Classification
advertisement

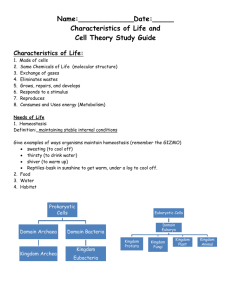
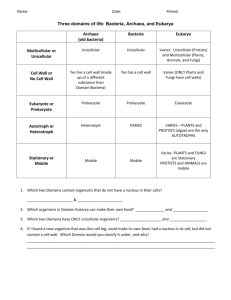
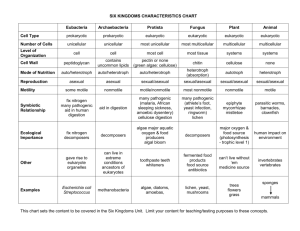
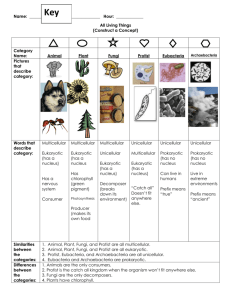
Classification Go to Section: Slide # 2 Domain: Archaea Kingdom: Archaebacteria Also called extremophiles Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Unicellular or Multicellular Autotroph or Heterotroph Cell Wall Present – Yes or No (made of) Other Defining Characteristics Prokaryotic Unicellular Both Yes, but does not contain peptidoglycan •Live in extreme environments •None cause human disease •Methanogens: live in intestinal tracts of humans & cows •Halophiles : live in Great Salt Lake, Dead Sea •Thermophiles: hydrothermal and volcanic vents. Bacillus infernus lives in deep sea vents in the ocean – obtains energy from Earth’s heat Go to Section: Slide # 3 Domain: Bacteria Kingdom: Eubacteria Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Unicellular or Multicellular Autotroph or Heterotroph Cell Wall Present – Yes or No (made of) Other Defining Characteristics Prokaryotic Unicellular Both Yes, it does contain peptidoglycan •Some cause disease such as Streptococcus & E. coli •Decomposers; involved in the Carbon and Nitrogen cycles Go to Section: E. coli Streptococcus Domain: Eukarya Kingdom Protista Slide #4 Very Diverse Kingdom Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Unicellular or Multicellular Autotroph or Heterotroph Cell Wall Present – Yes or No (made of) Eukaryotic Most are unicellular Some algae are multicellular Both Plant-like have cell wall Fungus-like have cell walls Animal-like do not have cell walls Other Defining Characteristics •Grouped by how they get food •Some can move: •Pseudopods: cytoplasmic projections •Cilia: hair like structures that surround cell •Flagella: whip-like structures Pseudopods Go to Section: Paramecium Green algae Amoeba Slide #5 Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Fungi Unusual Heterotrophs Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Unicellular or Multicellular Autotroph or Heterotroph Cell Wall Present – Yes or No (made of) Eukaryotic Mostly multicellular (yeast are unicellular) Heterotroph Yes, made of chitin Go to Mildew Section: on Leaf Other Defining Characteristics •Absorb food from surroundings •Parasites: absorb nutrients from living host; EX: ringworm & athletes foot •Saprophytes consume dead plants and animals (recycle nutrients in ecosystems) Mushroom Domain: Eukarya Kingdom: Plantae Slide # 6 Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Unicellular or Multicellular Autotroph or Heterotroph Cell Wall Present – Yes or No (made of) Eukaryotic Multicellular Autotropic Yes, made of cellulose Go to Section: The Last to Evolve! Other Defining Characteristics •Cells contain chloroplasts •Respond to environment by using hormones •EX: moss, ferns, trees, and bushes Domain: Eukarya Kingdom Animalia Slide #7 jellyfish Prokaryotic or Eukaryotic Unicellular or Multicellular Autotroph or Heterotroph Eukaryotic Multicellular Heterotroph Go to Poison dart frog Section: Cell Wall Present – Yes or No (made of) NONE Florida panther sponge Other Defining Characteristics Respond to environment by nervous tissue Must obtain food from others Some are parasites (ticks, fleas, tapeworms) EX: insects, fishes, mammals, sponges, worms Clown fish