The River Red Gum Ecosystem Powerpoint.

The River Red Gum Ecosystem
Developed by Paul Greenwood REEC and Sara Vanzella, Burrumbuttock Public School, June 2010 http://riverredgumrescue.blogspot.com/2008/09/fact-sheet-river-red-gum-eucalyptus.html
Eucalyptus camaldulensis
is also known as the River Red Gum.
• River red gums need 1100mm of water to remain healthy.
• They grow over much of Australia and can be found along river edges.
• River red gums can also grow in areas with lower rainfall.
They survive off the floodwaters during the winter and spring time.
On the flood plains of the Murray and Murrumbidgee Rivers,
River Red Gums grow in large forests called monocultures
No other species has adapted to spring flooding and dry summers like the River Red gums.
•The forests have natural channels called runners.
•The runners flow across the floodplain.
• Water flows into these runners in times of flood and spreads over the land
Plants in the River Red Gum ecosystem
There are no shrubs in River Red gum forests.
The understory plants have to survive floods and dry periods too
Swamp wallaby-grass Sedge Common spike rush Giant rush
Problems in the River Red Gum Ecosystem:
6. Catfish lay their eggs in pebble beds on the bottom of the river.
The sediment settles on the eggs killing the eggs
1. Carp feed by sucking up the mud like a vacuum
5. The banks erode causing turbid water
4. Eventually the River
Red Gum falls over
2. Erodes the river banks
3. The River Red Gum roots become exposed on the bank.
Animals
Mammal populations in red gum ecosystems include:
Terrestrial species
Yellow-footed antechinus Eastern grey kangaroo Many reptile species
Amphibian species
Perrons tree frog Eastern Banjo Spotted marsh frog
Growling Grass frog
Arboreal species
Superb fairy-wren Thornbills Superb parrot
Brush tailed possum Weebill Brown treecreeper
Striated pardalote Sulphur-crested White-plumed cockatoo honeyeater
Aquatic species
Fish- Murray cod Golden perch Catfish
Silver perch Purple spotted gudgeon
Trout cod Crismon spotted rainbow fish
Diagram of River Red Gum Ecosystem
5. Transpiration from River Red
Gum trees
1. Rainfall
2. River rises and floods with spring rains.
4. Water taken up by the roots
Runner
3. Water soaks down to the water table
Definitions
Eucalyptus camaldulensis: Is the scientific term for the River Red gum
Monoculture: is an area dominated by a single species. For examples lawns and crops.
Species: a group of animals or plants.
Runners: are the natural flood channels in low lying forests.
Ecosystem: A community of interdependent organisms living and
Interacting together in their physical environment.
Understory: the term for the area of a forest which grows at the lowest height
Sediment: matter that settles to the bottom of a liquid.
Turbid: having sediment or foreign particles stirred up or suspended.
Terrestrial species: animals that live on land.
Arboreal species: animals that live in trees.
Aquatic species: animals that live in water.
Amphibian species: are creatures which spend part of their life in water and part of their life on dry land.
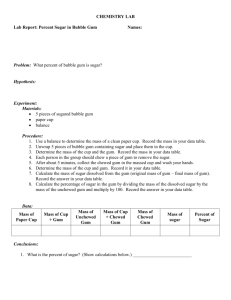
NAME:
River Red Gum Ecosystems Definitions
Monoculture:
__________________________________________________________________________________________________________
_____________________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Terrestrial species:
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________
____________________________________________________________________________________________________________ _______________
_______________________________________________________________________________________________________________
Amphibian species:
______________________________________________________________________________________