PowerPoint: Roosevelt and the New Deal
advertisement

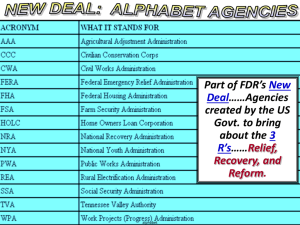
We will use some of the steps we have learned to assess President Roosevelt’s New Deal Policies and their effects on the United States after the Great Depression. For more info regarding the Public Policy Analyst steps click below: Define the problem Gather evidence * Identify causes * Evaluate a policy * * Develop solutions Select best solution http://www2.maxwell.syr.edu/plegal/pp ae/ppae1.html 1929- Stock Market Crash › Thousands of banks collapse › Decline of production across all markets 1933- 25% of America unemployed Song of the Great Depression › “Brother Can You Spare a Dime” But new hope with election of 1932 › Franklin Delano Roosevelt › “Happy Days Are Here Again” So long sad times Go long bad times We are rid of you at last Howdy gay times Cloudy gray times You are now a thing of the past Happy days are here again The skies above are clear again So let's sing a song of cheer again Happy days are here again Altogether shout it now There's no one Who can doubt it now So let's tell the world about it now Happy days are here again Your cares and troubles are gone There'll be no more from now on From now on ... Happy days are here again The skies above are clear again So, Let's sing a song of cheer again Happy times Happy nights Happy days Are here again Were the “Happy Days here again” with the New Deal ? After reading the lyrics to “Happy Days Are Here Again,” in your notebooks, take a few minutes to answer the Big Question. United States Great Depression (Unemployment) 1932 ELECTION 1 out of 4 was unemployed… national income was 50% of what it had been in 1929 Republicans nominated Hoover no hope Winner by a landslide = FRANKLIN DELANO ROOSEVELT (Democrat - N.Y. governor) FDR brought optimism to the country – spoke to the people- fireside chats New Deal for the people Creation of the modern government › Expanded federal government to greatest heights › A controversial expansion Progressivism firmly entrenched in the Democratic Power Myth- Hoover did nothing to spark New Deal Truth- The RFC – Reconstruction Finance Corporation Was the New Deal an appropriate response to the Great Depression? Did it go too far in expanding the federal government? Was it effective? How did life change for Americans through its policies? What were its criticisms Be sure to think about these questions as you analyze President Roosevelt’s New Deal Policies Use the following worksheet to document your evaluation Worksheet4: "Evaluating Existing Public Policies"(HTML) The Dust Bowl Government programs which provided direct relief to suffering Americans through government spending It was a revolution in American society - changed completely the way the government functions ……… Renew democracy Restore confidence in the banking Stimulate economy Social Engineers Put people back to work. Brain Trust Restore self confidence How? FDR’s 3 R’s Relief: ease suffering of the needy Recovery:begin economic growth Reform: help prevent future economic crises Roosevelt was very successful getting New Deal legislation passed-100 days ….FDR and Congress went to work providing for direct relief, recovery and reform. From March of 1933 to June of 1933, Roosevelt sent 15 proposals to Congress and all 15 were adopted Congress and President tried anything reasonable to overcome the Great Depression. Part of FDR’s New Deal……Agencie s created by the US Govt. to bring about the 3 R’s……Relief, Recovery, and Reform. RELIEF: Ease Suffering of the Needy WPA / 1933 to 1943 Works Progress Administration Employed 8.5 million workers in construction and other jobs, but more importantly provided work in arts, theater, and literary projects. •Works Progress Administration (WPA), the New Deals main relief agency. •People employed by the WPA at its peak was more than 3 million •2,500 hospitals •5,900 schools •13,000 playgrounds •125,000 public buildings RELIEF: Ease Suffering of the Needy CCC / 1933 to 1942 Civilian Conservation Corps •Sent 3 million young men to work camps to build bridges, replant forests and other conservation tasks. •Develop job skills and improve environment. • Removed surplus of workers from cities, provided healthy conditions for UNEMPLOYMENT - still a major problem FDR like Hoover was wary of gov't handouts - he wanted people to earn their keep so gov't agencies were created - temporarily - to address the unemp. problem CIVILIAN CONSERVATION CORPS (CCC) - in 1933 - set to establish work for young men (18-25) in areas of reforestation, soil conservation, flood control, road construction - also took them out of urban labour markets - but Blacks not permitted to enrol Created up to four million jobs in construction Provided jobs constructing huge public works such as bridges and dams Goals Create jobs Strengthen American industry •Also called the National Recovery Act. •Helped businesses organize codes setting prices and minimum wage. •Put people back to work at decent jobs, wages and working conditions. •Businesses were not forced to join this. •Declared unconstitutional by the Supreme Court in 1935 because it violated powers given to excutive branch by legislative branch . •Violated separation of powers, executive not allowed to enforce intrastate commerce NATIONAL INDUSTRIAL RECOVERY ACT (NIRA) and NATIONAL RECOVERY ADMIN (NRA) were established to end animosity between labor and business all was redirected to industrial growth fair labor codes established - wages, no child labor, shortened work hoursbusiness people challenged the NRA, claiming it was communist They formed the LIBERTY LEAGUE - at LL's urging, the Supreme Ct. overturned the NIRA & NRA, claiming that federal government was exceeding its authority (by interfering in state jurisdiction) RECOVERY: Begin Economic Growth AAA / 1933 Agricultural Adjustment Act •Protected farmers from price drops and over production.. • US Govt. Paid farmers (subsidies) •not to grow crops, produce dairy products such as milk and butter or raise pigs and lambs. •Goal of raising prices of agriculture •Prevent another Dust Bowl, teach farmers methods of preventing soil erosion. AGRUCULTURAL ADJUSTMENT ACT (AAA) passed in 1933 to aid farmers- its objective was to restore farmers' purchasing power and to restore the family farm - AAA had farmers cut back on crop production by paying them equivalent SUBSIDIES (paid not to produce) the goal was to increase prices of farm goods - bad side: 1) food production down when millions were starving 2) Black sharecroppers were hurt: white landowners paid not to farm so they got rid of Black tenant formers in 1935, AAA was declared unconstitutional by courts (too much control over individual states), so it was revised and introduced as new legislationSoil Conservation Act Second AAA EX: Food Stamp Act of 1939 - gave away surplus food to poor, also guaranteed (small) farmers a market RECOVERY: Begin Economic Growth TVA / 1933 Tennessee Valley Authority •Federal government built a series of dams to prevent flooding and sold electricity. •First public competition with private power industries. •Develop a poor section of the Southeast U.S. •Stimulate the economy and produce cheap electricity. •Control floods, planting new forests. •Bring this section into the 20th century. Controversial- is government overstepping bounds into private sector 94 percent of property owners and 98 percent of tenants did not have electricity. 30 percent of property owners and 41 percent of tenants had no toilet facilities whatsoever 65 percent of property owners and 78 percent of tenants had to travel at least 300 yards to get their household water. 8 percent of property owners and 3 percent of tenants owned radios (usually battery operated). 39 percent of property owners and 23 percent of tenants had phonographs (including record players that were operated with a hand crank). 50 percent of property owners and 25 percent of tenants read newspapers. 26 percent of property owners and 16 percent of tenants owned automobiles. 7 percent of property owners and 4 percent of tenants owned trucks. TENNESSEE VALLEY AUTHORITY (TVA) - used to promote hydroelectric power, control flooding lower rates private industry, manuf. fertilizer fed. gov't. took ownership (nationalization v. privatization) REFORM: Prevent Another Depression FDIC / 1933 Federal Deposit Insurance Corporation Created federally insured bank deposits ($2500 per investor at first) to prevent bank failures. The first phase of the New Deal dealt exclusively with economic reform - FDR believed government legislation/involvement was crucial to stimulate the economy Step 1 – deal with the banking crisis BANKING HOLIDAY- banks shut down and subject to government inspection, allowed to open when "healthy"- people's confidence returned in depositing in banks, allowing them to reinvest in the economy. Step 3 – Increase the money supply FDR went off the GOLD STANDARD (government could print more money than Fort Knox gold reserves would allow)With more money in circulation, wages and prices increased More inflation caused dollar value to lower which gave government spending power (Keynesian REFORM: Prevent Another Depression SEC / 1934 Securities and Exchange Commission Regulated stock market and restricted margin buying, and frauds. Stock Regulation Step 2 - Stock market reform Security Exchange Commission established to police the Stock Exchange -practice of buying on margin was regulated The National Labor Relations Act › also called the Wagner Act › It guaranteed workers the right to organize unions without › › › › interference from employers and to bargain collectively. The National Labor Relations Board (NLRB) which organized factory elections by secret to determine whether workers wanted a union. The NLRB then certified successful unions. The new law also set up a process whereby dissatisfied union members could take their complaints to binding arbitration, in which neutral party would listen to both sides and decide issues. The NLRB was authorized to investigate the actions of employers and had the power to issue “cease and desist” orders against unfair practices. The United Mine Workers union began to work with other unions to organize workers in industries where unions did not exist. To do this, they formed the CIO They began with automobile and steel industries—two of the largest industries In late December 1936, General Motors launched a sit-down strike do to the first sit-down strike due to the demotion of two workers Violence broke out in Flint when police launched a tear gas assault on one of the smaller plants. Afterward, GM broke down and recognized the CIO union, United Auto Workers as its employees sole bargaining organization. This led to others using the sit-down strike as a method in other industries. other agencies had specific mandates too...NATIONAL YOUTH ADMIN. (NYA) created jobs for young in urban areas FED. EMERGENCY RELIEF ACT (FERA) aimed at older workers- these and other similar agencies worked well, but unemp. was still at 6 million in 1941(solution for this would be the ind. boom of WW2) NEW DEAL - SOCIAL REFORM ASPECT- after 1935, w/ immediate economic relief & reform addressed, New Deal turned to Social Welfare - more legislation... National Labour Relations Act (aka Wagner Act)- it legitimized unions and labour tactics such as collective bargaining & collective action (strikes, etc...) - it outlawed BLACKLISTS & other anti-union practices •One of the most important features of the New Deal. •Established a retirement for persons over 65 funded by a tax on wages paid equally by employee and employer. •Old age insurance •Protect Americans who were unable to support themselves. •Unemployment compensation •Compensation to disabled workers and assistance to Social Security Act (1935)feared by opponents as "creeping socialism"- this act typifies the WELFARE STATE - unemployment insurance, old age pensions Problem: it took some $ out of circulation (payroll deductions) at a time when purchasing power was already low- also, it only covered the unemployed Roosevelt vs Landon FDR wins in a landslide this victory gave FDR a mandate to continue his New Deal policies first objective: to reorganize the Supreme Court - they disallowed some New Deal legislation Congressional opposition was beginning to grow; many of his laws, including the WPA, were taking a long time to get passed and met resistance. Schechter v. United States › The Schechter brothers had a poultry business in Brooklyn. › They had been convicted in 1933 of violating the NIRA’s Live Poultry Code; they had sold diseased chickens and violated the code’s wage-and-hour provisions. › Known as the “sick chicken case.” › The Supreme Court said that the Constitution did not allow the Congress to lend its powers to the executive; the NIRA was unconstitutional. › This suggested that the Supreme Court would make similar decisions in regards to the New Deal. •Supreme Court was striking down New Deal legislation. •Roosevelt proposed a bill to allow the president to name a new federal judge for each who did not retire by age 70 and 1/2. •6 justices over age limit. •Would have increased the number of justices from 9 to 15, giving FDR a majority of his own appointees on the court. •The court-packing bill was not passed by Congress. Criticisms of New Deal US government and President too powerful Violated laissez faire Supreme Court declared NIRA and AAA unconstitutional Critics: Father Charles Coughlin Dr. Francis Townsend Al Smith Huey Long Deficit spending: Govt. spends $$$ to stimulate the economy and help people even if it means US Govt. goes into debt. Welfare state----Created a population of Americans who relied on the US Govt. to live 100 days •A Roman Catholic priest. •Radio Priest in Detroit Michigan. •Criticized FDR in weekly radio program. •10 million listeners. •Criticized FDR’s farm program •Believed an international conspiracy of bankers existed and FDR was influenced by them. •He called for the nationalization of banks and utilities. (US Govt. controls banks, Socialism) •Fascist; Anti-Semitic overtones. •He wanted the government to help older citizens. •Retired California Physician. •Suggested a $200 per month pension for people over 60. (This is socialism) •Open jobs for the younger unemployed. •Spending all $200 would also be required to boost economic demand. •Townsend Clubs created all over the nation. •Influenced FDR’s creation of Social Security Successes of New Deal AMERICANS IN 1939 WHO WANTED THE NEW DEAL TO CONTINUE WAS 55%….. 37% REGARDED IT AS A BAD INFLUENCE AND WANTED A NEW PRESIDENT…………... Stimulated the economy Put people back to work…. Improved morale and self-confidence of the people US Govt’s. role changes and became directly involved in helping people WWII ended the Great Depression not FDR’s New Deal 100 days a 3rd revolution in American culture and politics- more gov't involvement but w/in the context of traditional U.S. democracy (not socialist…) New Deal helped in stimulating the U.S. economy, but only WWII would solve any lingering problems unemployed found jobs in munitions factories and the military as the U.S. became the ARSENAL OF DEMOCRACY New Deal saw expansion of U.S. gov't in : 1) economy. - constant government intervention/deficit spending 2) social reform - welfare state - after this pt the U.S. government was expected to play a role in any economic crisis Did the New Deal transform or reform American society?