from parabaloid. EM Wave Source 𝑃𝑡 (𝑊𝑎𝑡𝑡𝑠) Power Density increased in this region due to reflection from parabaloid. Increase in Power Density in a given direction is called GAIN, 𝐺𝑡 . Aperture Receiver (Rx) (Antenna) Detector Object Transmitter(Tx) Signal Generator Bistatic System Aperture Receiver (Rx) (Antenna) Signal +Noise (1) Detector Signal post-conditioning to enable detection (sampling and averaging) Signal preconditioning to enable detection (change frequency, amplitude, etc.) Electronic Noise (2) Aperture Receiver (Rx) Detector (Antenna) Circulator or Mixer STIMULATED Signal +Noise (1) Signal Generator Transmitter(Tx) Monostatic System Radar Basics: Pulses and Range Gates Ln Pr Transmitted Pulse Noiseless Receiver Time Signals and Noise Transmitted Pulse Ln Pr Observed Signal (target echo plus noise) Time Signal Averaging and Detection Transmitted Pulse Ln Pr Observed Signal plus noise After Signal Averaging (target echo plus noise) Time The Radar “Bright” Band Multiple “Bright” Bands Steradians A Radian "cuts out" a length of a circle's circumference equal to the radius. A Steradian* "cuts out" an area of a sphere equal to (radius)2. *The name steradian is made up from the Greek stereos for "solid" and radian. The SI Unit abbreviation is "sr". Sphere vs Steradian The surface area of a sphere is 4πr2. The surface area of a steradian is just r2. So a sphere measures 4π steradians, or about 12.57 steradians. Likewise a steradian is 1/12.57, or about 8% of a sphere.