Module 4.3 PubMed History & Advanced Search & Review
advertisement

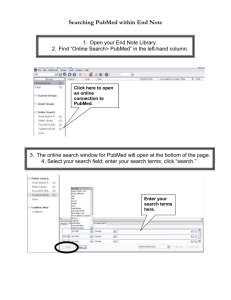
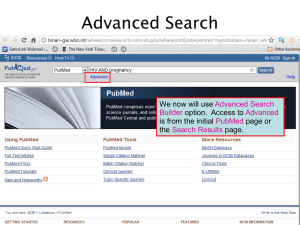
PubMed/History, Advanced Search and Review (module 4.3) MODULE 4.3 PubMed/History, Advanced Search & Review Instructions - This part of the: course is a PowerPoint demonstration intended to introduce you to PubMed/Preview, Index & History; accessing Full-Text Articles. module is off-line and is intended as an information resource for reference use. Table of Contents History Advanced Search Accessing full text articles from HINARI/PubMed Full text article access problems Before logging into the Partner Publisher services websites, we will Login to the HINARI site using the URL http://www.who.int/hinari/ You need to enter your HINARI User Name and Password in the appropriate boxes, then click on the Login button. To have access to the full text articles, you must properly sign in. If you do not use the Internet Explorer Web browser, this slide will not appear (as of 01 April 2014). If you use Internet Explorer, you will continue to have a two-step login process. Repeat the Login process on this 2nd page and you will be redirected to the HINARI Contents page. Remember - If you fail to use the Login page, you will have a second option on the Content sub-page. Once you are logged in to the HINARI Content page, access PubMed by clicking on Search inside HINARI full-text using PubMed. To access the History option, click on the Advanced Search option. We will discuss History, which is a feature of the Advanced Search Builder option. Access to Advanced Search is from the initial PubMed page or the Search Results page. Note that Search History will be lost after 8 hours and the maximum number of searches is 100. To build a search using History, begin by putting in your broadest search term. In this example, we will use treatment as our initial search term. The result for the treatment search is over 8 million articles. This can be viewed as a search set by clicking on the Advanced (History) page. On the Advanced Search Builder (History) page, our first search is given a set number identified by the # symbol - in this example it is #1. On the right side of the page, the number of articles is shown under the Items found column. In this case, a total of over 8 million citations. We will return to PubMed Home by clicking on the hypertext link. Note that the numbers for your searches may vary depending if you have previously searched that day in PubMed. We now have searched for malaria as a second search term and have 68106 citations. As in the previous result, the malaria search also can be viewed by returning to the Advanced (History) page. We now will click on Add for #1 AND #2 and click on Search - to create the combined result for the two search terms – treatment AND malaria. These two search terms are added to the Builder. The search has narrowed the results down further to 32754 articles. Click on the Advanced link to return to the Advanced Search (History) page. We now combine the latest search (#3) with the geographic term Africa by adding both terms in the Builder boxes and clicking on Search. You also can click on Add for #3 and then add Africa to the next line of the Builder. Search #4 now is treatment AND malaria AND Africa with a result of 8651 citations. Next we will open the searches’ Summary display setting by clicking on the Items Found #. Note: to clear these searches, click on Clear History button. This is the Summary display for the combined #4 search. We now will proceed to the Advanced Search slides.