WATER, ENVIRONMENT AND CLIMATE CHANGE

WATER, ENVIRONMENT AND CLIMATE CHANGE:
IMPLICATIONS FOR SUSTAINABILITY
Bakhshal Lashari, PhD, Post Docs
Professor/Director
Institute of Water Resources Engineering and Management
Mehran University of Engineering and Technology,
Sindh Pakistan
One Day Colloquium on
“Water Crises and Choices: Post Flood Scenario”
University of Agriculture Faisalabad
January 10, 2011
Water: Source of Life, Food and Fiber
Water also brings miseries
Hurricane Katrina (Sept. 2005) Kenya Drought (Spring 2006)
China Drought (Spring 2010)
Flood in Pakistan
(Aug. 2010)
Water and Energy
• Energy production needs a lot of water
– ~ 25 gallons per kWh
– ~ 39% of freshwater withdrawals in USA (excluding hydropower demand) are for thermoelectric plants (136 bgd)
Per-Capita Freshwater Availability (2000)
Precipitation Variability
Virtual Water Use
1 kg grain ≡ 1000 l of water
1 kg beef ≡ 15,000 l of water
• Meaty American and European diets
– 5,000 l of water/day
• Vegetarian African and Asian diets
– 2,000 l of water/day
• Meat consumption in China
– 20 kg (1995) & 50 kg (2009)
• Dietary habits difficult to be reversed!!
Climate Change Impacts on Hydrology
• Intensification of the hydrological cycle
– More floods and droughts
– More variability in rainfall
– Shorter snowfall season
– Early spring snowmelt
– Accelerated glacial melting
• May affect water availability, water quality, ecosystems, etc.
IPCC (2007) Freshwater Resources and their Management
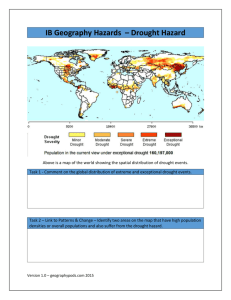
DROUGHTS:
SOME RECENT OCCURRENCES
Drought in, Water Surplus, Southwestern China
(Spring 2010)
Satellite Observations
(20 March, 2010)
Dark red shows severest drought. Most parts of Yunnan and Guizhou provinces suffered from the severest droughts. The drought was classified into five grades: severest, severer, moderate, mild, and normal.
Land, Rivers and Water Transportation During China
2010 Drought
Affected:
60 mn people
12 mn livestock
5 mn hect. crops
Cost = $3.5 billion
Severe Drought Fires in Russia
(2010)
FLOODS:
SOME RECENT OCCURRENCES
2010 Flood in China
15-21 June
Severity:
6-12 July
3000 Deaths; 1100 Missing
305 mn people; 1.36 mn Houses
13 Aug. 2010
28 Provinces
100,000 sqkm. Land
$ 41 bn in Damages
Pakistan 2010 Floods
(Worst Natural Disaster Ever: U.N.)
Severity:
2000+ Deaths
20 mn People Affected
1 mn Houses Damaged
160,000 sqkm. Land
$ 6 bn in Damages
$45 bn Total Economic
Impact
Total Rainfall During
1 July to 23 Aug.
15
Some facts in Pakistan’s context
Per capita Fresh water availability
1600
1400
1200
1000
800
600
400
200
0
1998 2005 2010
Water availability
2015
Population
2020 2025
100
50
0
300
250
200
150
Water storage capacity per person per year
Wheat yield
• Pakistan has good, abundant sunshine and excellent farmers
• Yet crop yield per ha and cubic meter is much lower than international benchmarks
Sindh’s Context
3000
2500
2000
1500
1000
500
0
Canal Diversion and Water logging in Sindh
40
30
20
10
0
60
50
Waterlogging Canal Diversion
How Engineers supply Irrigation
Water?
2,00
1,80
1,60
1,40
1,20
1,00
0,80
0,60
0,40
0,20
0,00
Head Middle Tail
How Farmers are using it?
Water supply and crop water requirements
0,2
0,18
0,16
0,14
0,12
0,1
0,08
0,06
0,04
0,02
0
0,3
0,28
0,26
0,24
0,22
Expenditure Trend on System Maintenance
Future water need for Sindh
Year Population Water Water Use (MAF)
Million MAF Irrigation Industry Home
2009
2025
41.23
52.6
48.76
72.0
40.5
59.8
4.9
7.2
3.4
5.0
Future water need in Sindh
Average water availability
(1991-2009)
Shortfall (as per water accord)
Water need in 2025 (Projected)
( irrig 83%, Ind 10% Mun 7%)
Short fall in 2025 (about)
Groundwater available
Net shortfall in 2025
41.76 MAF
7.0 MAF
72.0 MAF
30.0 MAF
5 MAF
25 MAF
Water Resources: Issues
• Water storage
• Flood and Drought due to climate change
• Lack of Institutional Coordination
• Knowledge gap/Capacity
• Low Irrigation Delivery and Application
Efficiencies
• Drainage and Salinity Problems
Water Management: Issues
• Enforcement of Regulations
• Changing Cropping Pattern
• Deteriorating Irrigation Infrastructure
• Inequitable Distribution of Water
• Sea water intrusion-Coastal area
• Deterioration of groundwater
• Pollution of Wetlands-Lakes
Water Resources: Challenge
• Two Main challenges
– Enough water of good quality:
• to all people,
• at all places,
• at all times and
• at an affordable cost
– Sufficient resilience against floods and droughts
30
SUSTAINABLE WATER RESOURCES
MANAGEMENT
31
Integrated Water Resources Management
(IWRM)
• Simultaneous consideration of:
– Surface and groundwater
– Quantity and quality
– Watershed and water bodies
– Hydrology, hydraulics, environment, policy and socio-economics
– Multiple sectors, stakeholders, and decision makers
Strategies for Sustainable
Water Use
CONSER-
VATION
DEVELOP
ADDITIONAL
SOURCES
• DESALINATION
EFFICIENT
USE
WATER
SUPPPLY
REUSE
TREAT-
MENT
RECYCLE
IWRM
The Way Forward!
• Innovative, revolutionary, and selfsustaining programs
• Diverse and multi-institutional partnerships
• Pricing and valuing water for enhancing water-use efficiency
• Strongly integrated planning for water, energy and agriculture
• Robust regional-capacity building
35